| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229579 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
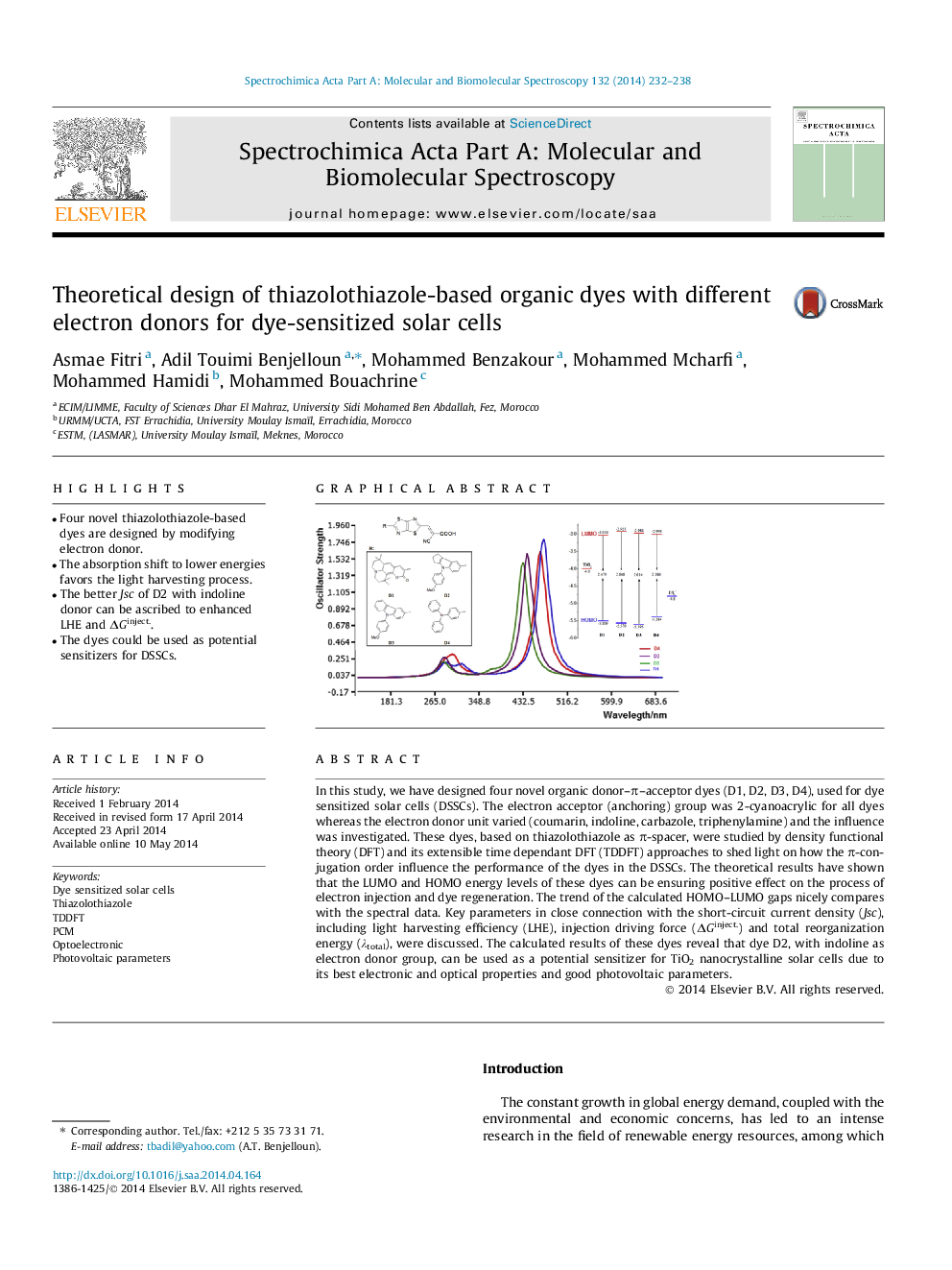
•Four novel thiazolothiazole-based dyes are designed by modifying electron donor.•The absorption shift to lower energies favors the light harvesting process.•The better Jsc of D2 with indoline donor can be ascribed to enhanced LHE and ΔGinject..•The dyes could be used as potential sensitizers for DSSCs.
In this study, we have designed four novel organic donor–π–acceptor dyes (D1, D2, D3, D4), used for dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The electron acceptor (anchoring) group was 2-cyanoacrylic for all dyes whereas the electron donor unit varied (coumarin, indoline, carbazole, triphenylamine) and the influence was investigated. These dyes, based on thiazolothiazole as π-spacer, were studied by density functional theory (DFT) and its extensible time dependant DFT (TDDFT) approaches to shed light on how the π-conjugation order influence the performance of the dyes in the DSSCs. The theoretical results have shown that the LUMO and HOMO energy levels of these dyes can be ensuring positive effect on the process of electron injection and dye regeneration. The trend of the calculated HOMO–LUMO gaps nicely compares with the spectral data. Key parameters in close connection with the short-circuit current density (Jsc), including light harvesting efficiency (LHE), injection driving force (ΔGinject.) and total reorganization energy (λtotal), were discussed. The calculated results of these dyes reveal that dye D2, with indoline as electron donor group, can be used as a potential sensitizer for TiO2 nanocrystalline solar cells due to its best electronic and optical properties and good photovoltaic parameters.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide