| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229255 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
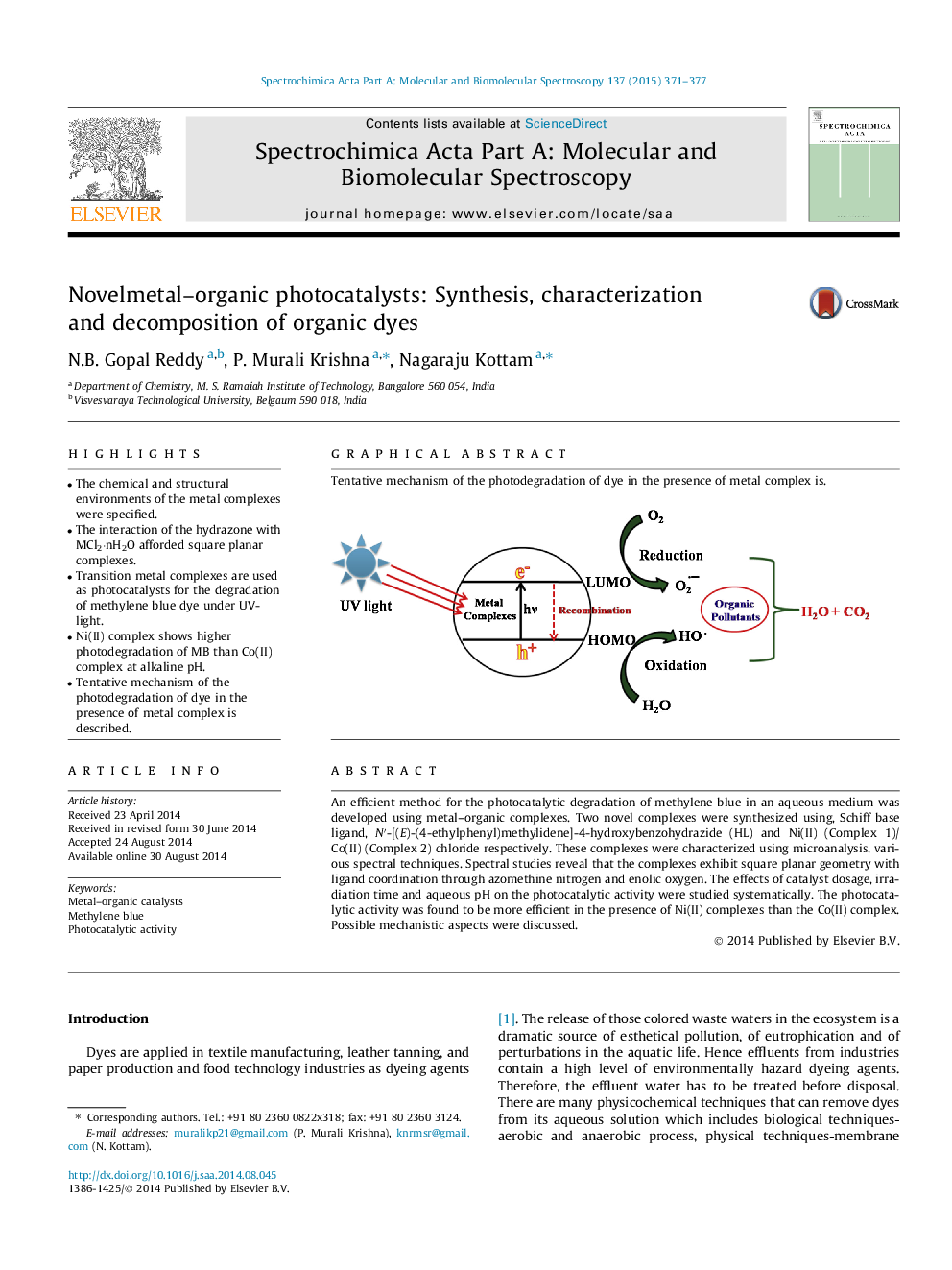
•The chemical and structural environments of the metal complexes were specified.•The interaction of the hydrazone with MCl2⋅nH2O afforded square planar complexes.•Transition metal complexes are used as photocatalysts for the degradation of methylene blue dye under UV-light.•Ni(II) complex shows higher photodegradation of MB than Co(II) complex at alkaline pH.•Tentative mechanism of the photodegradation of dye in the presence of metal complex is described.
An efficient method for the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in an aqueous medium was developed using metal–organic complexes. Two novel complexes were synthesized using, Schiff base ligand, N′-[(E)-(4-ethylphenyl)methylidene]-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide (HL) and Ni(II) (Complex 1)/Co(II) (Complex 2) chloride respectively. These complexes were characterized using microanalysis, various spectral techniques. Spectral studies reveal that the complexes exhibit square planar geometry with ligand coordination through azomethine nitrogen and enolic oxygen. The effects of catalyst dosage, irradiation time and aqueous pH on the photocatalytic activity were studied systematically. The photocatalytic activity was found to be more efficient in the presence of Ni(II) complexes than the Co(II) complex. Possible mechanistic aspects were discussed.
Graphical abstractTentative mechanism of the photodegradation of dye in the presence of metal complex is.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide