| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229086 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•SeO2/TiO2 was successfully synthesized by sol–gel method.•This new method of preparation gives a homogeneous dispersion of SeO2 on TiO2.•The catalyst is found to be reusable.•COD measurements reveal the complete mineralization of dye molecules.•Addition of oxidants enhances the degradation efficiency significantly.
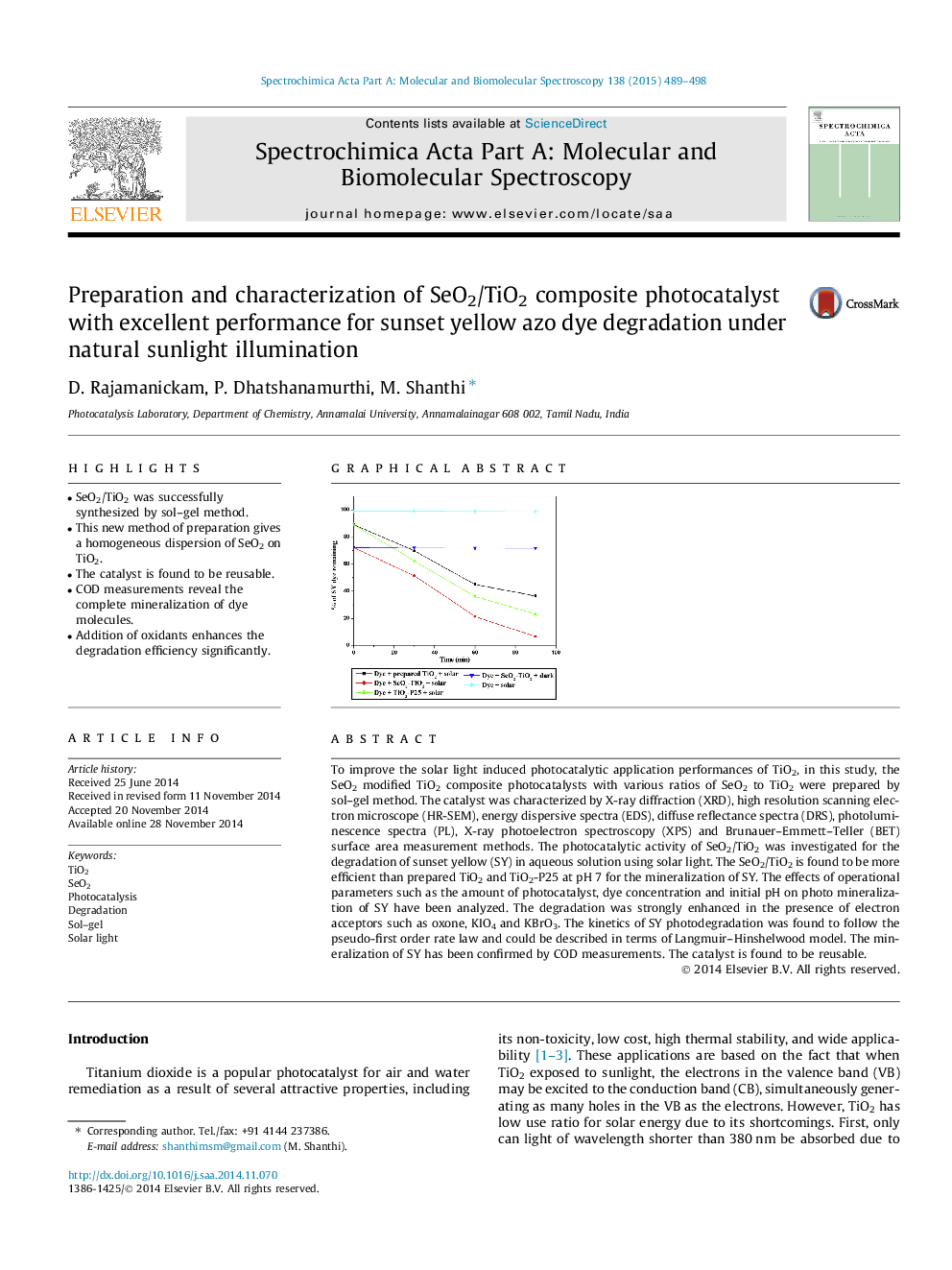
To improve the solar light induced photocatalytic application performances of TiO2, in this study, the SeO2 modified TiO2 composite photocatalysts with various ratios of SeO2 to TiO2 were prepared by sol–gel method. The catalyst was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution scanning electron microscope (HR-SEM), energy dispersive spectra (EDS), diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS), photoluminescence spectra (PL), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement methods. The photocatalytic activity of SeO2/TiO2 was investigated for the degradation of sunset yellow (SY) in aqueous solution using solar light. The SeO2/TiO2 is found to be more efficient than prepared TiO2 and TiO2-P25 at pH 7 for the mineralization of SY. The effects of operational parameters such as the amount of photocatalyst, dye concentration and initial pH on photo mineralization of SY have been analyzed. The degradation was strongly enhanced in the presence of electron acceptors such as oxone, KIO4 and KBrO3. The kinetics of SY photodegradation was found to follow the pseudo-first order rate law and could be described in terms of Langmuir–Hinshelwood model. The mineralization of SY has been confirmed by COD measurements. The catalyst is found to be reusable.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide