| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229486 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 5 Pages |
•A novel spectrofluorimetric method determining the illegal feed additive was proposed.•The method was applied for analysis of clenbuterol in porcine muscle and swine urine.•It is a suitable method for an accurate, rapid and less expensive determination.•The mechanism of the fluorescence quenching of the supramolecular complex was discussed.
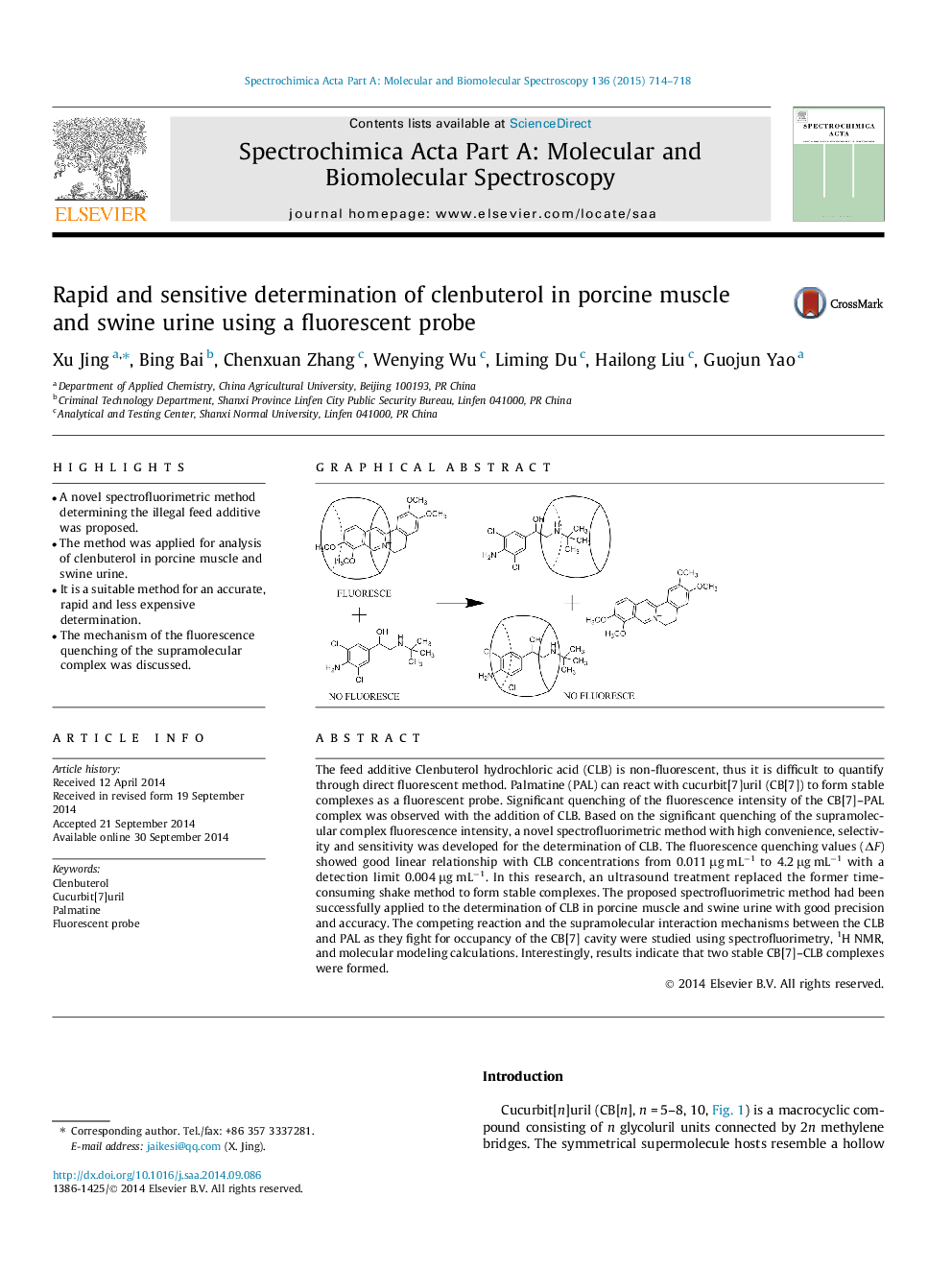
The feed additive Clenbuterol hydrochloric acid (CLB) is non-fluorescent, thus it is difficult to quantify through direct fluorescent method. Palmatine (PAL) can react with cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]) to form stable complexes as a fluorescent probe. Significant quenching of the fluorescence intensity of the CB[7]–PAL complex was observed with the addition of CLB. Based on the significant quenching of the supramolecular complex fluorescence intensity, a novel spectrofluorimetric method with high convenience, selectivity and sensitivity was developed for the determination of CLB. The fluorescence quenching values (ΔF) showed good linear relationship with CLB concentrations from 0.011 μg mL−1 to 4.2 μg mL−1 with a detection limit 0.004 μg mL−1. In this research, an ultrasound treatment replaced the former time-consuming shake method to form stable complexes. The proposed spectrofluorimetric method had been successfully applied to the determination of CLB in porcine muscle and swine urine with good precision and accuracy. The competing reaction and the supramolecular interaction mechanisms between the CLB and PAL as they fight for occupancy of the CB[7] cavity were studied using spectrofluorimetry, 1H NMR, and molecular modeling calculations. Interestingly, results indicate that two stable CB[7]–CLB complexes were formed.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide