| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1228827 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
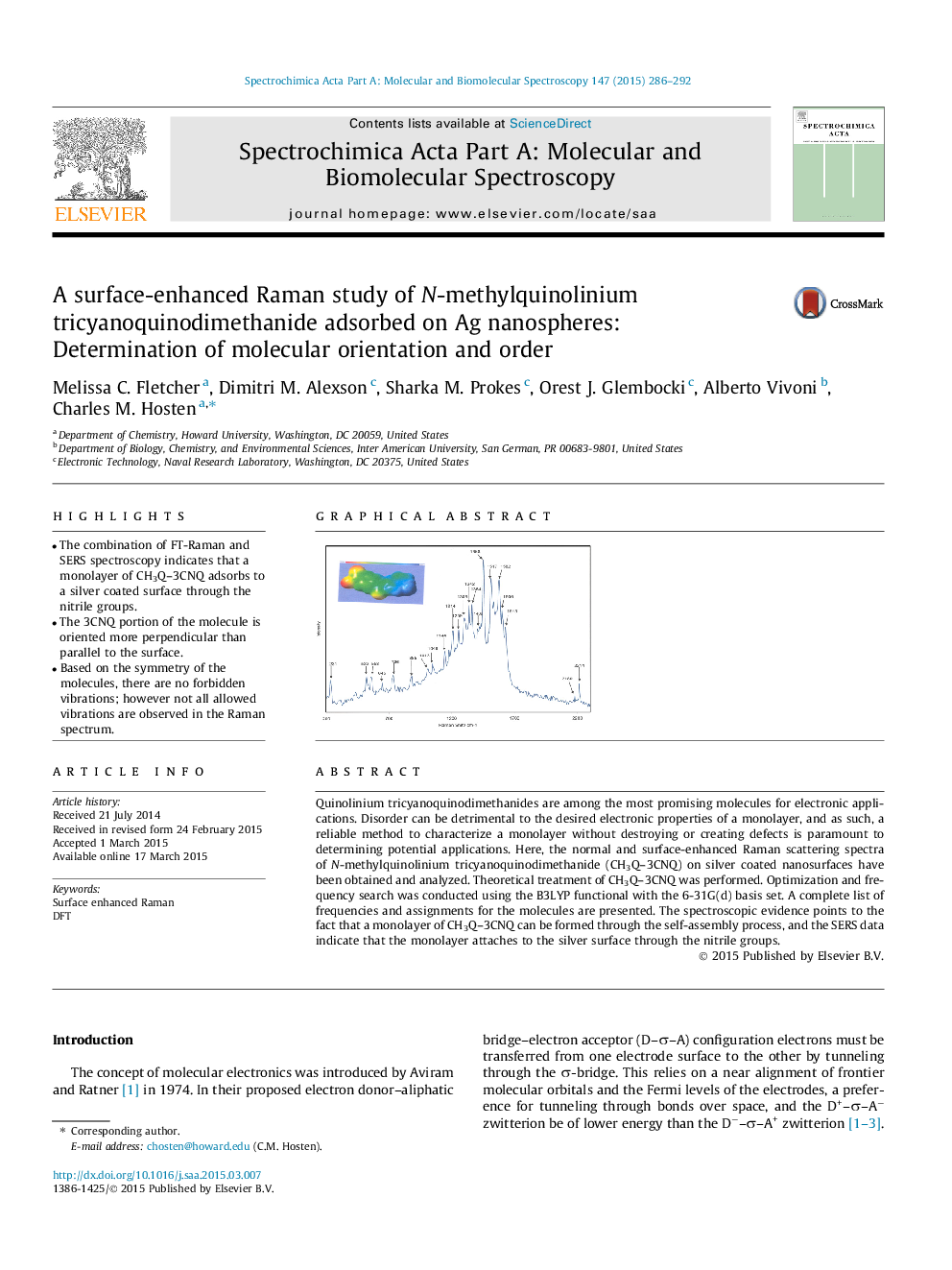
•The combination of FT-Raman and SERS spectroscopy indicates that a monolayer of CH3Q–3CNQ adsorbs to a silver coated surface through the nitrile groups.•The 3CNQ portion of the molecule is oriented more perpendicular than parallel to the surface.•Based on the symmetry of the molecules, there are no forbidden vibrations; however not all allowed vibrations are observed in the Raman spectrum.
Quinolinium tricyanoquinodimethanides are among the most promising molecules for electronic applications. Disorder can be detrimental to the desired electronic properties of a monolayer, and as such, a reliable method to characterize a monolayer without destroying or creating defects is paramount to determining potential applications. Here, the normal and surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra of N-methylquinolinium tricyanoquinodimethanide (CH3Q–3CNQ) on silver coated nanosurfaces have been obtained and analyzed. Theoretical treatment of CH3Q–3CNQ was performed. Optimization and frequency search was conducted using the B3LYP functional with the 6-31G(d) basis set. A complete list of frequencies and assignments for the molecules are presented. The spectroscopic evidence points to the fact that a monolayer of CH3Q–3CNQ can be formed through the self-assembly process, and the SERS data indicate that the monolayer attaches to the silver surface through the nitrile groups.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide