| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229584 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•Three types of complexes were found for the complexes of hypohalous acids and phosphine derivatives.•There is competition among hydrogen bond, halogen bond, and pnicogen bond.•This competition is related to the nature of hypohalous acids and phosphine derivatives.
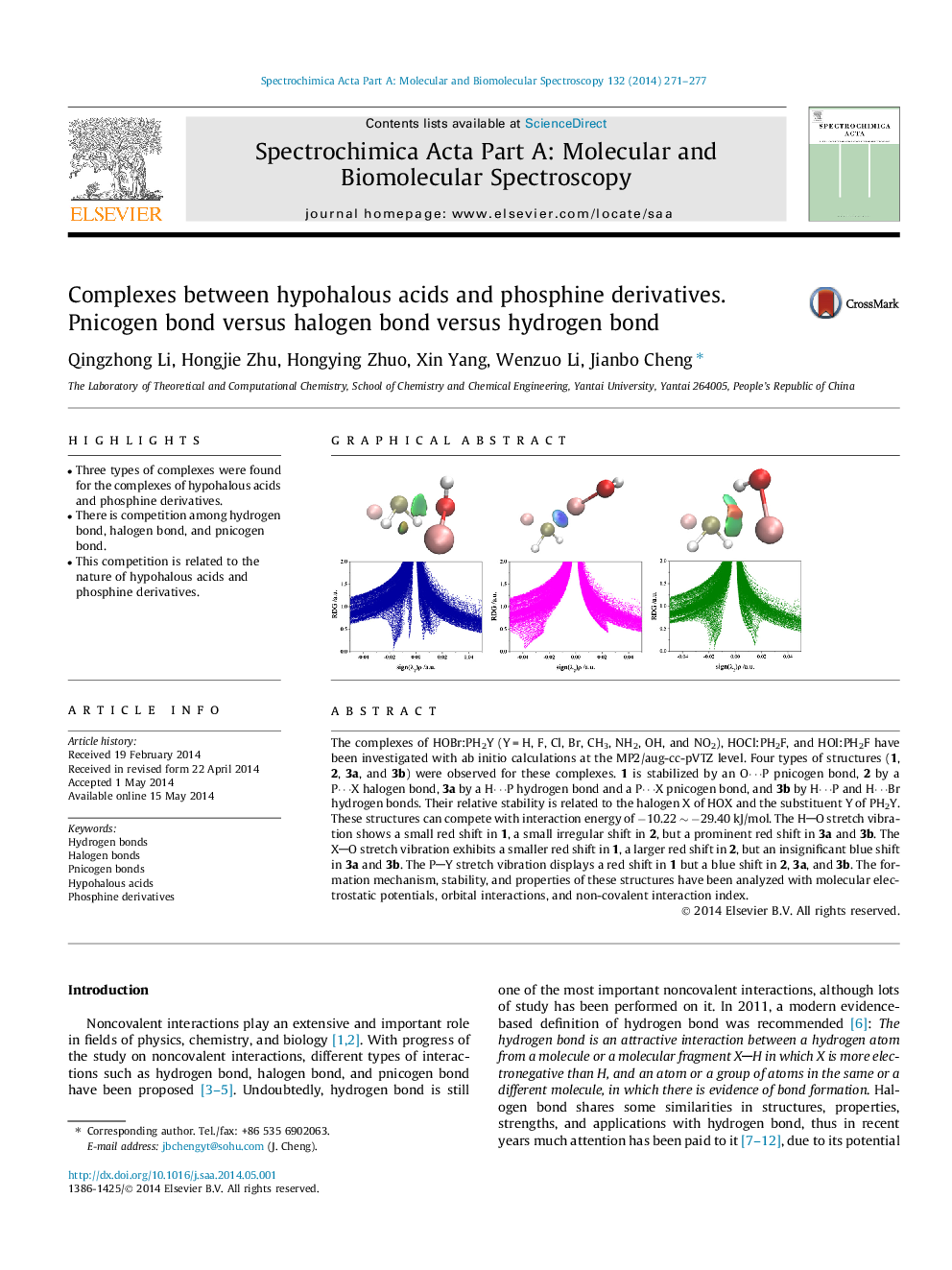
The complexes of HOBr:PH2Y (Y = H, F, Cl, Br, CH3, NH2, OH, and NO2), HOCl:PH2F, and HOI:PH2F have been investigated with ab initio calculations at the MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ level. Four types of structures (1, 2, 3a, and 3b) were observed for these complexes. 1 is stabilized by an O⋯P pnicogen bond, 2 by a P⋯X halogen bond, 3a by a H⋯P hydrogen bond and a P⋯X pnicogen bond, and 3b by H⋯P and H⋯Br hydrogen bonds. Their relative stability is related to the halogen X of HOX and the substituent Y of PH2Y. These structures can compete with interaction energy of −10.22 ∼ −29.40 kJ/mol. The HO stretch vibration shows a small red shift in 1, a small irregular shift in 2, but a prominent red shift in 3a and 3b. The XO stretch vibration exhibits a smaller red shift in 1, a larger red shift in 2, but an insignificant blue shift in 3a and 3b. The PY stretch vibration displays a red shift in 1 but a blue shift in 2, 3a, and 3b. The formation mechanism, stability, and properties of these structures have been analyzed with molecular electrostatic potentials, orbital interactions, and non-covalent interaction index.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide