| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229045 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 8 Pages |
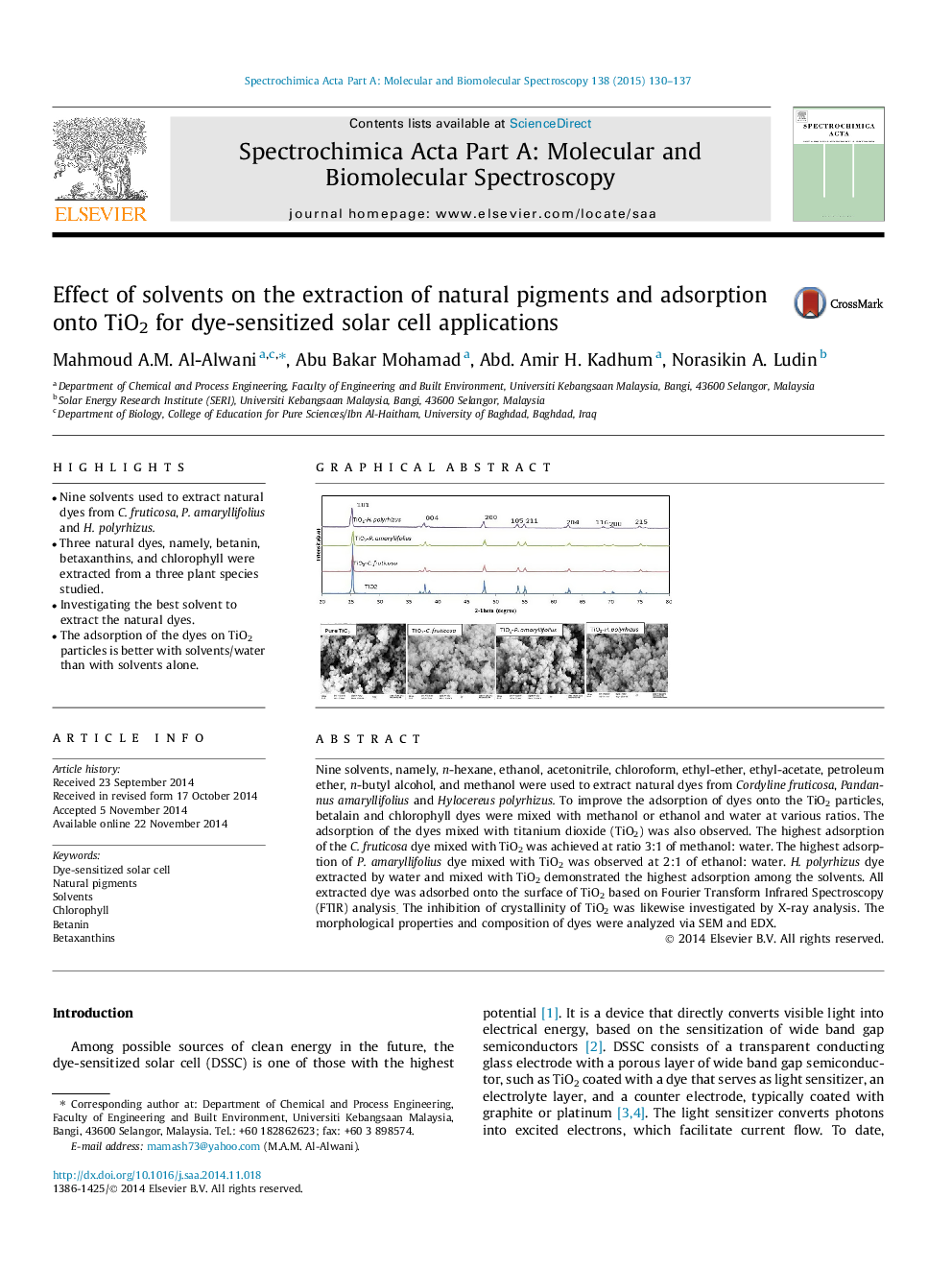
•Nine solvents used to extract natural dyes from C. fruticosa, P. amaryllifolius and H. polyrhizus.•Three natural dyes, namely, betanin, betaxanthins, and chlorophyll were extracted from a three plant species studied.•Investigating the best solvent to extract the natural dyes.•The adsorption of the dyes on TiO2 particles is better with solvents/water than with solvents alone.
Nine solvents, namely, n-hexane, ethanol, acetonitrile, chloroform, ethyl-ether, ethyl-acetate, petroleum ether, n-butyl alcohol, and methanol were used to extract natural dyes from Cordyline fruticosa, Pandannus amaryllifolius and Hylocereus polyrhizus. To improve the adsorption of dyes onto the TiO2 particles, betalain and chlorophyll dyes were mixed with methanol or ethanol and water at various ratios. The adsorption of the dyes mixed with titanium dioxide (TiO2) was also observed. The highest adsorption of the C.fruticosa dye mixed with TiO2 was achieved at ratio 3:1 of methanol: water. The highest adsorption of P.amaryllifolius dye mixed with TiO2 was observed at 2:1 of ethanol: water. H.polyrhizus dye extracted by water and mixed with TiO2 demonstrated the highest adsorption among the solvents. All extracted dye was adsorbed onto the surface of TiO2 based on Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis. The inhibition of crystallinity of TiO2 was likewise investigated by X-ray analysis. The morphological properties and composition of dyes were analyzed via SEM and EDX.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide