| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229051 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 11 Pages |
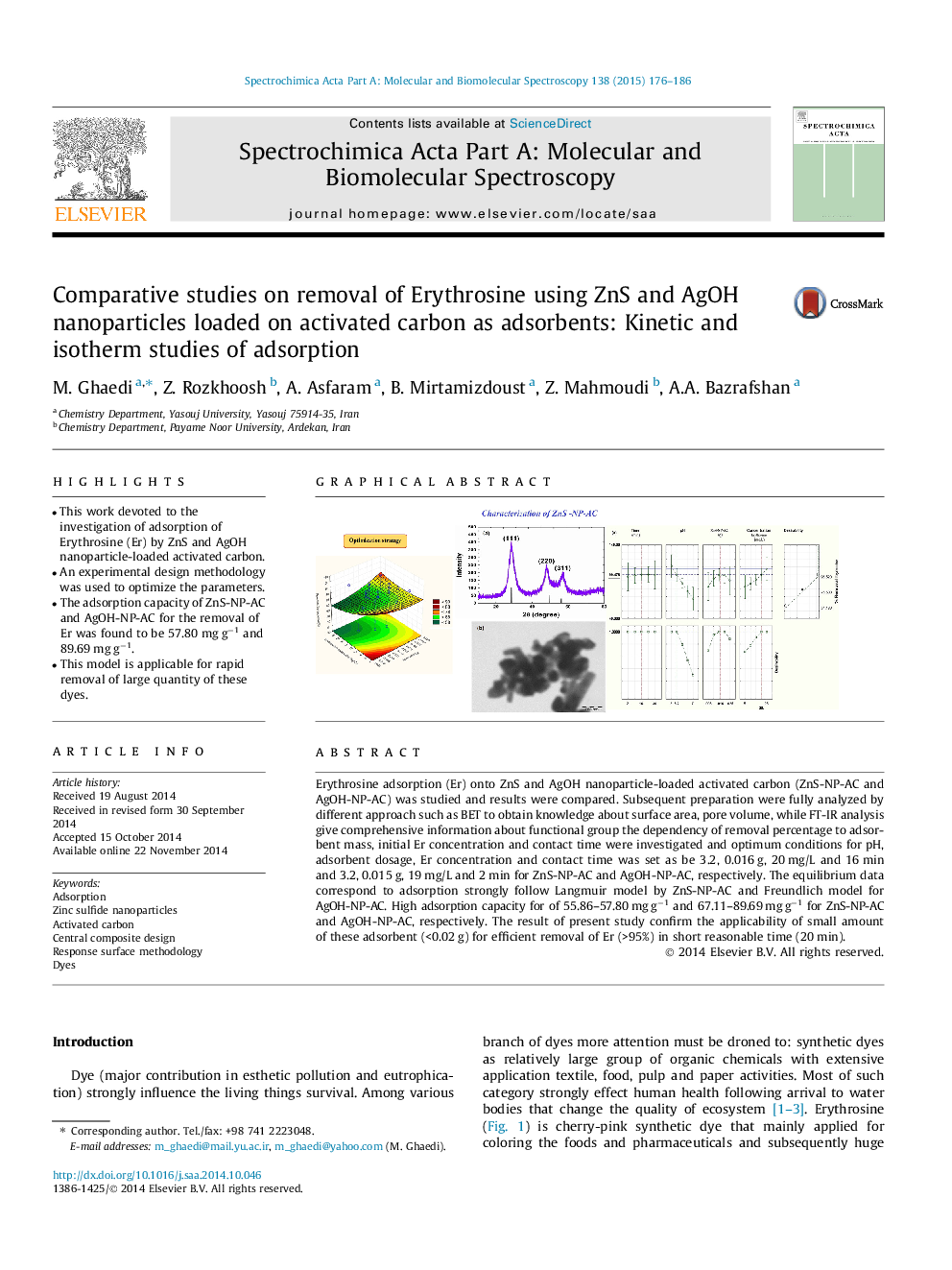
•This work devoted to the investigation of adsorption of Erythrosine (Er) by ZnS and AgOH nanoparticle-loaded activated carbon.•An experimental design methodology was used to optimize the parameters.•The adsorption capacity of ZnS-NP-AC and AgOH-NP-AC for the removal of Er was found to be 57.80 mg g−1 and 89.69 mg g−1.•This model is applicable for rapid removal of large quantity of these dyes.
Erythrosine adsorption (Er) onto ZnS and AgOH nanoparticle-loaded activated carbon (ZnS-NP-AC and AgOH-NP-AC) was studied and results were compared. Subsequent preparation were fully analyzed by different approach such as BET to obtain knowledge about surface area, pore volume, while FT-IR analysis give comprehensive information about functional group the dependency of removal percentage to adsorbent mass, initial Er concentration and contact time were investigated and optimum conditions for pH, adsorbent dosage, Er concentration and contact time was set as be 3.2, 0.016 g, 20 mg/L and 16 min and 3.2, 0.015 g, 19 mg/L and 2 min for ZnS-NP-AC and AgOH-NP-AC, respectively. The equilibrium data correspond to adsorption strongly follow Langmuir model by ZnS-NP-AC and Freundlich model for AgOH-NP-AC. High adsorption capacity for of 55.86–57.80 mg g−1 and 67.11–89.69 mg g−1 for ZnS-NP-AC and AgOH-NP-AC, respectively. The result of present study confirm the applicability of small amount of these adsorbent (<0.02 g) for efficient removal of Er (>95%) in short reasonable time (20 min).
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide