| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229562 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
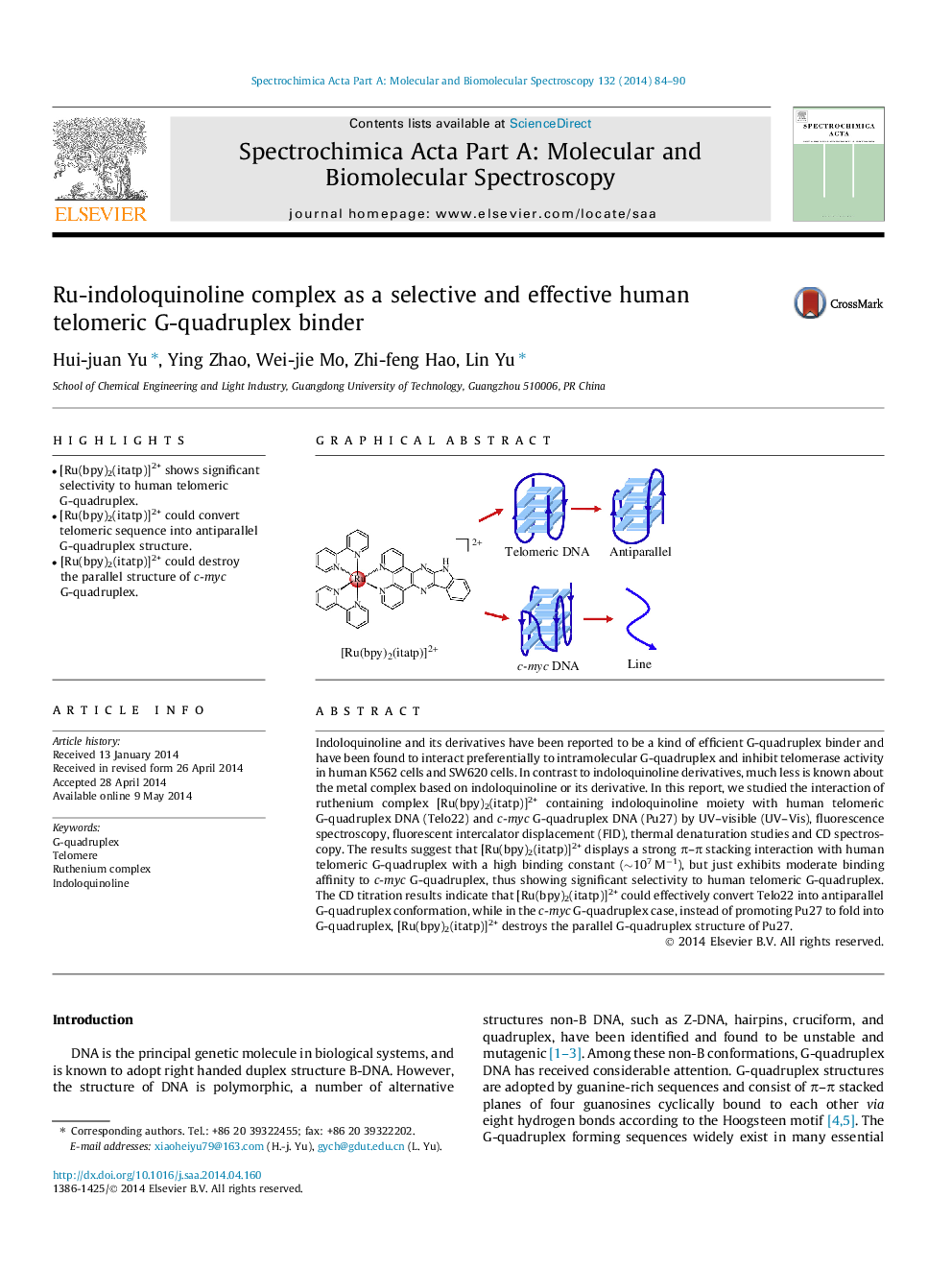
•[Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ shows significant selectivity to human telomeric G-quadruplex.•[Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ could convert telomeric sequence into antiparallel G-quadruplex structure.•[Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ could destroy the parallel structure of c-myc G-quadruplex.
Indoloquinoline and its derivatives have been reported to be a kind of efficient G-quadruplex binder and have been found to interact preferentially to intramolecular G-quadruplex and inhibit telomerase activity in human K562 cells and SW620 cells. In contrast to indoloquinoline derivatives, much less is known about the metal complex based on indoloquinoline or its derivative. In this report, we studied the interaction of ruthenium complex [Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ containing indoloquinoline moiety with human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA (Telo22) and c-myc G-quadruplex DNA (Pu27) by UV–visible (UV–Vis), fluorescence spectroscopy, fluorescent intercalator displacement (FID), thermal denaturation studies and CD spectroscopy. The results suggest that [Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ displays a strong π–π stacking interaction with human telomeric G-quadruplex with a high binding constant (∼107 M−1), but just exhibits moderate binding affinity to c-myc G-quadruplex, thus showing significant selectivity to human telomeric G-quadruplex. The CD titration results indicate that [Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ could effectively convert Telo22 into antiparallel G-quadruplex conformation, while in the c-myc G-quadruplex case, instead of promoting Pu27 to fold into G-quadruplex, [Ru(bpy)2(itatp)]2+ destroys the parallel G-quadruplex structure of Pu27.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide