| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229123 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 4 Pages |
•An improved procedure for determination of the mean aggregation number of micelles is presented.•This model assumes that a part of quencher molecules are in the aqueous phase.•The aggregation numbers of sodium dodecyl sulfonate in aqueous dipeptide solution are determined.•The association constant for quencher–micelle association can be calculated.
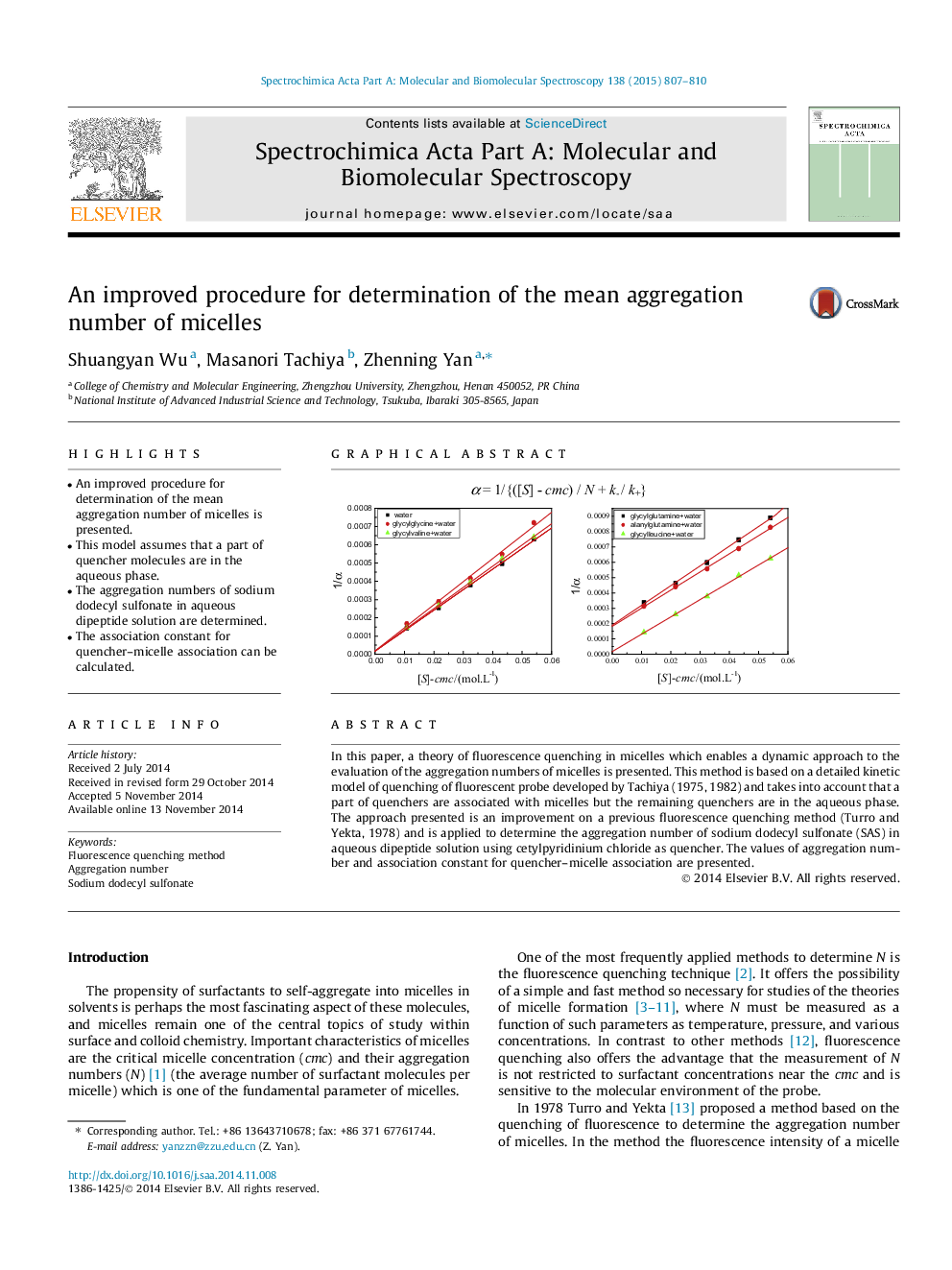
In this paper, a theory of fluorescence quenching in micelles which enables a dynamic approach to the evaluation of the aggregation numbers of micelles is presented. This method is based on a detailed kinetic model of quenching of fluorescent probe developed by Tachiya (1975, 1982) and takes into account that a part of quenchers are associated with micelles but the remaining quenchers are in the aqueous phase. The approach presented is an improvement on a previous fluorescence quenching method (Turro and Yekta, 1978) and is applied to determine the aggregation number of sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SAS) in aqueous dipeptide solution using cetylpyridinium chloride as quencher. The values of aggregation number and association constant for quencher–micelle association are presented.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide