| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229620 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•Aqueous fraction showed highest percentage extraction yield.•Ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions exhibited strong antioxidative properties.•Significant correlation existed between IC50 of DPPH with flavonoids.•Significant correlation existed between total antioxidant with phenol and flavonoids.•Whole fruit appears to be much beneficial than its peel and pulp.
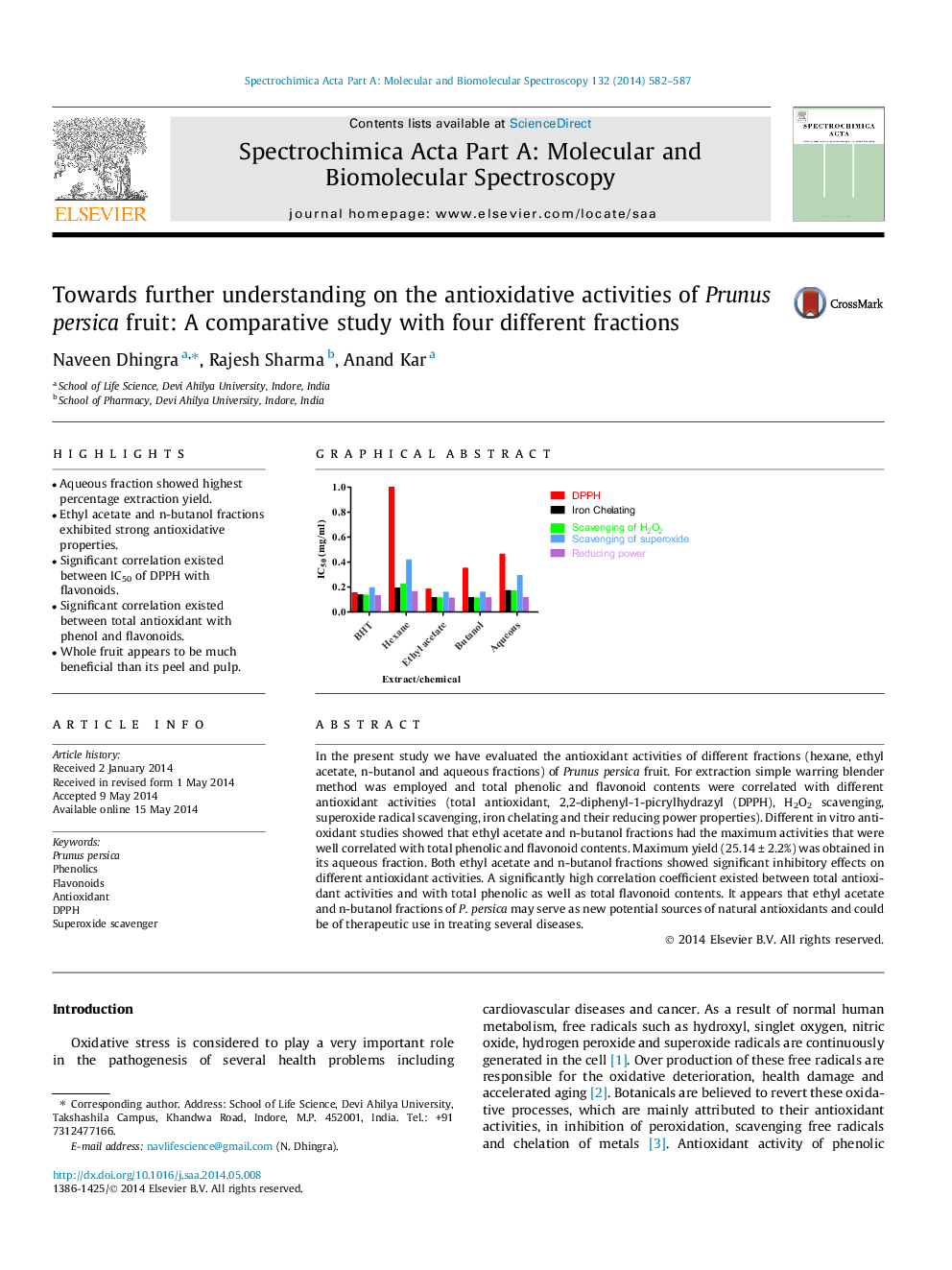
In the present study we have evaluated the antioxidant activities of different fractions (hexane, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and aqueous fractions) of Prunus persica fruit. For extraction simple warring blender method was employed and total phenolic and flavonoid contents were correlated with different antioxidant activities (total antioxidant, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), H2O2 scavenging, superoxide radical scavenging, iron chelating and their reducing power properties). Different in vitro antioxidant studies showed that ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions had the maximum activities that were well correlated with total phenolic and flavonoid contents. Maximum yield (25.14 ± 2.2%) was obtained in its aqueous fraction. Both ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions showed significant inhibitory effects on different antioxidant activities. A significantly high correlation coefficient existed between total antioxidant activities and with total phenolic as well as total flavonoid contents. It appears that ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions of P. persica may serve as new potential sources of natural antioxidants and could be of therapeutic use in treating several diseases.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide