| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229179 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 14 Pages |
•TAME5OX, is a symmetric and strong tripodal metal chelator.•Above physiological pH, ML (M = Fe, Al and Cr) was found with interesting photophysical properties.•The quenching of fluorescence for Fe3+ and Cr3+ is activated through the PET phenomena.•Reverse effect of PPT was observed for Al3+ which greatly enhanced the fluorescence.•TD-DFT reveals the good agreement with the available experimental data.
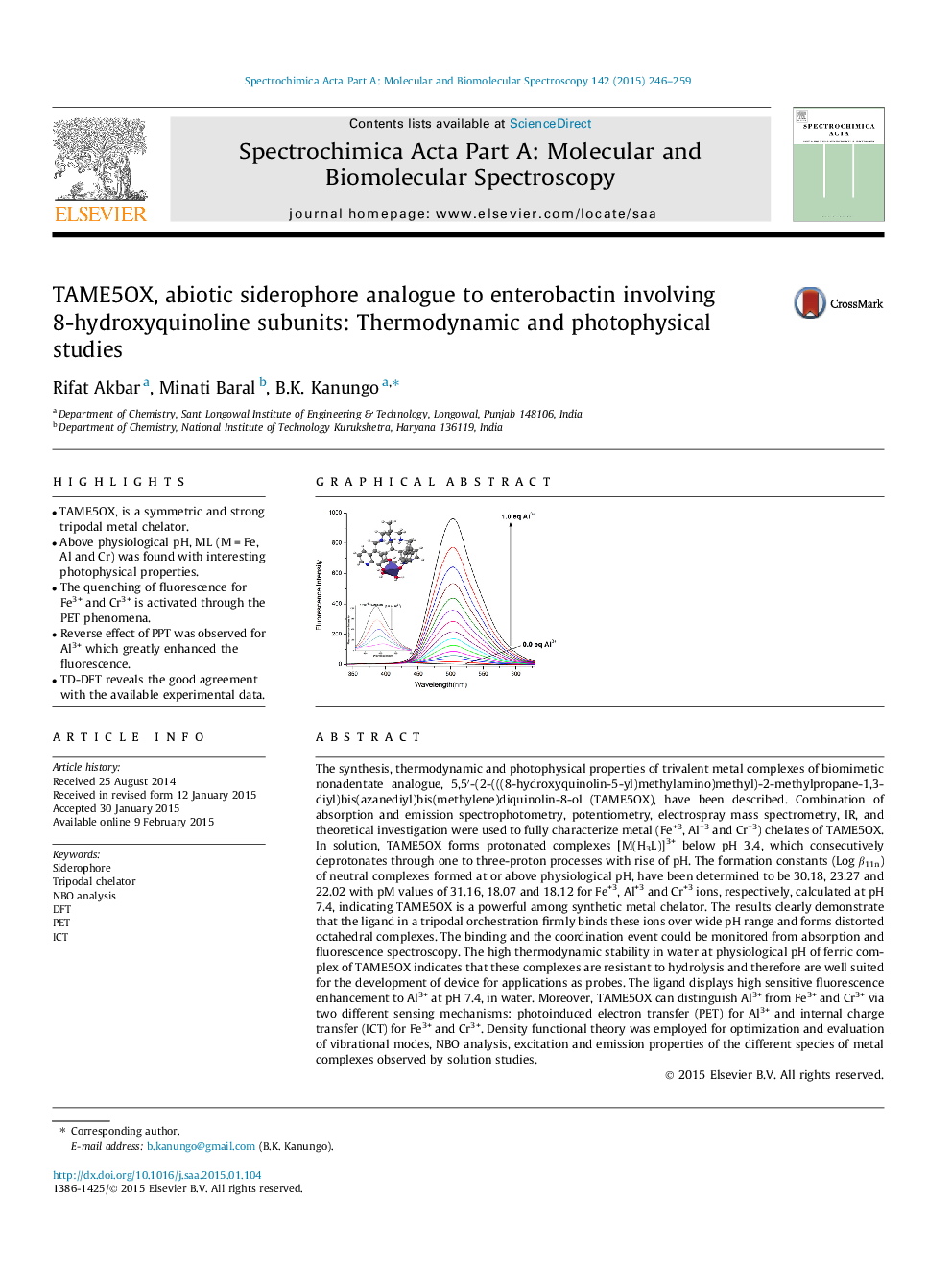
The synthesis, thermodynamic and photophysical properties of trivalent metal complexes of biomimetic nonadentate analogue, 5,5′-(2-(((8-hydroxyquinolin-5-yl)methylamino)methyl)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanediyl)bis(methylene)diquinolin-8-ol (TAME5OX), have been described. Combination of absorption and emission spectrophotometry, potentiometry, electrospray mass spectrometry, IR, and theoretical investigation were used to fully characterize metal (Fe+3, Al+3 and Cr+3) chelates of TAME5OX. In solution, TAME5OX forms protonated complexes [M(H3L)]3+ below pH 3.4, which consecutively deprotonates through one to three-proton processes with rise of pH. The formation constants (Log β11n) of neutral complexes formed at or above physiological pH, have been determined to be 30.18, 23.27 and 22.02 with pM values of 31.16, 18.07 and 18.12 for Fe+3, Al+3 and Cr+3 ions, respectively, calculated at pH 7.4, indicating TAME5OX is a powerful among synthetic metal chelator. The results clearly demonstrate that the ligand in a tripodal orchestration firmly binds these ions over wide pH range and forms distorted octahedral complexes. The binding and the coordination event could be monitored from absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. The high thermodynamic stability in water at physiological pH of ferric complex of TAME5OX indicates that these complexes are resistant to hydrolysis and therefore are well suited for the development of device for applications as probes. The ligand displays high sensitive fluorescence enhancement to Al3+ at pH 7.4, in water. Moreover, TAME5OX can distinguish Al3+ from Fe3+ and Cr3+ via two different sensing mechanisms: photoinduced electron transfer (PET) for Al3+ and internal charge transfer (ICT) for Fe3+ and Cr3+. Density functional theory was employed for optimization and evaluation of vibrational modes, NBO analysis, excitation and emission properties of the different species of metal complexes observed by solution studies.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide