| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229008 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•The binding of phenanthridine derivatives to HSA was investigated by different methods.•The binding intensity was BTQ > BFQ > DFQ.•The effects of ions on the binding affinity of phenanthridine derivatives to HSA were examined.
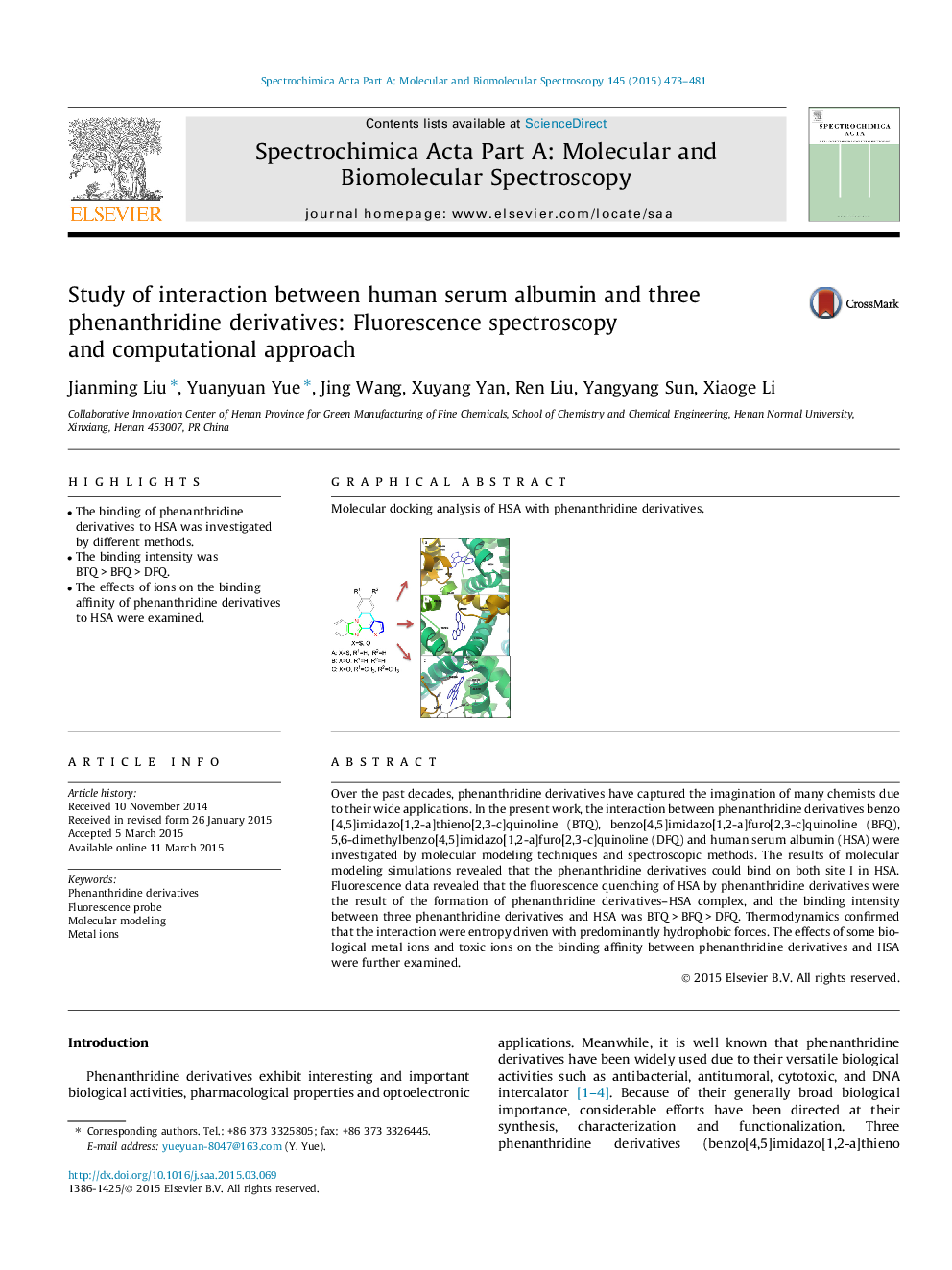
Over the past decades, phenanthridine derivatives have captured the imagination of many chemists due to their wide applications. In the present work, the interaction between phenanthridine derivatives benzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]thieno[2,3-c]quinoline (BTQ), benzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]furo[2,3-c]quinoline (BFQ), 5,6-dimethylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]furo[2,3-c]quinoline (DFQ) and human serum albumin (HSA) were investigated by molecular modeling techniques and spectroscopic methods. The results of molecular modeling simulations revealed that the phenanthridine derivatives could bind on both site I in HSA. Fluorescence data revealed that the fluorescence quenching of HSA by phenanthridine derivatives were the result of the formation of phenanthridine derivatives–HSA complex, and the binding intensity between three phenanthridine derivatives and HSA was BTQ > BFQ > DFQ. Thermodynamics confirmed that the interaction were entropy driven with predominantly hydrophobic forces. The effects of some biological metal ions and toxic ions on the binding affinity between phenanthridine derivatives and HSA were further examined.
Graphical abstractMolecular docking analysis of HSA with phenanthridine derivatives.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide