| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229210 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
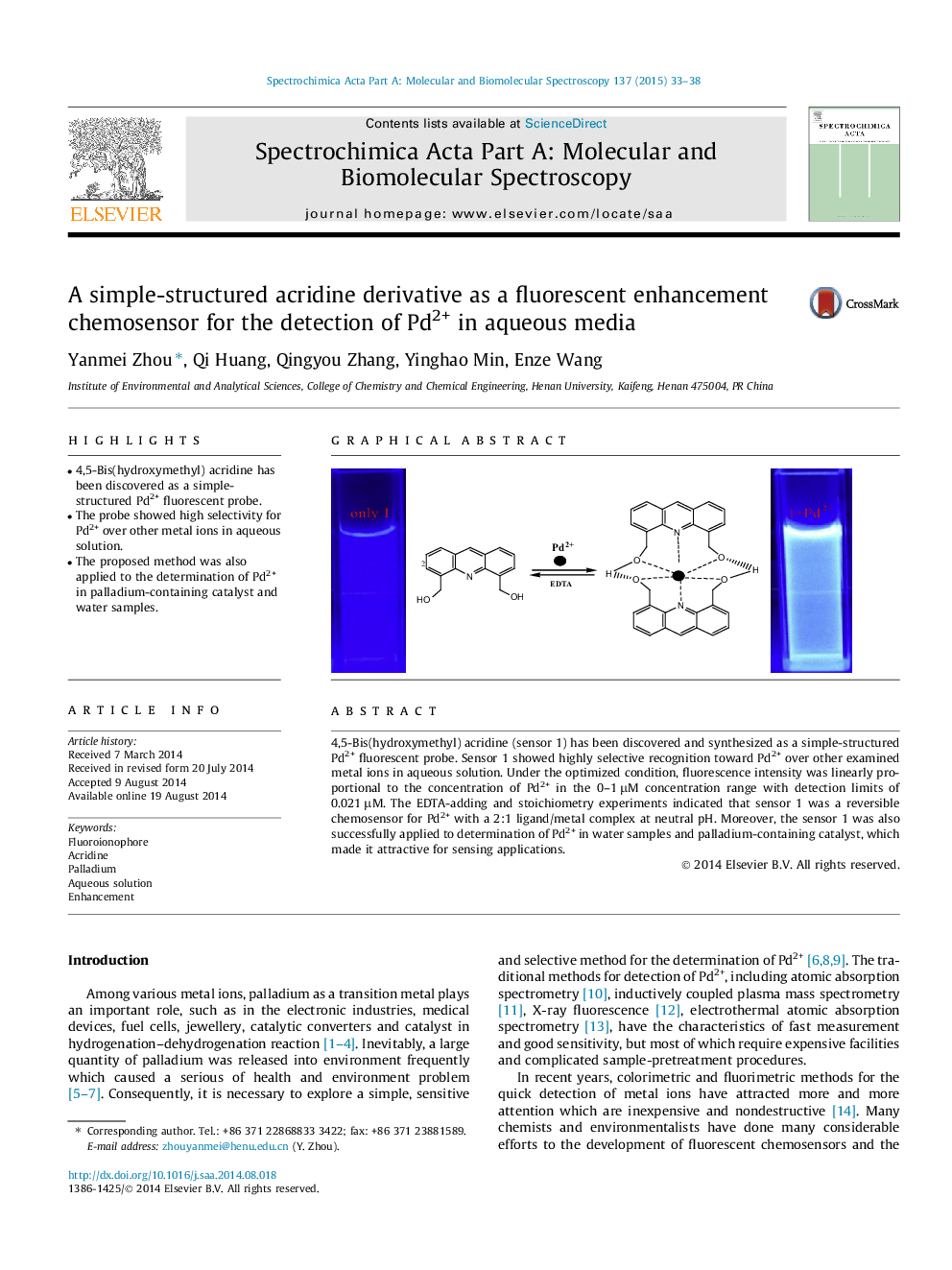
•4,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl) acridine has been discovered as a simple-structured Pd2+ fluorescent probe.•The probe showed high selectivity for Pd2+ over other metal ions in aqueous solution.•The proposed method was also applied to the determination of Pd2+ in palladium-containing catalyst and water samples.
4,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl) acridine (sensor 1) has been discovered and synthesized as a simple-structured Pd2+ fluorescent probe. Sensor 1 showed highly selective recognition toward Pd2+ over other examined metal ions in aqueous solution. Under the optimized condition, fluorescence intensity was linearly proportional to the concentration of Pd2+ in the 0–1 μM concentration range with detection limits of 0.021 μM. The EDTA-adding and stoichiometry experiments indicated that sensor 1 was a reversible chemosensor for Pd2+ with a 2:1 ligand/metal complex at neutral pH. Moreover, the sensor 1 was also successfully applied to determination of Pd2+ in water samples and palladium-containing catalyst, which made it attractive for sensing applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide