| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229110 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 9 Pages |
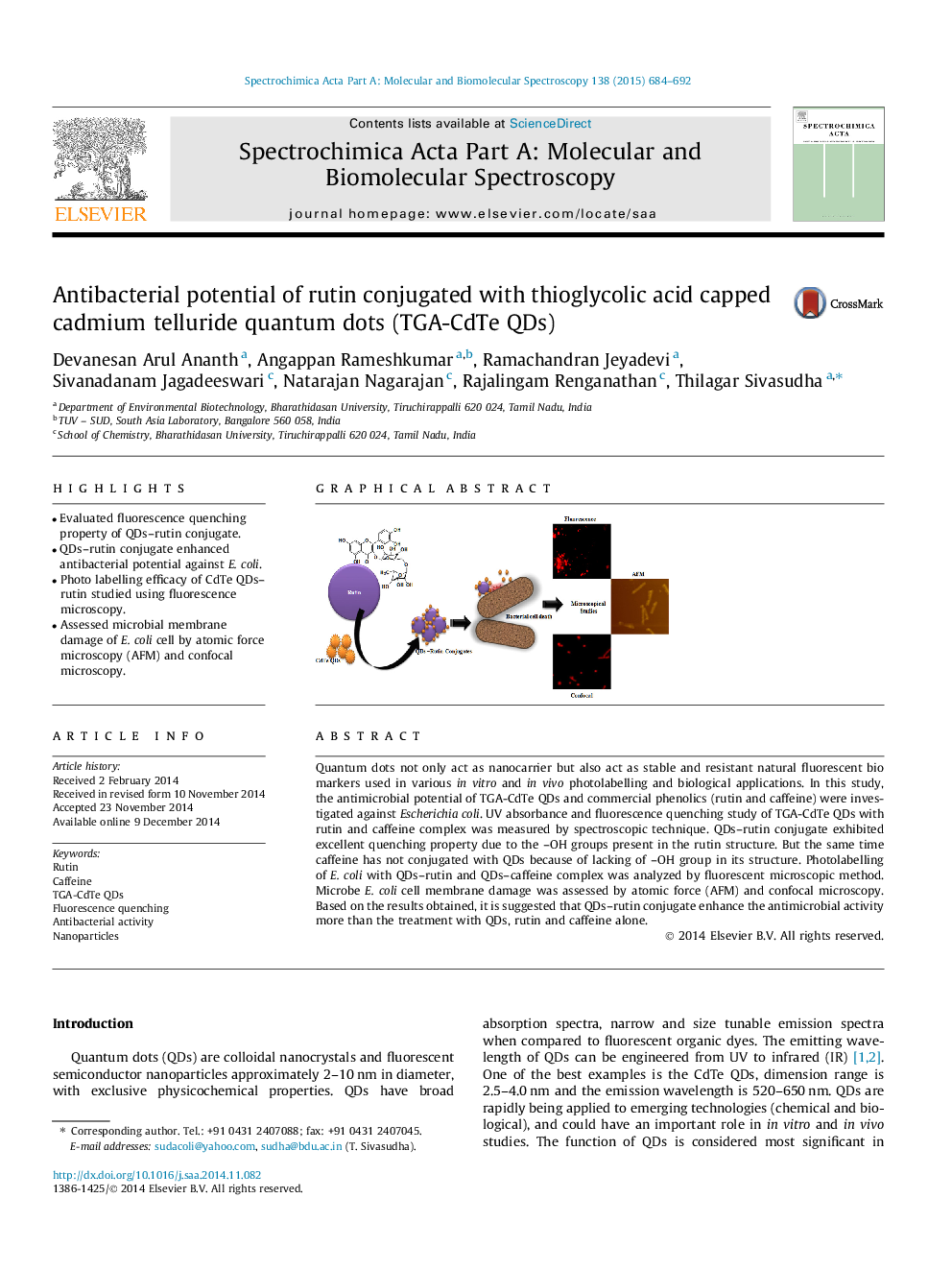
•Evaluated fluorescence quenching property of QDs–rutin conjugate.•QDs–rutin conjugate enhanced antibacterial potential against E. coli.•Photo labelling efficacy of CdTe QDs–rutin studied using fluorescence microscopy.•Assessed microbial membrane damage of E. coli cell by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and confocal microscopy.
Quantum dots not only act as nanocarrier but also act as stable and resistant natural fluorescent bio markers used in various in vitro and in vivo photolabelling and biological applications. In this study, the antimicrobial potential of TGA-CdTe QDs and commercial phenolics (rutin and caffeine) were investigated against Escherichiacoli. UV absorbance and fluorescence quenching study of TGA-CdTe QDs with rutin and caffeine complex was measured by spectroscopic technique. QDs–rutin conjugate exhibited excellent quenching property due to the –OH groups present in the rutin structure. But the same time caffeine has not conjugated with QDs because of lacking of –OH group in its structure. Photolabelling of E. coli with QDs–rutin and QDs–caffeine complex was analyzed by fluorescent microscopic method. Microbe E. coli cell membrane damage was assessed by atomic force (AFM) and confocal microscopy. Based on the results obtained, it is suggested that QDs–rutin conjugate enhance the antimicrobial activity more than the treatment with QDs, rutin and caffeine alone.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide