| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5746076 | 1618785 | 2017 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
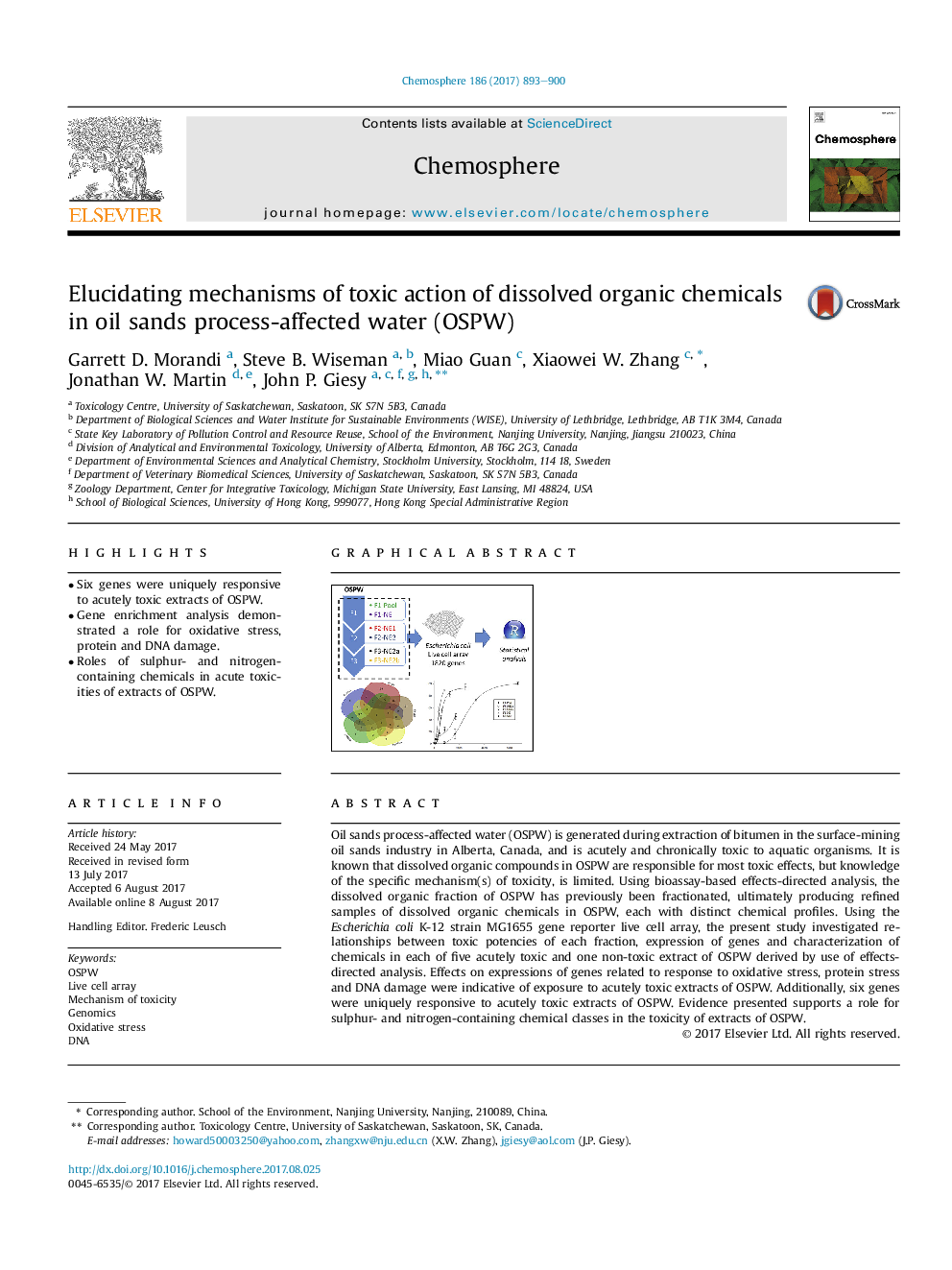
- Six genes were uniquely responsive to acutely toxic extracts of OSPW.
- Gene enrichment analysis demonstrated a role for oxidative stress, protein and DNA damage.
- Roles of sulphur- and nitrogen-containing chemicals in acute toxicities of extracts of OSPW.
Oil sands process-affected water (OSPW) is generated during extraction of bitumen in the surface-mining oil sands industry in Alberta, Canada, and is acutely and chronically toxic to aquatic organisms. It is known that dissolved organic compounds in OSPW are responsible for most toxic effects, but knowledge of the specific mechanism(s) of toxicity, is limited. Using bioassay-based effects-directed analysis, the dissolved organic fraction of OSPW has previously been fractionated, ultimately producing refined samples of dissolved organic chemicals in OSPW, each with distinct chemical profiles. Using the Escherichia coli K-12 strain MG1655 gene reporter live cell array, the present study investigated relationships between toxic potencies of each fraction, expression of genes and characterization of chemicals in each of five acutely toxic and one non-toxic extract of OSPW derived by use of effects-directed analysis. Effects on expressions of genes related to response to oxidative stress, protein stress and DNA damage were indicative of exposure to acutely toxic extracts of OSPW. Additionally, six genes were uniquely responsive to acutely toxic extracts of OSPW. Evidence presented supports a role for sulphur- and nitrogen-containing chemical classes in the toxicity of extracts of OSPW.
182
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 186, November 2017, Pages 893-900