| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229598 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 10 Pages |
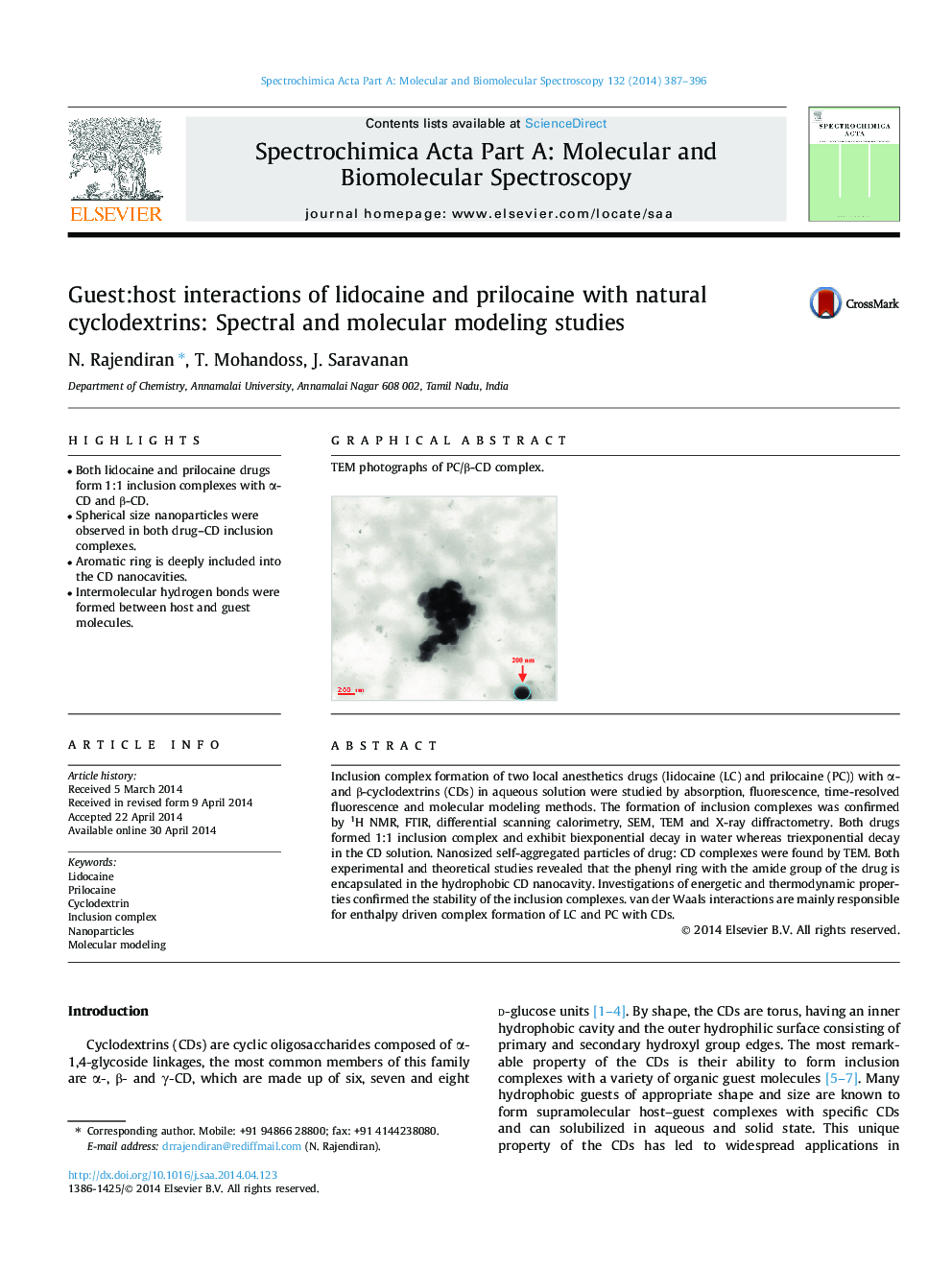
•Both lidocaine and prilocaine drugs form 1:1 inclusion complexes with α-CD and β-CD.•Spherical size nanoparticles were observed in both drug–CD inclusion complexes.•Aromatic ring is deeply included into the CD nanocavities.•Intermolecular hydrogen bonds were formed between host and guest molecules.
Inclusion complex formation of two local anesthetics drugs (lidocaine (LC) and prilocaine (PC)) with α- and β-cyclodextrins (CDs) in aqueous solution were studied by absorption, fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence and molecular modeling methods. The formation of inclusion complexes was confirmed by 1H NMR, FTIR, differential scanning calorimetry, SEM, TEM and X-ray diffractometry. Both drugs formed 1:1 inclusion complex and exhibit biexponential decay in water whereas triexponential decay in the CD solution. Nanosized self-aggregated particles of drug: CD complexes were found by TEM. Both experimental and theoretical studies revealed that the phenyl ring with the amide group of the drug is encapsulated in the hydrophobic CD nanocavity. Investigations of energetic and thermodynamic properties confirmed the stability of the inclusion complexes. van der Waals interactions are mainly responsible for enthalpy driven complex formation of LC and PC with CDs.
Graphical abstractTEM photographs of PC/β-CD complex.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide