| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229273 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•A maleimide bearing naphthalimide was proposed as new two-photon probe for Cys.•Response mechanism was investigated by theoretical and experimental methods.•Sensitive and selective detection of Cys over GSH and Hcy was achieved.•The probe was successfully applied for two-photon imaging of intracellular Cys.
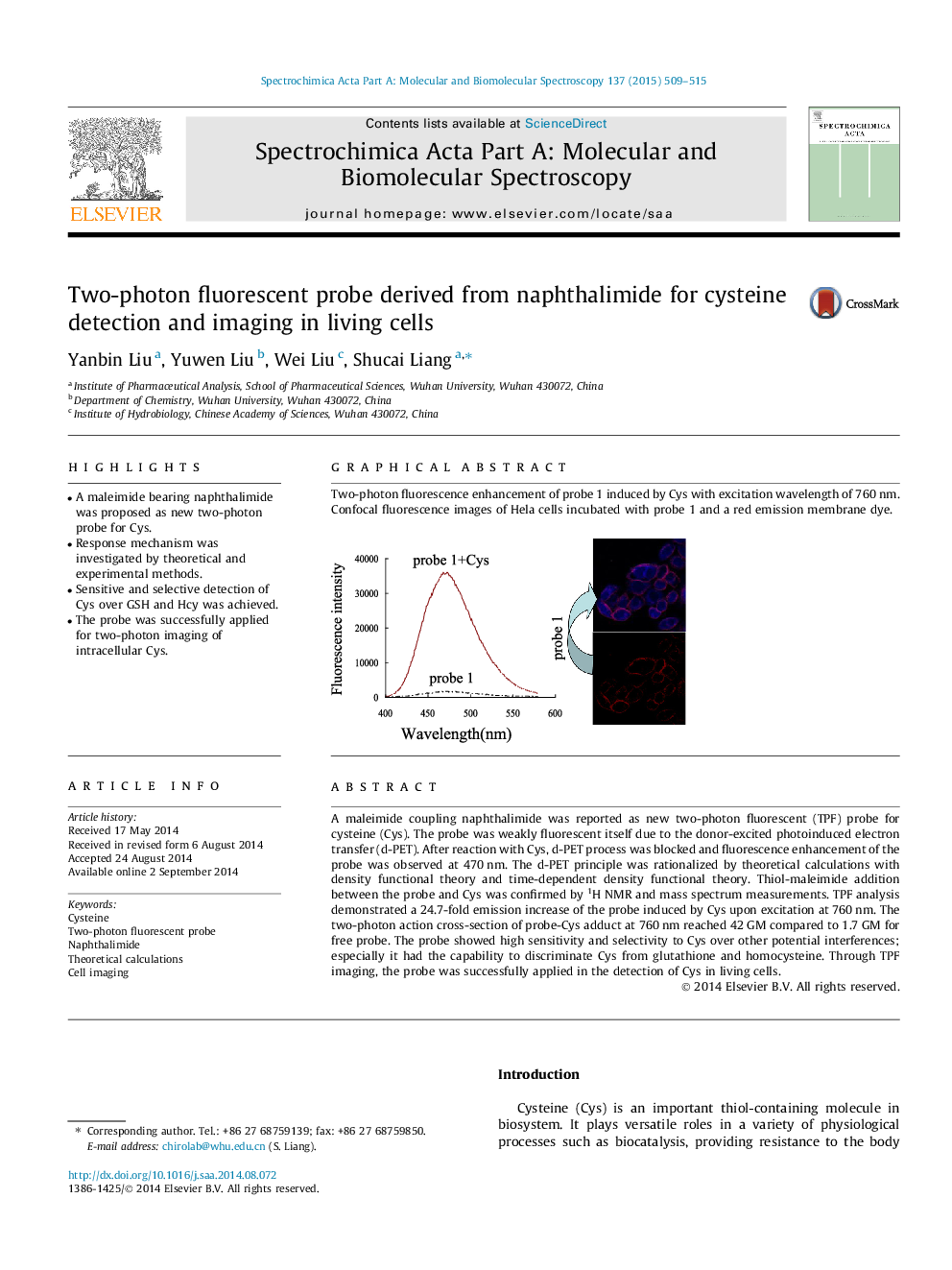
A maleimide coupling naphthalimide was reported as new two-photon fluorescent (TPF) probe for cysteine (Cys). The probe was weakly fluorescent itself due to the donor-excited photoinduced electron transfer (d-PET). After reaction with Cys, d-PET process was blocked and fluorescence enhancement of the probe was observed at 470 nm. The d-PET principle was rationalized by theoretical calculations with density functional theory and time-dependent density functional theory. Thiol-maleimide addition between the probe and Cys was confirmed by 1H NMR and mass spectrum measurements. TPF analysis demonstrated a 24.7-fold emission increase of the probe induced by Cys upon excitation at 760 nm. The two-photon action cross-section of probe-Cys adduct at 760 nm reached 42 GM compared to 1.7 GM for free probe. The probe showed high sensitivity and selectivity to Cys over other potential interferences; especially it had the capability to discriminate Cys from glutathione and homocysteine. Through TPF imaging, the probe was successfully applied in the detection of Cys in living cells.
Graphical abstractTwo-photon fluorescence enhancement of probe 1 induced by Cys with excitation wavelength of 760 nm. Confocal fluorescence images of Hela cells incubated with probe 1 and a red emission membrane dye.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide