| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229457 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•Powdered crystal XRD was studied by pure sample BaTiO3 and Fe doped using solid state techniques.•Powder XRD diffraction and BDS analysis were reported.•Crystalline properties were studied by VSM.•Conductivity, impedance dielectric loss studied.
A comparative study of the surface morphology, dielectric and magnetic properties of the BaTi0.5Fe0.5O3 (BTFO) ceramics materials. This has been carried out by synthesizing the samples in different routes. BTFO samples have shown single phased 12R type hexagonal structure with R3m‾, P4mm space group. Interfacial effects on the dielectric properties of the samples have been understood by Cole–Cole plots in complex impedance and modulus formalism. It has been identified that huge dielectric constant (103–106) at lower frequencies is largely contributed by the heterogeneous electronic microstructure at the interfaces of grains. Modulus formalism has identified the effects of both grain and grain boundary microstructure on the dielectric properties, particularly in chemical routed samples. The order of grain boundary resistivity suggests the semiconductor/insulator class of the material. The grain boundary resistivity of the mechanical alloyed samples is remarkably lower than the solid state and chemical routed samples. Few samples have of the samples have exhibited signature of ferromagnetism at the room temperature.
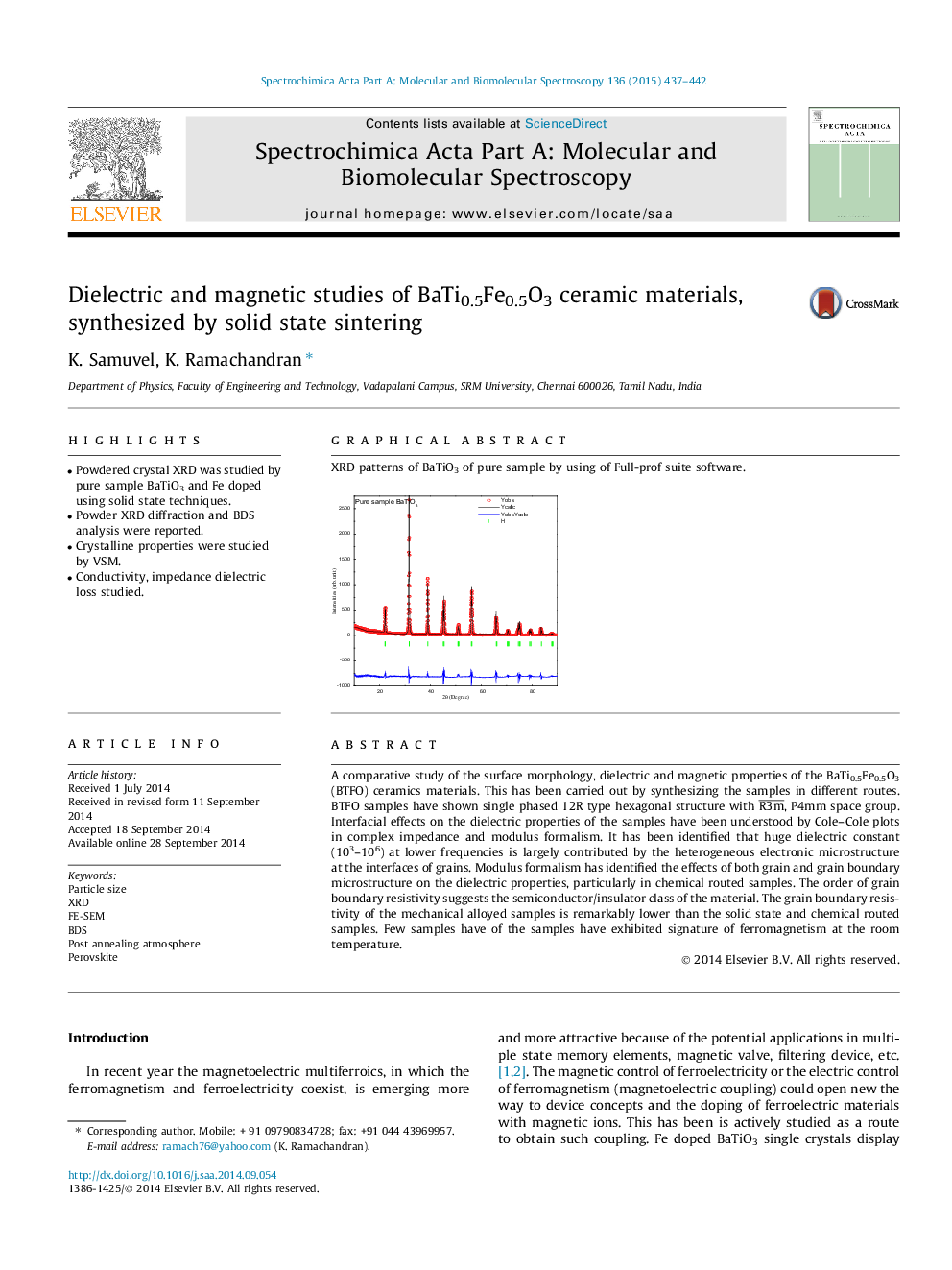
Graphical abstractXRD patterns of BaTiO3 of pure sample by using of Full-prof suite software.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide