| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 229953 | 1427361 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• 1,8-Diazobicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene conversion was mainly influenced by temperature.
• Oxidant ratio greatly influenced N- and C-species distribution in product stream.
• Alcohol addition enhanced DBU destruction, TOC removal % and N products yield %.
• Alcohol addition shifted N species towards gaseous nitrogen.
The present work investigates the destruction of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic hydrocarbons frequently encountered in hazardous wastes by supercritical water oxidation (SCWO), with focus on the process enhancement using isopropyl alcohol (IPA) as co-fuel. 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU) was selected for SCWO in a continuous plug flow reactor, under a range of temperatures (400–525 °C), oxidant ratios nSR (0.8–2.0) and IPA/DBU ratios (0.5–3.5). Experimental results were presented in terms of total organic carbon (TOC) removal %, and nitrogenous products yield %. Based on GC–MS analysis, a free radical reaction mechanism for SCWO of DBU was proposed. Results showed that temperature was the predominant factor to influence the rate of DBU oxidation, while oxidant ratio (nSR) significantly affected the N speciation in the exit stream. IPA addition had a significant impact on shifting recalcitrant aqueous ammonia NH4+ in the liquid stream to gaseous nitrogen. It also increased TOC removal % (DBU + IPA) due to the increased free radicals produced by IPA oxidation.
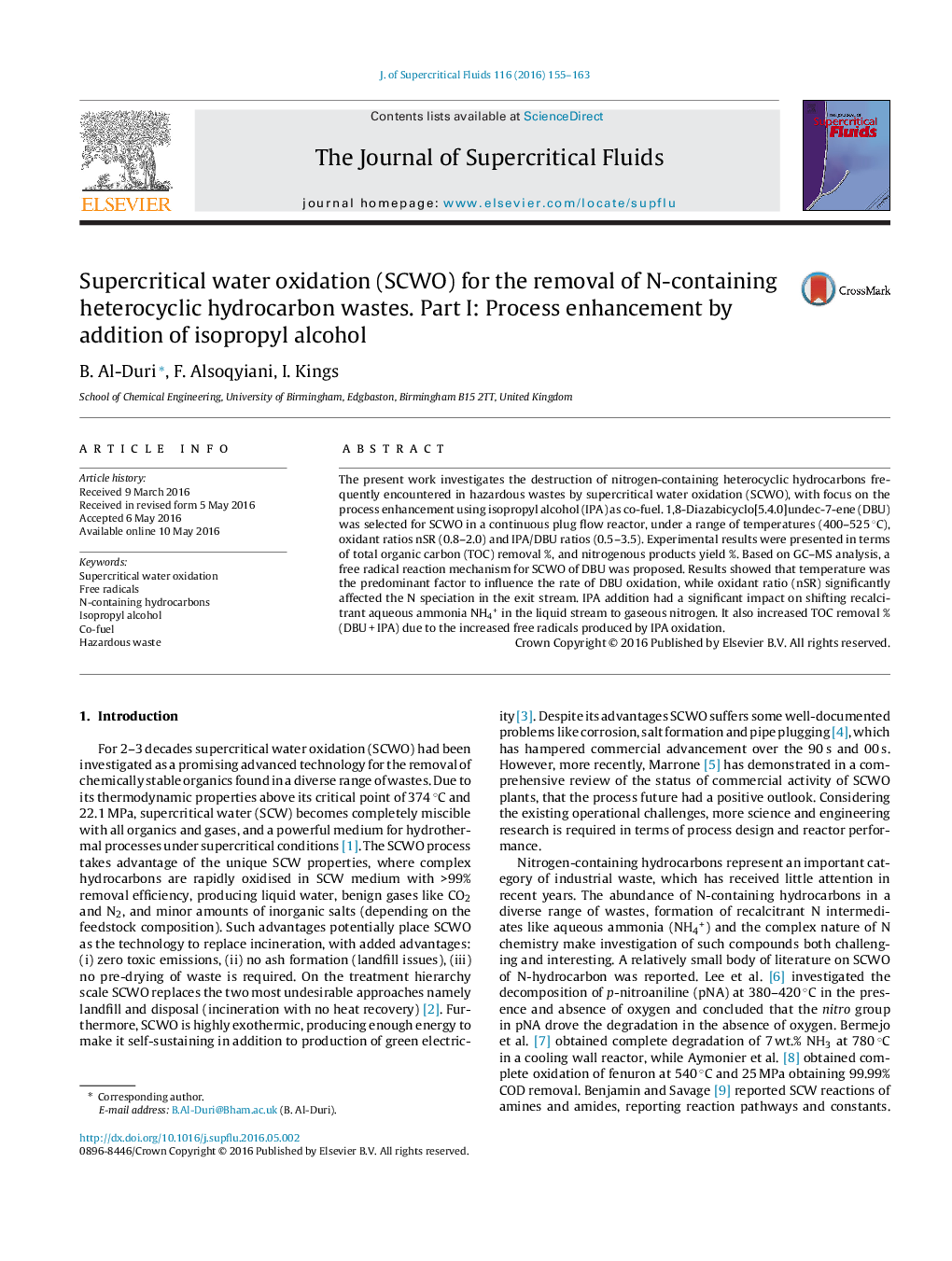
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideConcentration profiles (mg L−1) for N-compounds released during SCWO of DBU, as function of oxidant ratio (nSR). Reactions were conducted at T = 400, Co,DBU = 5 mM; with and without IPA as co-fuel. This graph illustrates that IPA addition as co-fuel reduced aqueous ammonia and total nitrogen in the liquid phase indicating that it was converted to gaseous nitrogen.
Journal: The Journal of Supercritical Fluids - Volume 116, October 2016, Pages 155–163