| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229227 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•Impact of synthesized conditions on the reactivity of Fe NPs was studied.•Fe NPs were used for the degradation of MG.•90.56% of MG was removed using Fe NPs.•Fe NPs were characterized by various techniques.
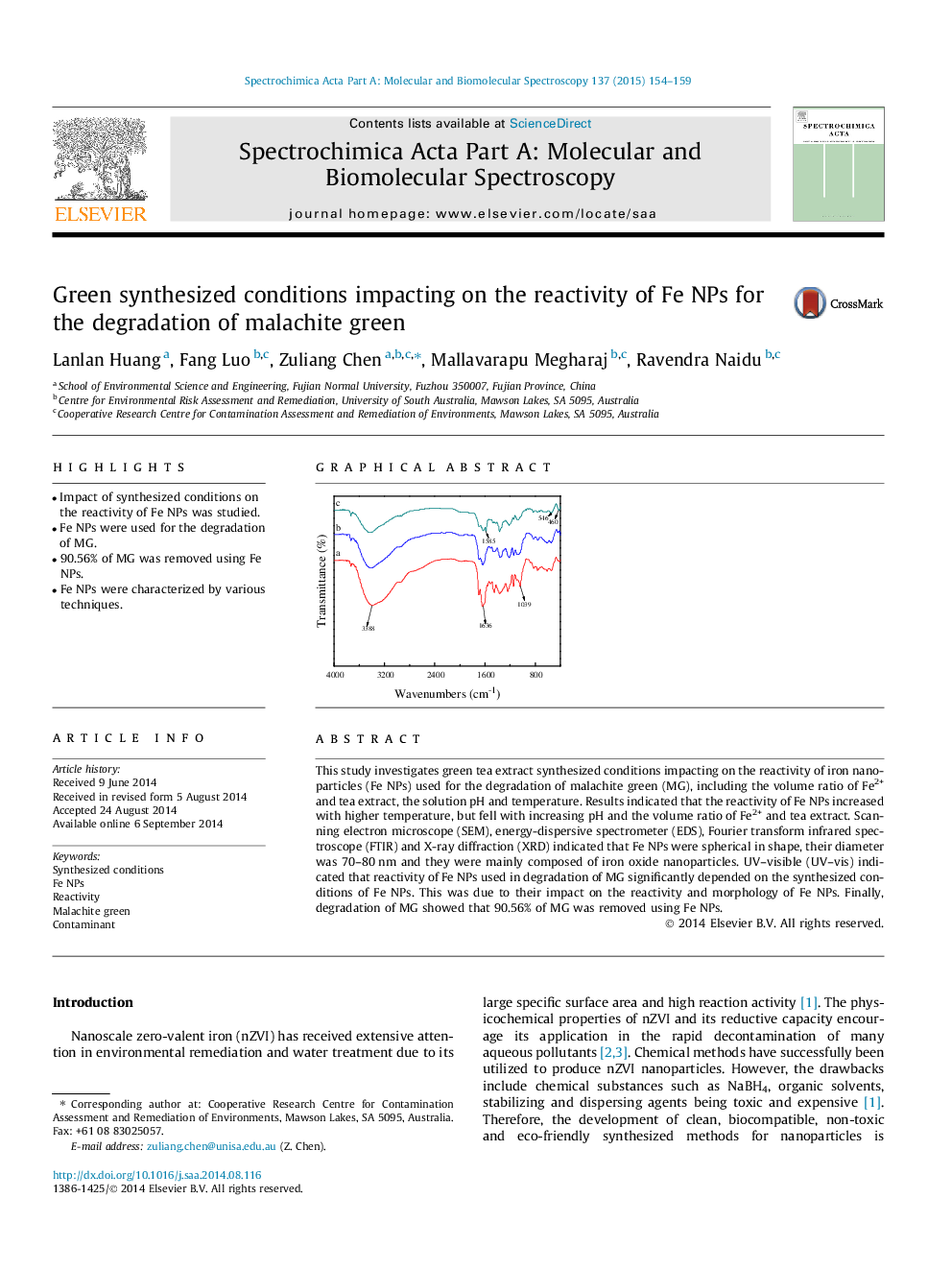
This study investigates green tea extract synthesized conditions impacting on the reactivity of iron nanoparticles (Fe NPs) used for the degradation of malachite green (MG), including the volume ratio of Fe2+ and tea extract, the solution pH and temperature. Results indicated that the reactivity of Fe NPs increased with higher temperature, but fell with increasing pH and the volume ratio of Fe2+ and tea extract. Scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) indicated that Fe NPs were spherical in shape, their diameter was 70–80 nm and they were mainly composed of iron oxide nanoparticles. UV–visible (UV–vis) indicated that reactivity of Fe NPs used in degradation of MG significantly depended on the synthesized conditions of Fe NPs. This was due to their impact on the reactivity and morphology of Fe NPs. Finally, degradation of MG showed that 90.56% of MG was removed using Fe NPs.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide