| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10673674 | CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology | 2005 | 4 Pages |
Abstract
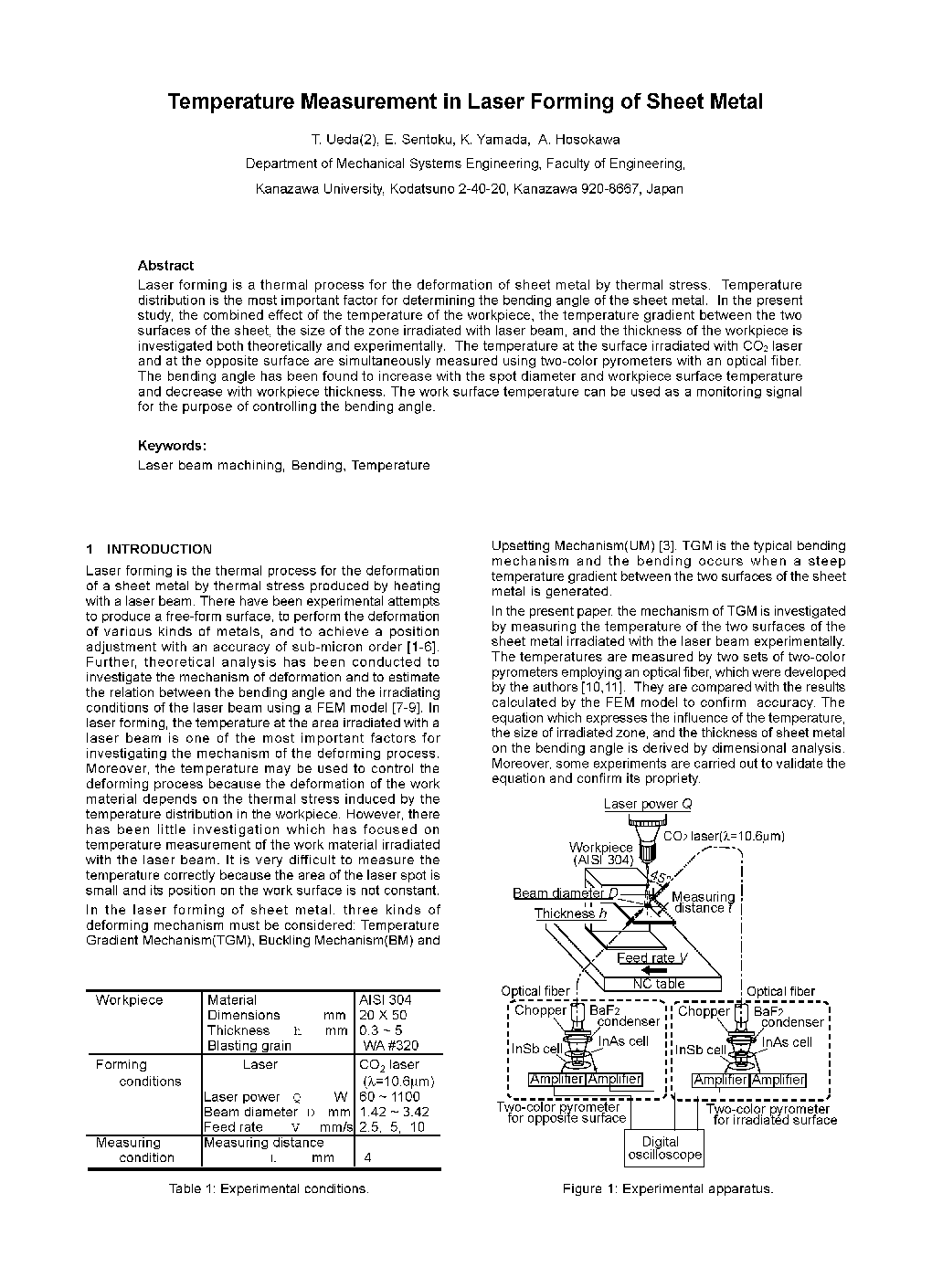
Laser forming is a thermal process for the deformation of sheet metal by thermal stress. Temperature distribution is the most important factor for determining the bending angle of the sheet metal. In the present study, the combined effect of the temperature of the workpiece, the temperature gradient between the two surfaces of the sheet, the size of the zone irradiated with laser beam, and the thickness of the workpiece is investigated both theoretically and experimentally. The temperature at the surface irradiated with C02 laser and at the opposite surface are simultaneously measured using two-color pyrometers with an optical fiber. The bending angle has been found to increase with the spot diameter and workpiece surface temperature and decrease with workpiece thickness. The work surface temperature can be used as a monitoring signal for the purpose of controlling the bending angle.
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Engineering
Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering
Authors
T. Ueda, E. Sentoku, K. Yamada, A. Hosokawa,