| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231622 | 1495219 | 2015 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
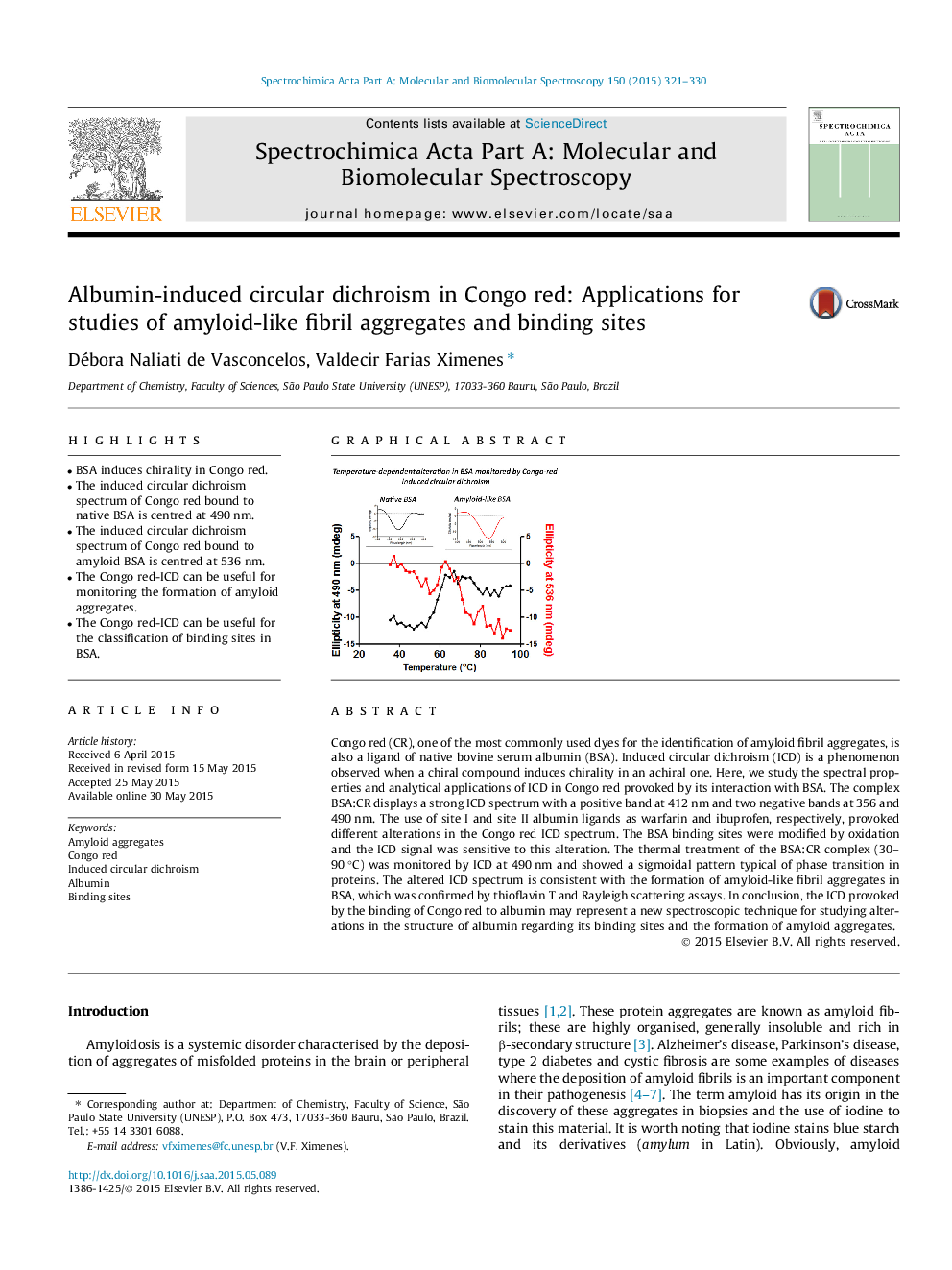
• BSA induces chirality in Congo red.
• The induced circular dichroism spectrum of Congo red bound to native BSA is centred at 490 nm.
• The induced circular dichroism spectrum of Congo red bound to amyloid BSA is centred at 536 nm.
• The Congo red-ICD can be useful for monitoring the formation of amyloid aggregates.
• The Congo red-ICD can be useful for the classification of binding sites in BSA.
Congo red (CR), one of the most commonly used dyes for the identification of amyloid fibril aggregates, is also a ligand of native bovine serum albumin (BSA). Induced circular dichroism (ICD) is a phenomenon observed when a chiral compound induces chirality in an achiral one. Here, we study the spectral properties and analytical applications of ICD in Congo red provoked by its interaction with BSA. The complex BSA:CR displays a strong ICD spectrum with a positive band at 412 nm and two negative bands at 356 and 490 nm. The use of site I and site II albumin ligands as warfarin and ibuprofen, respectively, provoked different alterations in the Congo red ICD spectrum. The BSA binding sites were modified by oxidation and the ICD signal was sensitive to this alteration. The thermal treatment of the BSA:CR complex (30–90 °C) was monitored by ICD at 490 nm and showed a sigmoidal pattern typical of phase transition in proteins. The altered ICD spectrum is consistent with the formation of amyloid-like fibril aggregates in BSA, which was confirmed by thioflavin T and Rayleigh scattering assays. In conclusion, the ICD provoked by the binding of Congo red to albumin may represent a new spectroscopic technique for studying alterations in the structure of albumin regarding its binding sites and the formation of amyloid aggregates.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy - Volume 150, 5 November 2015, Pages 321–330