| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229797 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2016 | 7 Pages |
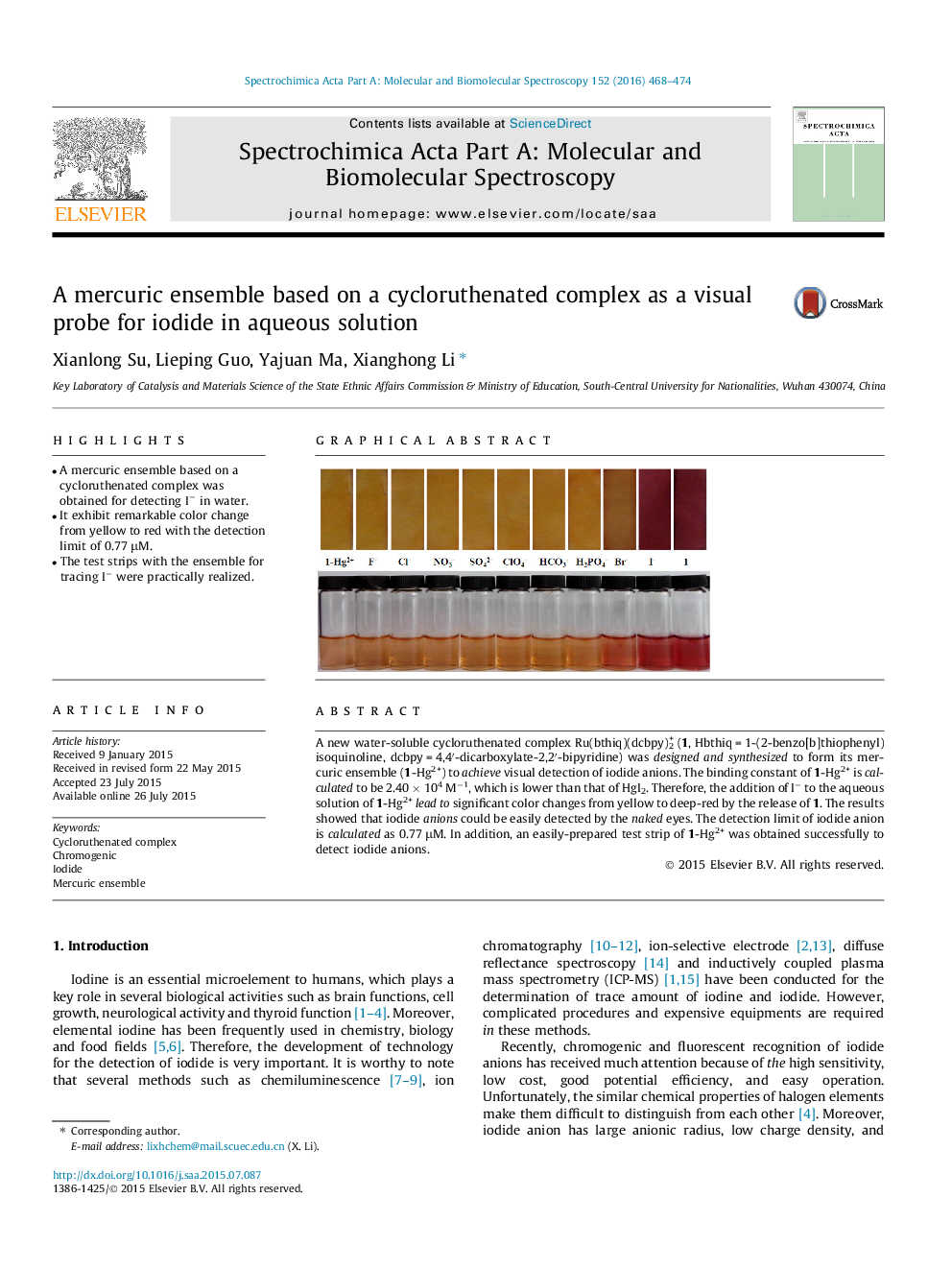
•A mercuric ensemble based on a cycloruthenated complex was obtained for detecting I− in water.•It exhibit remarkable color change from yellow to red with the detection limit of 0.77 μM.•The test strips with the ensemble for tracing I− were practically realized.
A new water-soluble cycloruthenated complex Ru(bthiq)(dcbpy)2+ (1, Hbthiq = 1-(2-benzo[b]thiophenyl)isoquinoline, dcbpy = 4,4′-dicarboxylate-2,2′-bipyridine) was designed and synthesized to form its mercuric ensemble (1-Hg2+) to achieve visual detection of iodide anions. The binding constant of 1-Hg2+ is calculated to be 2.40 × 104 M−1, which is lower than that of HgI2. Therefore, the addition of I− to the aqueous solution of 1-Hg2+lead to significant color changes from yellow to deep-red by the release of 1. The results showed that iodide anions could be easily detected by the naked eyes. The detection limit of iodide anion is calculated as 0.77 μM. In addition, an easily-prepared test strip of 1-Hg2+ was obtained successfully to detect iodide anions.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide