| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229287 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 11 Pages |
•Synthesis and depiction of azomethines using dihydroxy coumarin and aromatic amines.•Characterization of octahedral metal complexes using various spectroscopic techniques.•Thermal data confirms the higher stability of the mononuclear metal complexes.•Cu(II) complexes shows promising antimicrobial, anthelmintic and DNA cleavage activities.
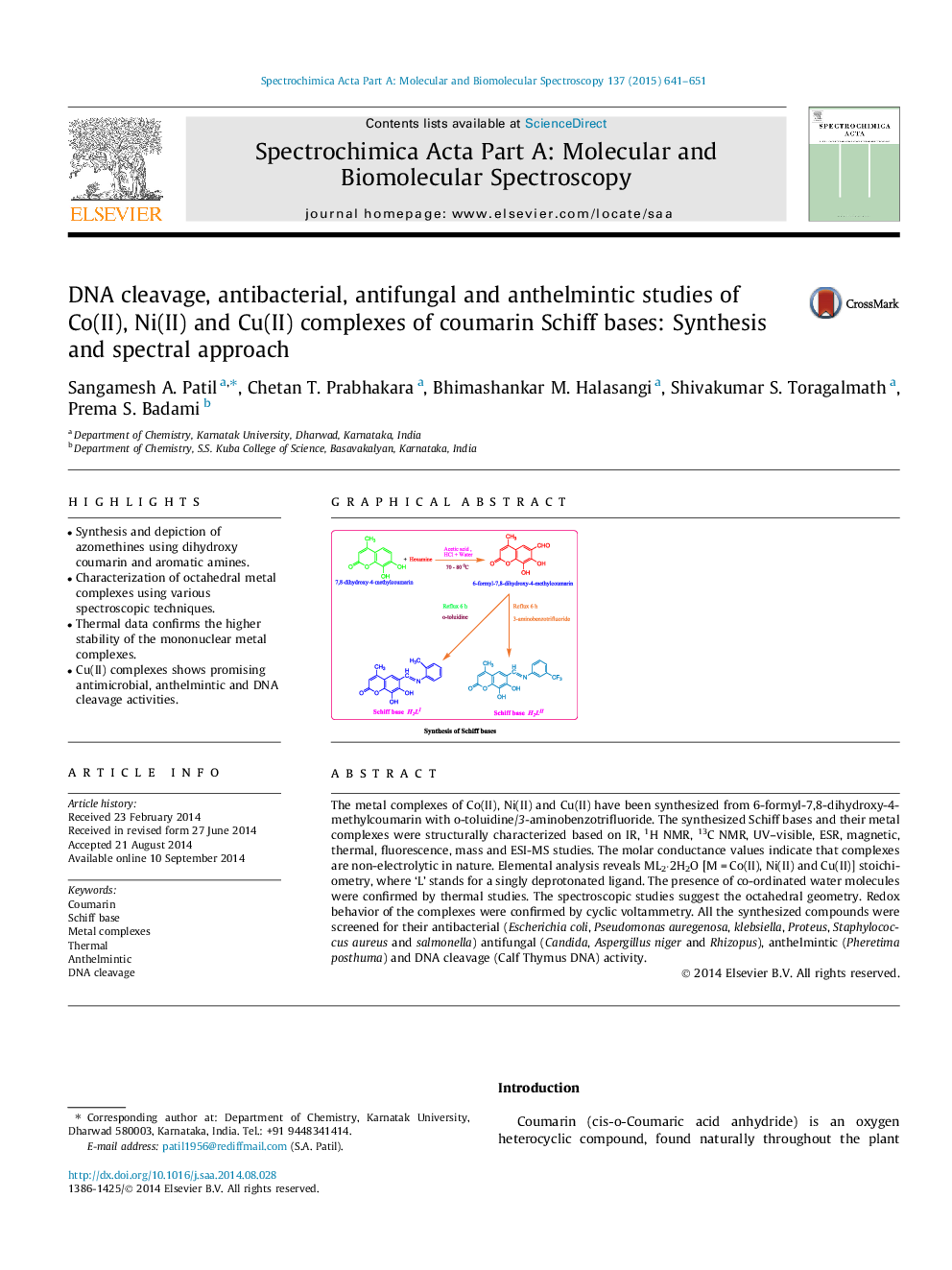
The metal complexes of Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) have been synthesized from 6-formyl-7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin with o-toluidine/3-aminobenzotrifluoride. The synthesized Schiff bases and their metal complexes were structurally characterized based on IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, UV–visible, ESR, magnetic, thermal, fluorescence, mass and ESI-MS studies. The molar conductance values indicate that complexes are non-electrolytic in nature. Elemental analysis reveals ML2·2H2O [M = Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II)] stoichiometry, where ‘L’ stands for a singly deprotonated ligand. The presence of co-ordinated water molecules were confirmed by thermal studies. The spectroscopic studies suggest the octahedral geometry. Redox behavior of the complexes were confirmed by cyclic voltammetry. All the synthesized compounds were screened for their antibacterial (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas auregenosa, klebsiella, Proteus, Staphylococcus aureus and salmonella) antifungal (Candida, Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus), anthelmintic (Pheretima posthuma) and DNA cleavage (Calf Thymus DNA) activity.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide