| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229050 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
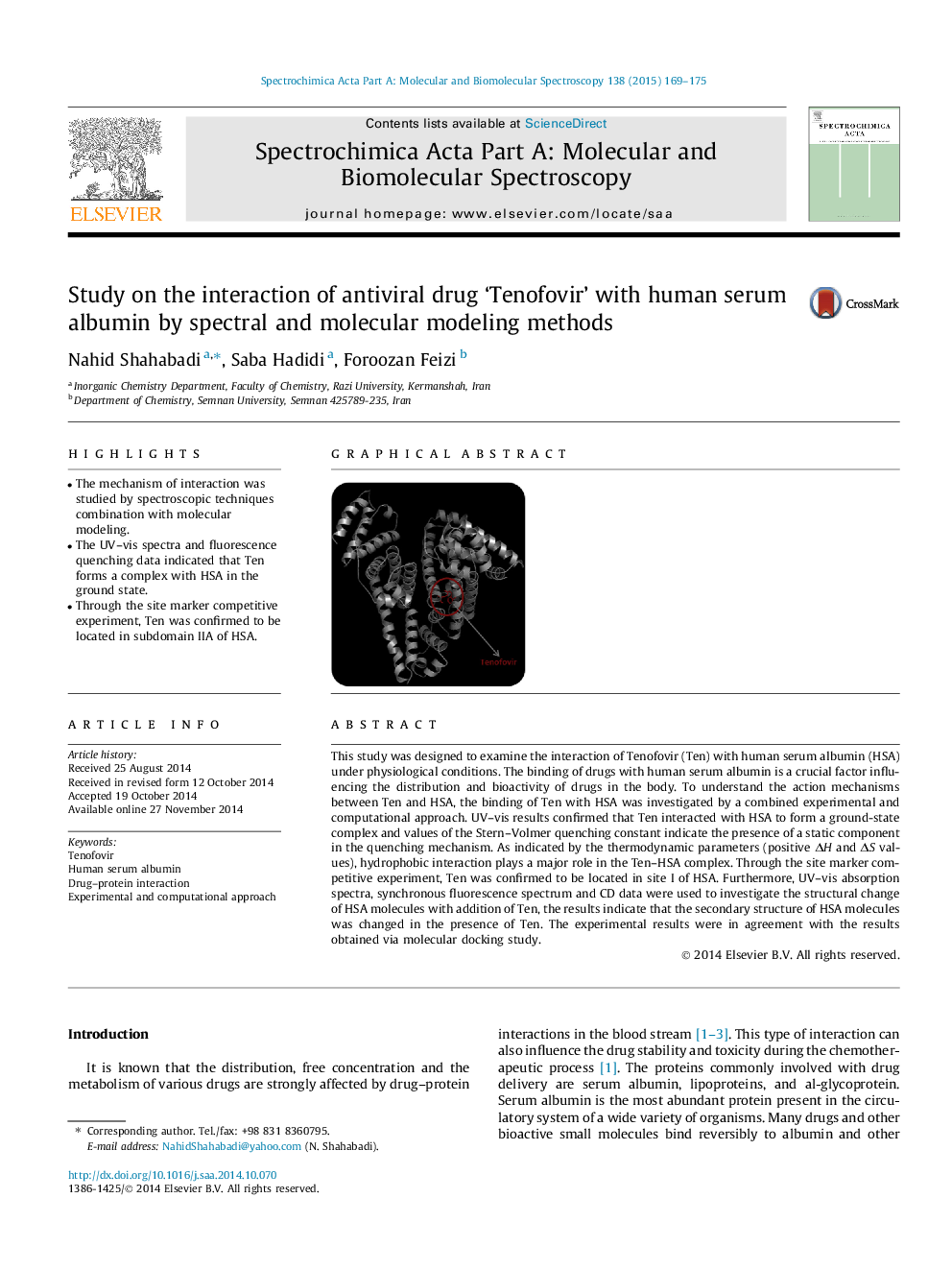
•The mechanism of interaction was studied by spectroscopic techniques combination with molecular modeling.•The UV–vis spectra and fluorescence quenching data indicated that Ten forms a complex with HSA in the ground state.•Through the site marker competitive experiment, Ten was confirmed to be located in subdomain IIA of HSA.
This study was designed to examine the interaction of Tenofovir (Ten) with human serum albumin (HSA) under physiological conditions. The binding of drugs with human serum albumin is a crucial factor influencing the distribution and bioactivity of drugs in the body. To understand the action mechanisms between Ten and HSA, the binding of Ten with HSA was investigated by a combined experimental and computational approach. UV–vis results confirmed that Ten interacted with HSA to form a ground-state complex and values of the Stern–Volmer quenching constant indicate the presence of a static component in the quenching mechanism. As indicated by the thermodynamic parameters (positive ΔH and ΔS values), hydrophobic interaction plays a major role in the Ten–HSA complex. Through the site marker competitive experiment, Ten was confirmed to be located in site I of HSA. Furthermore, UV–vis absorption spectra, synchronous fluorescence spectrum and CD data were used to investigate the structural change of HSA molecules with addition of Ten, the results indicate that the secondary structure of HSA molecules was changed in the presence of Ten. The experimental results were in agreement with the results obtained via molecular docking study.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide