| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5131068 | 1490882 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
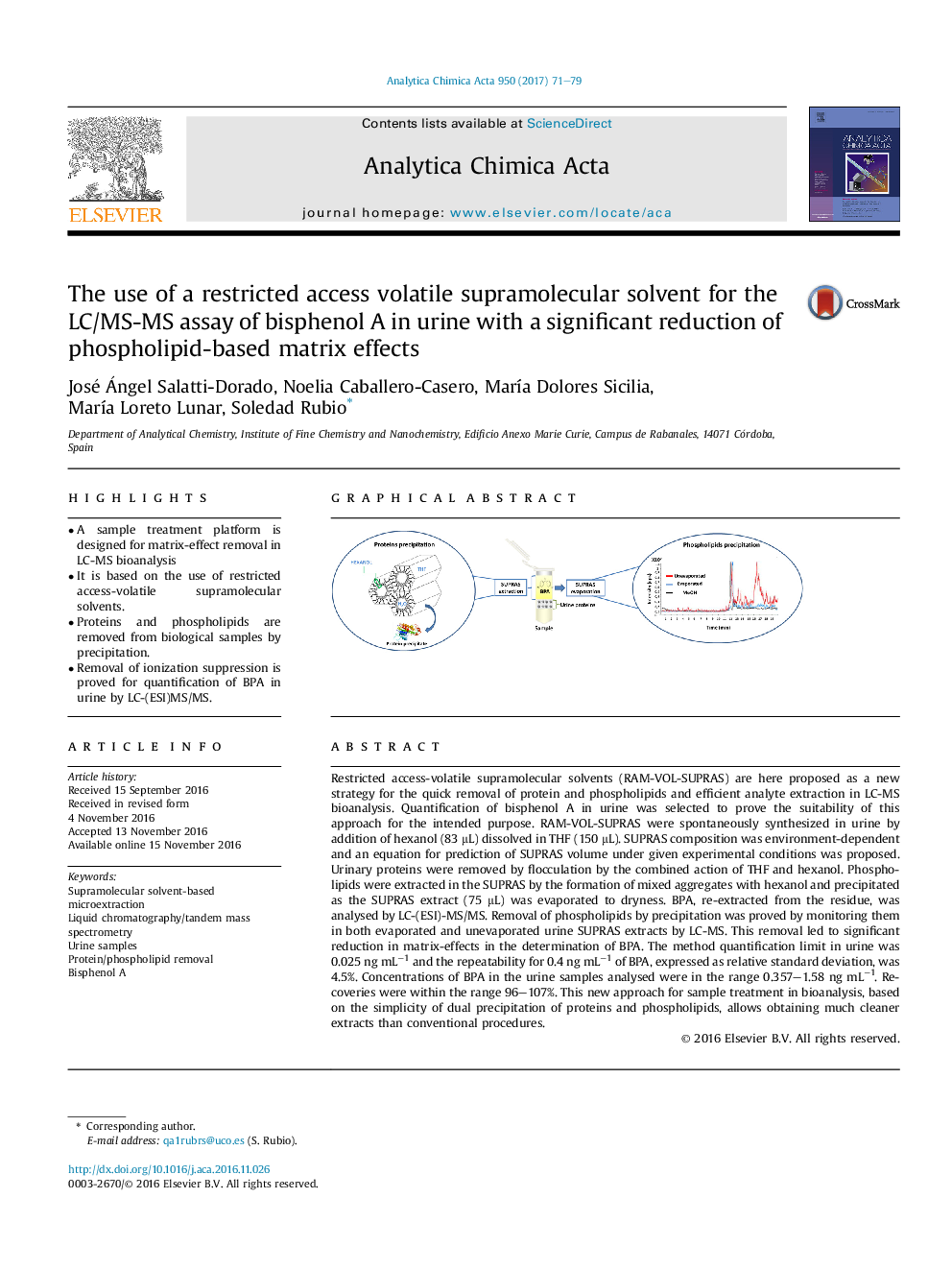
- A sample treatment platform is designed for matrix-effect removal in LC-MS bioanalysis
- It is based on the use of restricted access-volatile supramolecular solvents.
- Proteins and phospholipids are removed from biological samples by precipitation.
- Removal of ionization suppression is proved for quantification of BPA in urine by LC-(ESI)MS/MS.
Restricted access-volatile supramolecular solvents (RAM-VOL-SUPRAS) are here proposed as a new strategy for the quick removal of protein and phospholipids and efficient analyte extraction in LC-MS bioanalysis. Quantification of bisphenol A in urine was selected to prove the suitability of this approach for the intended purpose. RAM-VOL-SUPRAS were spontaneously synthesized in urine by addition of hexanol (83 μL) dissolved in THF (150 μL). SUPRAS composition was environment-dependent and an equation for prediction of SUPRAS volume under given experimental conditions was proposed. Urinary proteins were removed by flocculation by the combined action of THF and hexanol. Phospholipids were extracted in the SUPRAS by the formation of mixed aggregates with hexanol and precipitated as the SUPRAS extract (75 μL) was evaporated to dryness. BPA, re-extracted from the residue, was analysed by LC-(ESI)-MS/MS. Removal of phospholipids by precipitation was proved by monitoring them in both evaporated and unevaporated urine SUPRAS extracts by LC-MS. This removal led to significant reduction in matrix-effects in the determination of BPA. The method quantification limit in urine was 0.025 ng mLâ1 and the repeatability for 0.4 ng mLâ1 of BPA, expressed as relative standard deviation, was 4.5%. Concentrations of BPA in the urine samples analysed were in the range 0.357-1.58 ng mLâ1. Recoveries were within the range 96-107%. This new approach for sample treatment in bioanalysis, based on the simplicity of dual precipitation of proteins and phospholipids, allows obtaining much cleaner extracts than conventional procedures.
178
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 950, 15 January 2017, Pages 71-79