| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229504 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•We synthesized ZnO nanoparticles with wurtzite hexagonal structure using green synthesis.•Method is simple, novel, nontoxic and cost effective and environment friendly.•Antibacterial activity of ZnO greenly synthesized by Solanum nigrum.
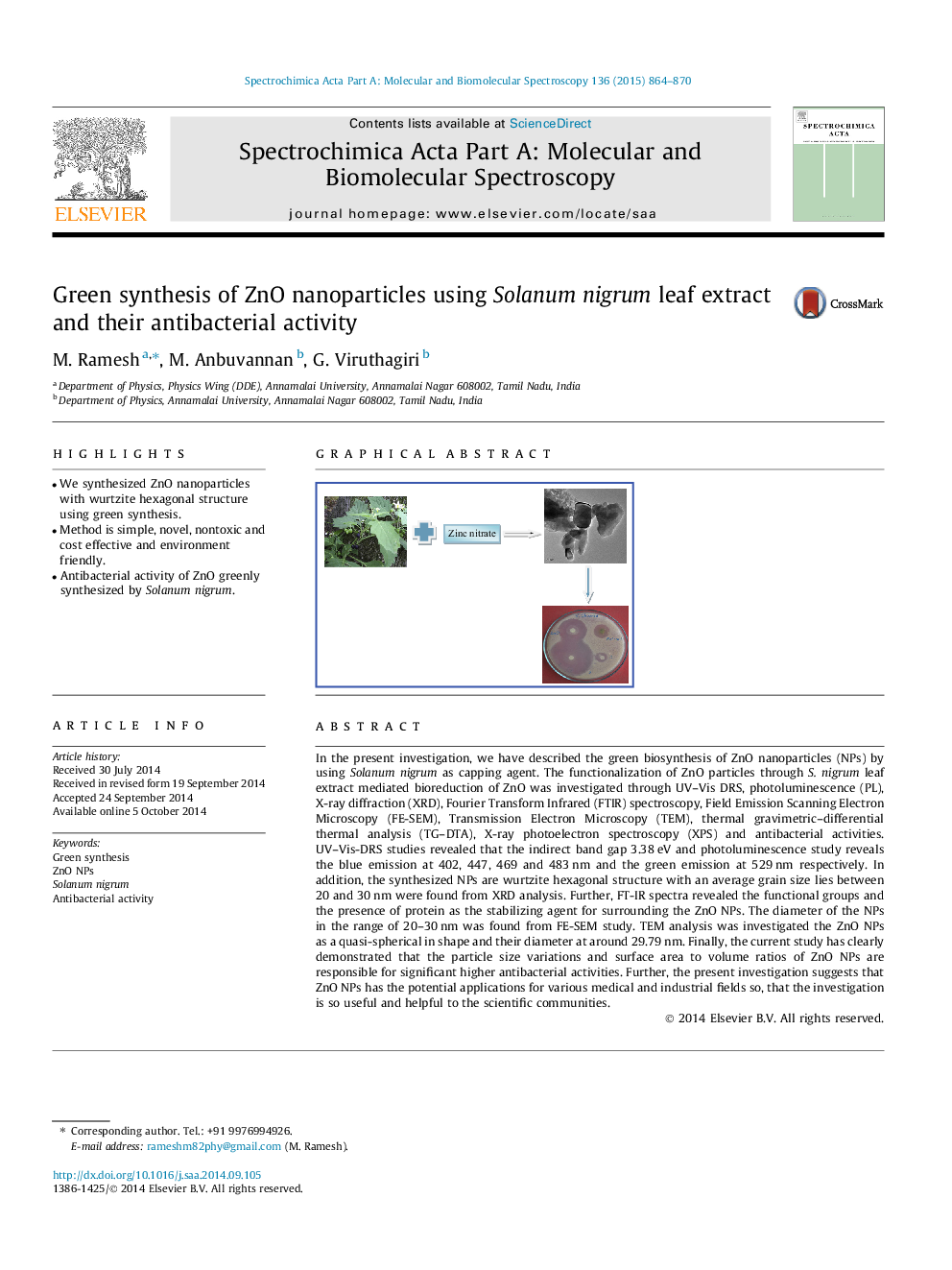
In the present investigation, we have described the green biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) by using Solanum nigrum as capping agent. The functionalization of ZnO particles through S. nigrum leaf extract mediated bioreduction of ZnO was investigated through UV–Vis DRS, photoluminescence (PL), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), thermal gravimetric–differential thermal analysis (TG–DTA), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and antibacterial activities. UV–Vis-DRS studies revealed that the indirect band gap 3.38 eV and photoluminescence study reveals the blue emission at 402, 447, 469 and 483 nm and the green emission at 529 nm respectively. In addition, the synthesized NPs are wurtzite hexagonal structure with an average grain size lies between 20 and 30 nm were found from XRD analysis. Further, FT-IR spectra revealed the functional groups and the presence of protein as the stabilizing agent for surrounding the ZnO NPs. The diameter of the NPs in the range of 20–30 nm was found from FE-SEM study. TEM analysis was investigated the ZnO NPs as a quasi-spherical in shape and their diameter at around 29.79 nm. Finally, the current study has clearly demonstrated that the particle size variations and surface area to volume ratios of ZnO NPs are responsible for significant higher antibacterial activities. Further, the present investigation suggests that ZnO NPs has the potential applications for various medical and industrial fields so, that the investigation is so useful and helpful to the scientific communities.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide