| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1228966 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 5 Pages |
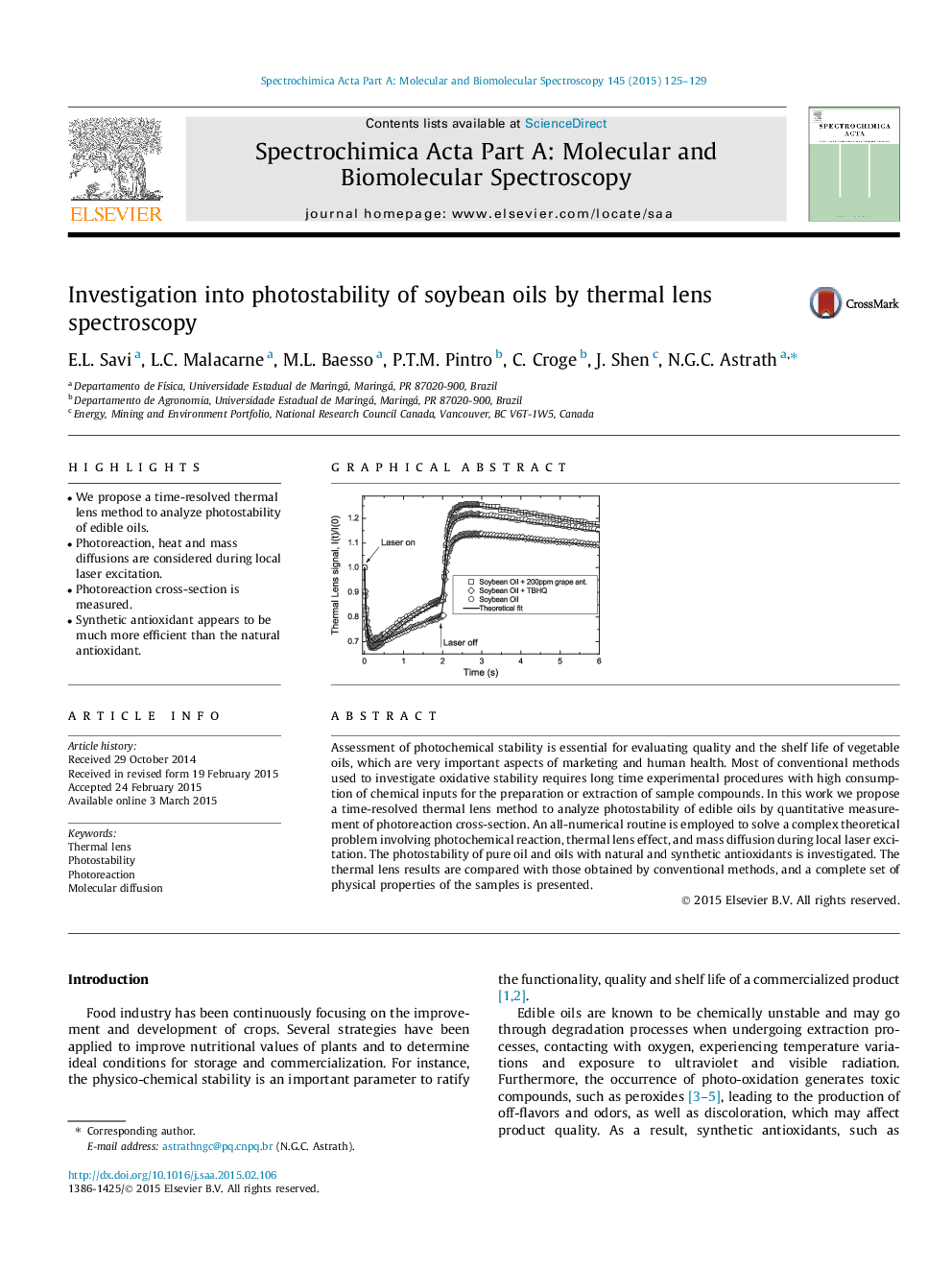
•We propose a time-resolved thermal lens method to analyze photostability of edible oils.•Photoreaction, heat and mass diffusions are considered during local laser excitation.•Photoreaction cross-section is measured.•Synthetic antioxidant appears to be much more efficient than the natural antioxidant.
Assessment of photochemical stability is essential for evaluating quality and the shelf life of vegetable oils, which are very important aspects of marketing and human health. Most of conventional methods used to investigate oxidative stability requires long time experimental procedures with high consumption of chemical inputs for the preparation or extraction of sample compounds. In this work we propose a time-resolved thermal lens method to analyze photostability of edible oils by quantitative measurement of photoreaction cross-section. An all-numerical routine is employed to solve a complex theoretical problem involving photochemical reaction, thermal lens effect, and mass diffusion during local laser excitation. The photostability of pure oil and oils with natural and synthetic antioxidants is investigated. The thermal lens results are compared with those obtained by conventional methods, and a complete set of physical properties of the samples is presented.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide