| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229448 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•For the first time we have studied the effect of Nd3+ and Zr4+ ions on structural changes of BaTiO3 lattice.•Ti metal powder was used instead of TiO2 to synthesize the ceramics using sol–gel.•Fourier transform infrared spectra and Raman spectra were recorded for BaTiO3 based ceramics.•In dielectric measurements the transition from normal to diffuse phase transition (DPT) with doping is observed.
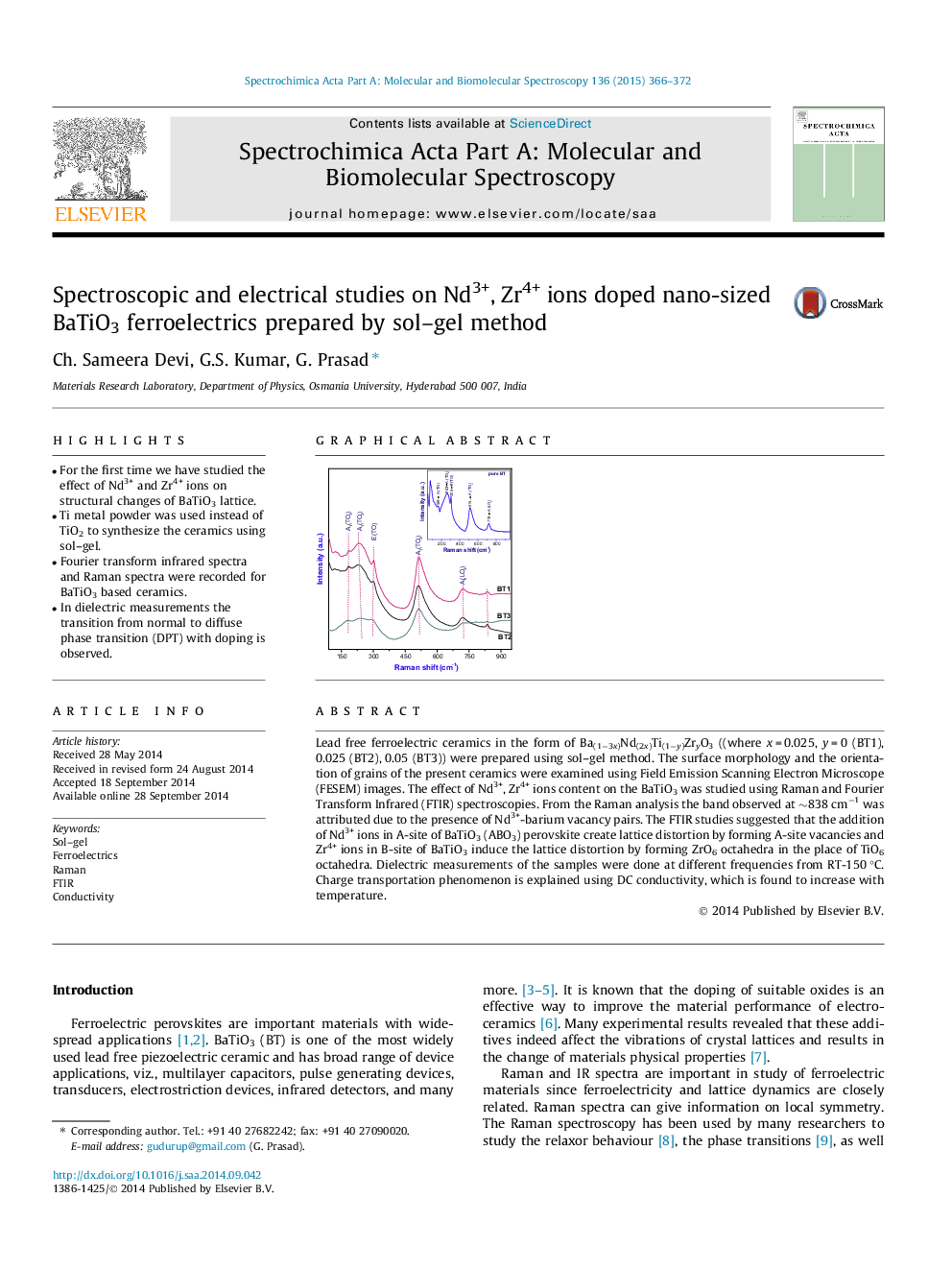
Lead free ferroelectric ceramics in the form of Ba(1−3x)Nd(2x)Ti(1−y)ZryO3 ((where x = 0.025, y = 0 (BT1), 0.025 (BT2), 0.05 (BT3)) were prepared using sol–gel method. The surface morphology and the orientation of grains of the present ceramics were examined using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM) images. The effect of Nd3+, Zr4+ ions content on the BaTiO3 was studied using Raman and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopies. From the Raman analysis the band observed at ∼838 cm−1 was attributed due to the presence of Nd3+-barium vacancy pairs. The FTIR studies suggested that the addition of Nd3+ ions in A-site of BaTiO3 (ABO3) perovskite create lattice distortion by forming A-site vacancies and Zr4+ ions in B-site of BaTiO3 induce the lattice distortion by forming ZrO6 octahedra in the place of TiO6 octahedra. Dielectric measurements of the samples were done at different frequencies from RT-150 °C. Charge transportation phenomenon is explained using DC conductivity, which is found to increase with temperature.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide