| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2042649 | 1073228 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
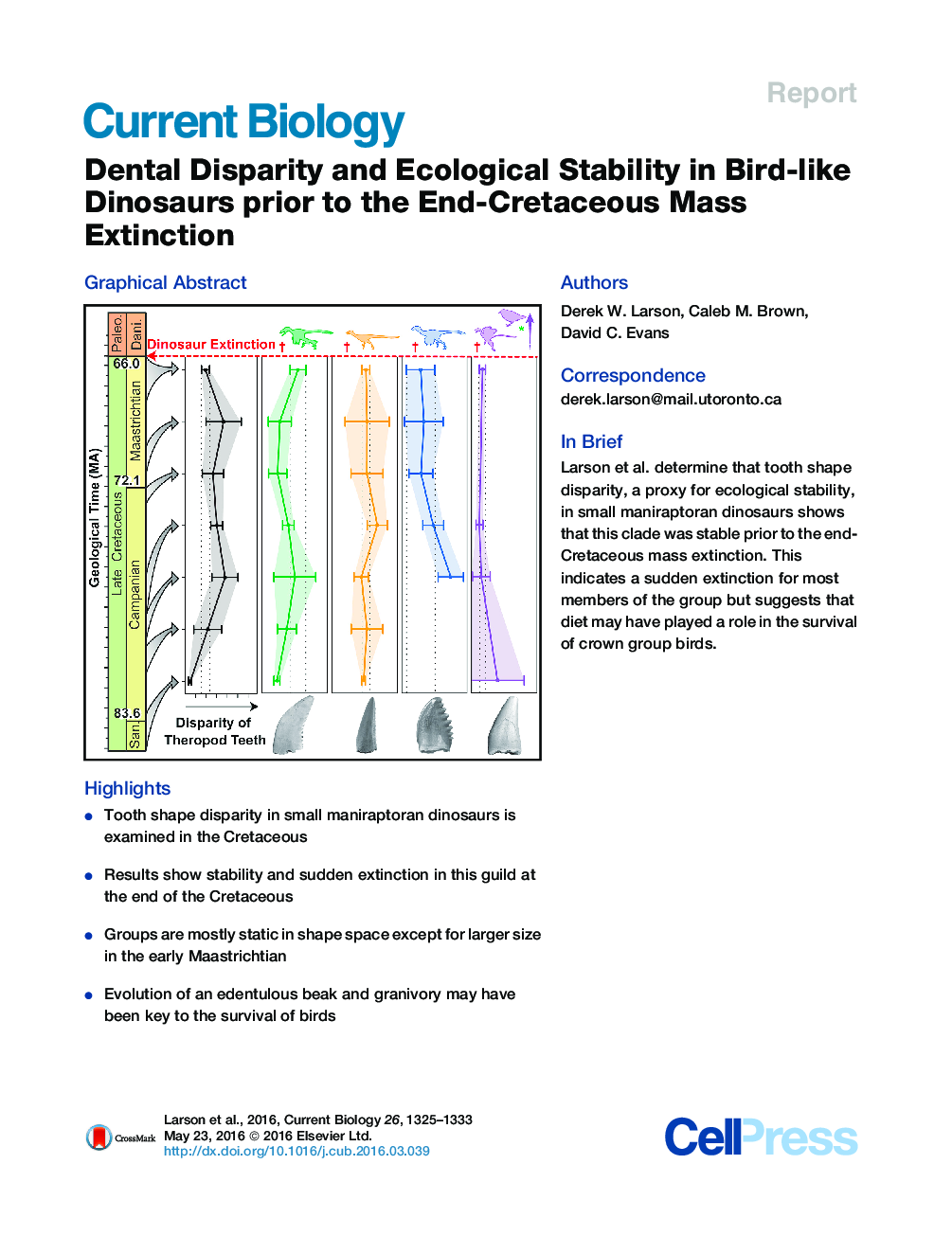
• Tooth shape disparity in small maniraptoran dinosaurs is examined in the Cretaceous
• Results show stability and sudden extinction in this guild at the end of the Cretaceous
• Groups are mostly static in shape space except for larger size in the early Maastrichtian
• Evolution of an edentulous beak and granivory may have been key to the survival of birds
SummaryThe causes, rate, and selectivity of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction continue to be highly debated [1, 2, 3, 4 and 5]. Extinction patterns in small, feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs (including birds) are important for understanding extant biodiversity and present an enigma considering the survival of crown group birds (Neornithes) and the extinction of their close kin across the end-Cretaceous boundary [6]. Because of the patchy Cretaceous fossil record of small maniraptorans [7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12], this important transition has not been closely examined in this group. Here, we test the hypothesis that morphological disparity in bird-like dinosaurs was decreasing leading up to the end-Cretaceous mass extinction, as has been hypothesized in some dinosaurs [13 and 14]. To test this, we examined tooth morphology, an ecological indicator in fossil reptiles [15, 16, 17, 18 and 19], from over 3,100 maniraptoran teeth from four groups (Troodontidae, Dromaeosauridae, Richardoestesia, and cf. Aves) across the last 18 million years of the Cretaceous. We demonstrate that tooth disparity, a proxy for variation in feeding ecology, shows no significant decline leading up to the extinction event within any of the groups. Tooth morphospace occupation also remains static over this time interval except for increased size during the early Maastrichtian. Our data provide strong support that extinction within this group occurred suddenly after a prolonged period of ecological stability. To explain this sudden extinction of toothed maniraptorans and the survival of Neornithes, we propose that diet may have been an extinction filter and suggest that granivory associated with an edentulous beak was a key ecological trait in the survival of some lineages.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (273 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 26, Issue 10, 23 May 2016, Pages 1325–1333