| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229793 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2016 | 5 Pages |
•We expanded the traditional electrolysis method.•Anion- and cation-codoped crystals can be colored electrolytically.•O2−- and Mg2+-codoped LiF crystal is colored electrolytically for the first time.•V, F, F-aggregate and Mg-perturbed centers are produced in colored crystals.•V centers are produced directly and F as well as F-aggregate centers indirectly.
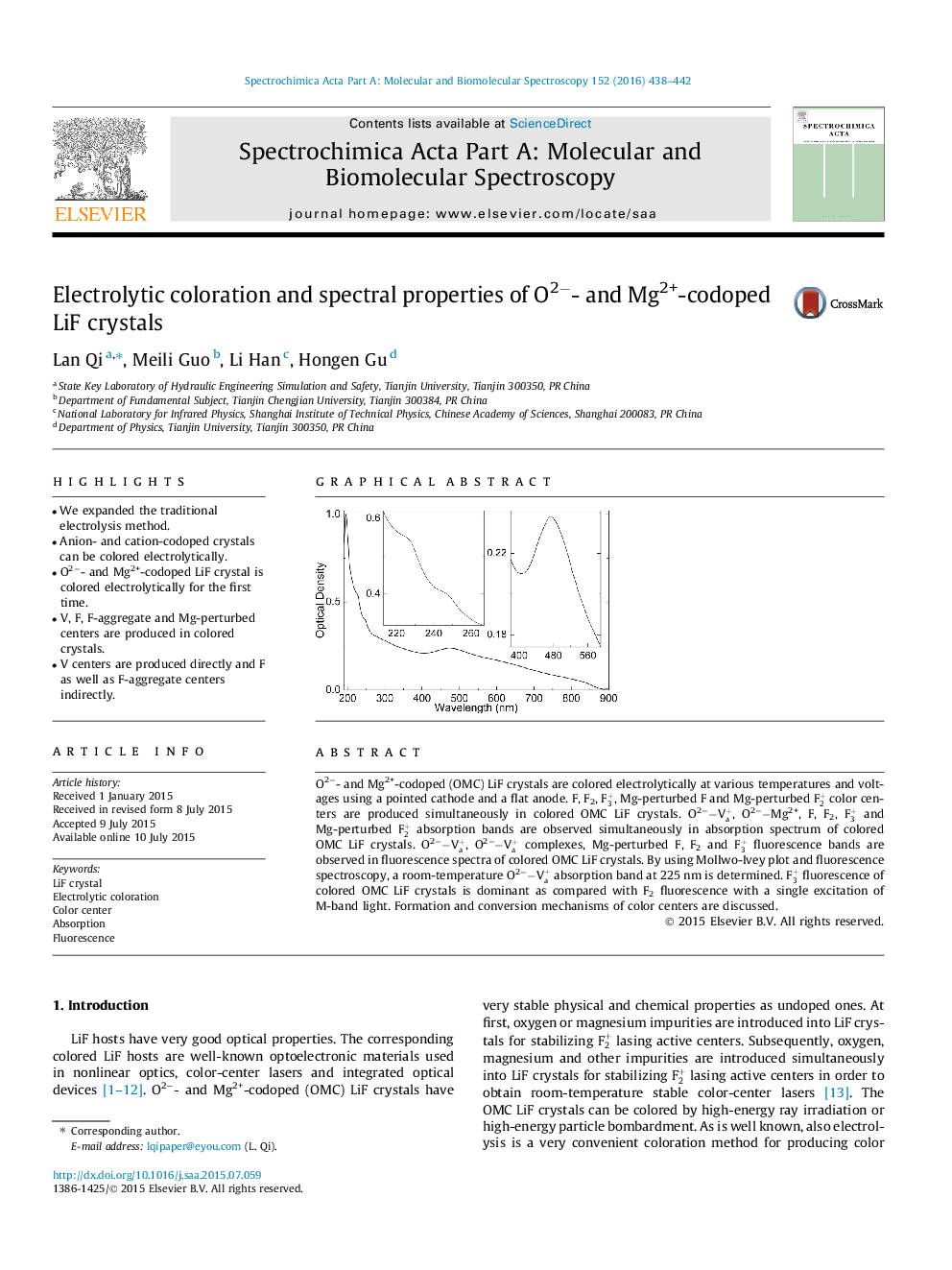
O2−- and Mg2+-codoped (OMC) LiF crystals are colored electrolytically at various temperatures and voltages using a pointed cathode and a flat anode. F, F2, F3+, Mg-perturbed F and Mg-perturbed F2+ color centers are produced simultaneously in colored OMC LiF crystals. O2−−Va+, O2−−Mg2+, F, F2, F3+ and Mg-perturbed F2+ absorption bands are observed simultaneously in absorption spectrum of colored OMC LiF crystals. O2−−Va+, O2−−Va+ complexes, Mg-perturbed F, F2 and F3+ fluorescence bands are observed in fluorescence spectra of colored OMC LiF crystals. By using Mollwo-Ivey plot and fluorescence spectroscopy, a room-temperature O2−−Va+ absorption band at 225 nm is determined. F3+ fluorescence of colored OMC LiF crystals is dominant as compared with F2 fluorescence with a single excitation of M-band light. Formation and conversion mechanisms of color centers are discussed.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide