| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229167 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 9 Pages |
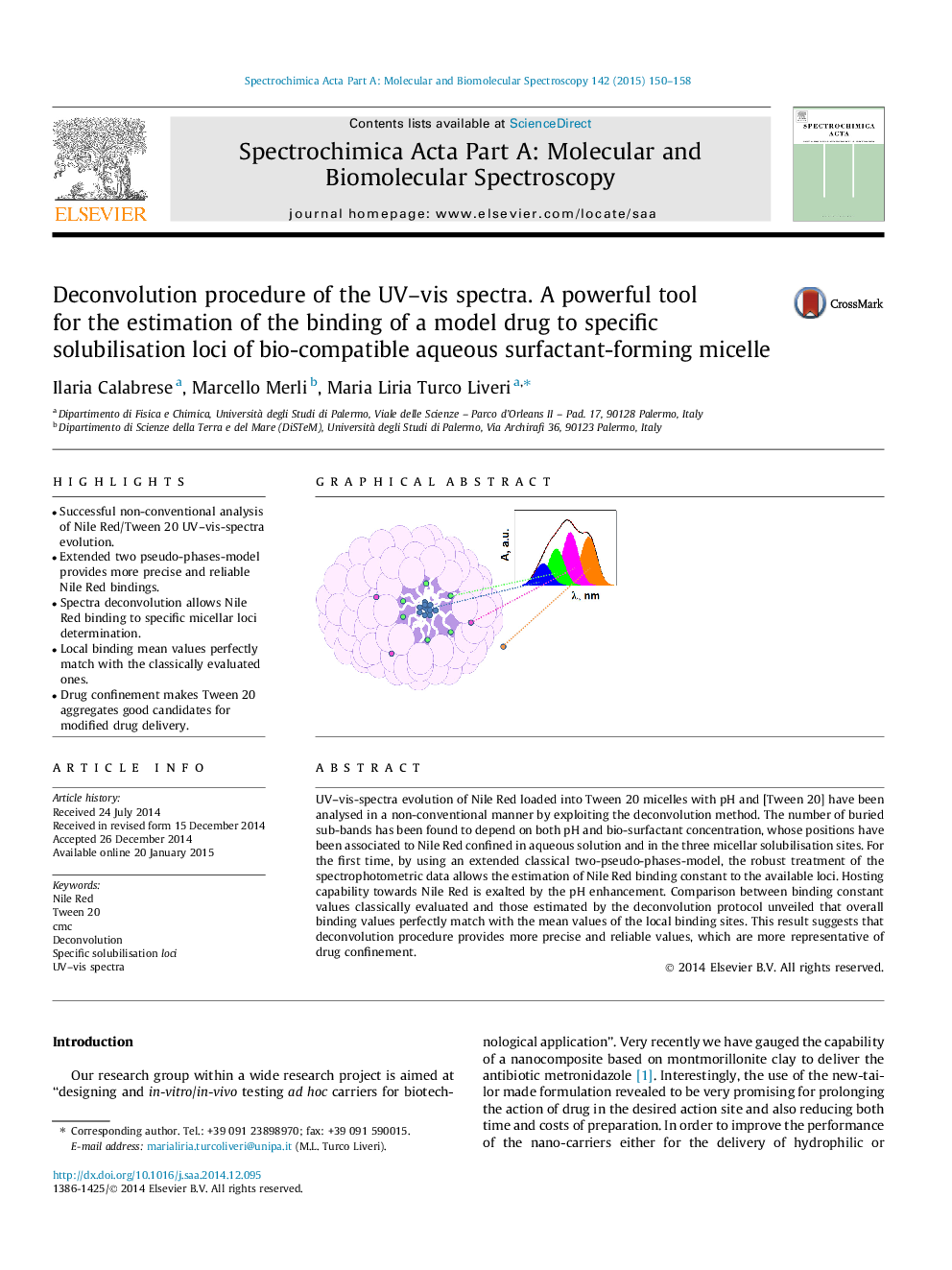
•Successful non-conventional analysis of Nile Red/Tween 20 UV–vis-spectra evolution.•Extended two pseudo-phases-model provides more precise and reliable Nile Red bindings.•Spectra deconvolution allows Nile Red binding to specific micellar loci determination.•Local binding mean values perfectly match with the classically evaluated ones.•Drug confinement makes Tween 20 aggregates good candidates for modified drug delivery.
UV–vis-spectra evolution of Nile Red loaded into Tween 20 micelles with pH and [Tween 20] have been analysed in a non-conventional manner by exploiting the deconvolution method. The number of buried sub-bands has been found to depend on both pH and bio-surfactant concentration, whose positions have been associated to Nile Red confined in aqueous solution and in the three micellar solubilisation sites. For the first time, by using an extended classical two-pseudo-phases-model, the robust treatment of the spectrophotometric data allows the estimation of Nile Red binding constant to the available loci. Hosting capability towards Nile Red is exalted by the pH enhancement. Comparison between binding constant values classically evaluated and those estimated by the deconvolution protocol unveiled that overall binding values perfectly match with the mean values of the local binding sites. This result suggests that deconvolution procedure provides more precise and reliable values, which are more representative of drug confinement.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide