| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229492 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•Water soluble new copper(II) complexes and the diquarternary salt of dmphen have been synthesized and characterized.•Single crystals X-ray study confirms the structure of the copper(II) complexes.•DNA binding studies reveal that these compounds bind to CT-DNA via intercalation.•The copper(II) complexes efficiently cleavage the super-coiled pBR322 plasmid DNA.•XTT assay of the copper(II) complexes show prominent cytotoxic activity against the selected human tumor cell lines.
Two new water-soluble copper(II) complexes, [Cu(dmphen)2(NO3)]NO3 (1), [Cu(dmphen)(tyr)(H2O)]NO3·H2O (2) and the diquarternary salt of dmphen (dmphen = 4,7-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline and tyr = l-tyrosine), have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, 1H NMR, 13C NMR and IR spectroscopy, thermal analysis and single crystal X-ray diffraction techniques. The CT-DNA binding properties of these compounds have been investigated by absorption, emission spectroscopy and thermal denaturation measurements. The supercoiled pBR322 plasmid DNA cleavage activity of these compounds has been explored by agarose gel electrophoresis. The cytotoxicity of these compounds against MCF-7, Caco-2, A549 cancer cells and BEAS-2B healthy cells was also studied by the XTT method. Complexes 1 and 2 exhibit significant cytotoxicity, with lower IC50 values than those of cisplatin.
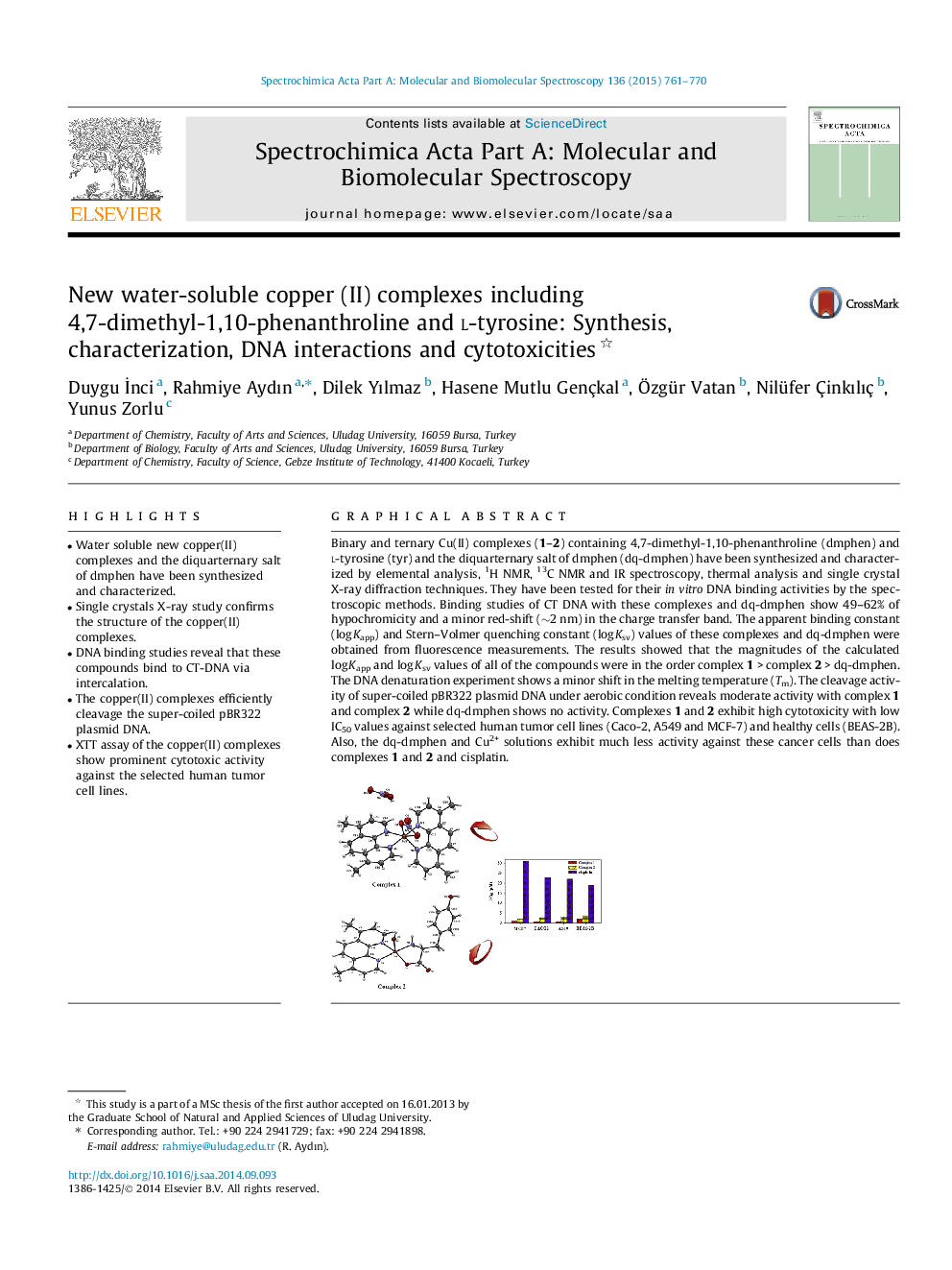
Graphical abstractBinary and ternary Cu(II) complexes (1–2) containing 4,7-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline (dmphen) and l-tyrosine (tyr) and the diquarternary salt of dmphen (dq-dmphen) have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, 1H NMR, 13C NMR and IR spectroscopy, thermal analysis and single crystal X-ray diffraction techniques. They have been tested for their in vitro DNA binding activities by the spectroscopic methods. Binding studies of CT DNA with these complexes and dq-dmphen show 49–62% of hypochromicity and a minor red-shift (∼2 nm) in the charge transfer band. The apparent binding constant (log Kapp) and Stern–Volmer quenching constant (log Ksv) values of these complexes and dq-dmphen were obtained from fluorescence measurements. The results showed that the magnitudes of the calculated log Kapp and log Ksv values of all of the compounds were in the order complex 1 > complex 2 > dq-dmphen. The DNA denaturation experiment shows a minor shift in the melting temperature (Tm). The cleavage activity of super-coiled pBR322 plasmid DNA under aerobic condition reveals moderate activity with complex 1 and complex 2 while dq-dmphen shows no activity. Complexes 1 and 2 exhibit high cytotoxicity with low IC50 values against selected human tumor cell lines (Caco-2, A549 and MCF-7) and healthy cells (BEAS-2B). Also, the dq-dmphen and Cu2+ solutions exhibit much less activity against these cancer cells than does complexes 1 and 2 and cisplatin.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide