| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10702278 | Icarus | 2005 | 5 Pages |
Abstract
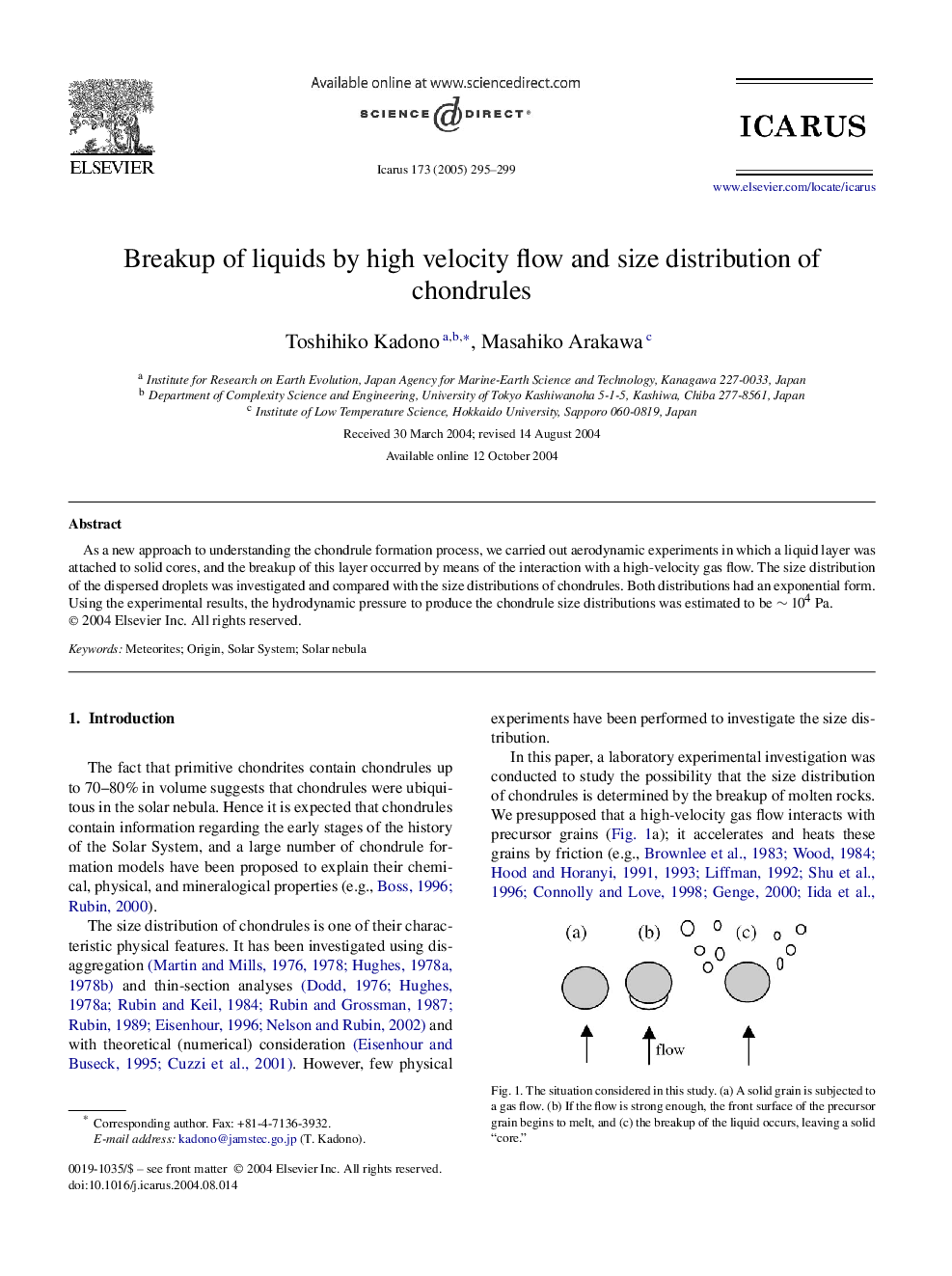
As a new approach to understanding the chondrule formation process, we carried out aerodynamic experiments in which a liquid layer was attached to solid cores, and the breakup of this layer occurred by means of the interaction with a high-velocity gas flow. The size distribution of the dispersed droplets was investigated and compared with the size distributions of chondrules. Both distributions had an exponential form. Using the experimental results, the hydrodynamic pressure to produce the chondrule size distributions was estimated to be â¼ 104 Pa.
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Earth and Planetary Sciences
Space and Planetary Science
Authors
Toshihiko Kadono, Masahiko Arakawa,