| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229249 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 5 Pages |
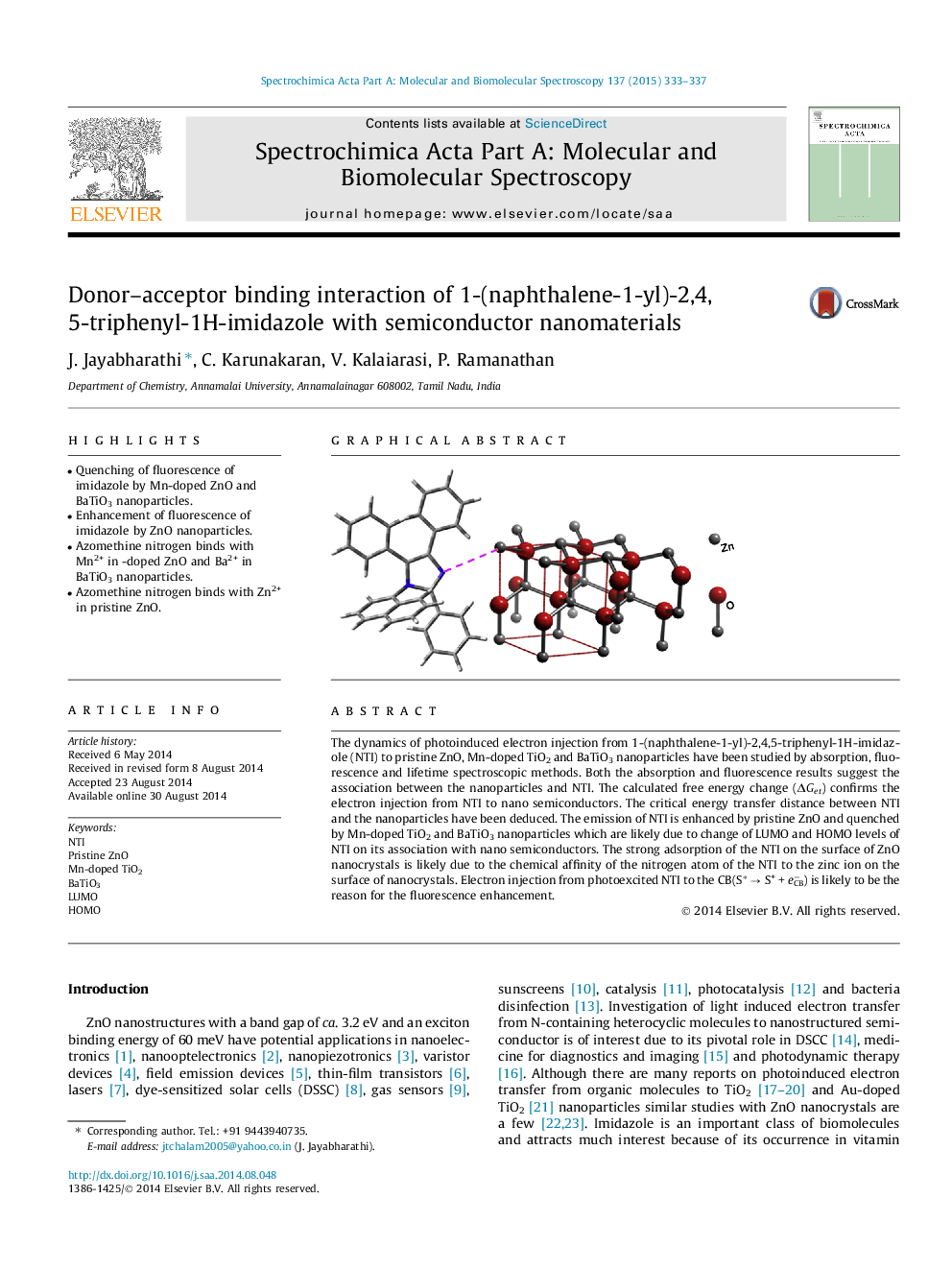
•Quenching of fluorescence of imidazole by Mn-doped ZnO and BaTiO3 nanoparticles.•Enhancement of fluorescence of imidazole by ZnO nanoparticles.•Azomethine nitrogen binds with Mn2+ in -doped ZnO and Ba2+ in BaTiO3 nanoparticles.•Azomethine nitrogen binds with Zn2+ in pristine ZnO.
The dynamics of photoinduced electron injection from 1-(naphthalene-1-yl)-2,4,5-triphenyl-1H-imidazole (NTI) to pristine ZnO, Mn-doped TiO2 and BaTiO3 nanoparticles have been studied by absorption, fluorescence and lifetime spectroscopic methods. Both the absorption and fluorescence results suggest the association between the nanoparticles and NTI. The calculated free energy change (ΔGet) confirms the electron injection from NTI to nano semiconductors. The critical energy transfer distance between NTI and the nanoparticles have been deduced. The emission of NTI is enhanced by pristine ZnO and quenched by Mn-doped TiO2 and BaTiO3 nanoparticles which are likely due to change of LUMO and HOMO levels of NTI on its association with nano semiconductors. The strong adsorption of the NTI on the surface of ZnO nanocrystals is likely due to the chemical affinity of the nitrogen atom of the NTI to the zinc ion on the surface of nanocrystals. Electron injection from photoexcited NTI to the CB(S∗ → S+ + e−CB) is likely to be the reason for the fluorescence enhancement.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide