| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229897 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•The 4-BPPN crystallizes in the monoclinic system P21/c.•X-ray diffraction, DTA–TG measurements IR and Raman spectral were reported.•All observed vibrational bands have been discussed and assigned to normal mode on the basis on our DFT calculations.•The ability of ions to form spontaneous three-dimensional structure through N–H⋯O hydrogen bond is fully utilized.
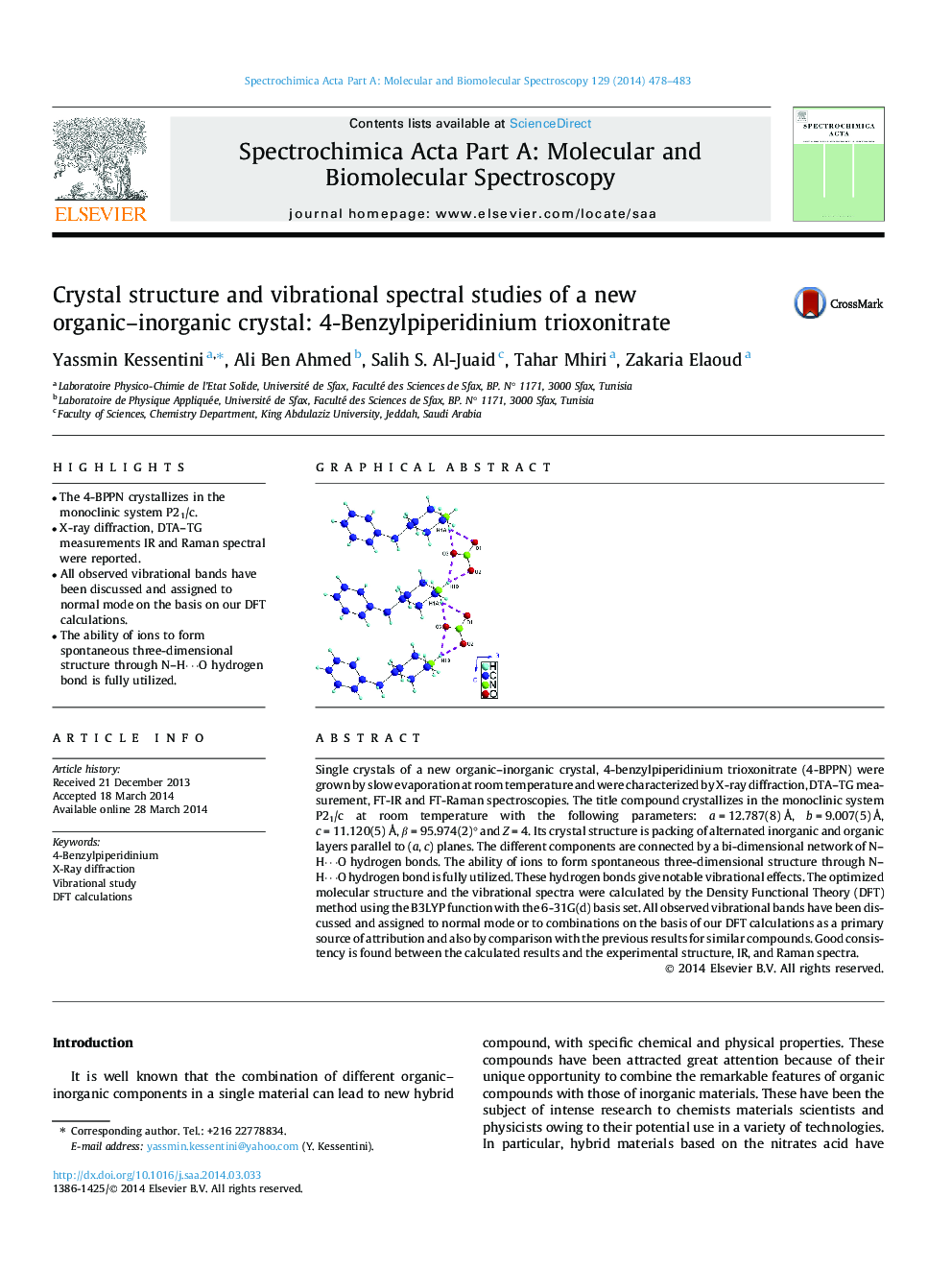
Single crystals of a new organic–inorganic crystal, 4-benzylpiperidinium trioxonitrate (4-BPPN) were grown by slow evaporation at room temperature and were characterized by X-ray diffraction, DTA–TG measurement, FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopies. The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic system P21/c at room temperature with the following parameters: a = 12.787(8) Å, b = 9.007(5) Å, c = 11.120(5) Å, β = 95.974(2)° and Z = 4. Its crystal structure is packing of alternated inorganic and organic layers parallel to (a, c) planes. The different components are connected by a bi-dimensional network of N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The ability of ions to form spontaneous three-dimensional structure through N–H⋯O hydrogen bond is fully utilized. These hydrogen bonds give notable vibrational effects. The optimized molecular structure and the vibrational spectra were calculated by the Density Functional Theory (DFT) method using the B3LYP function with the 6-31G(d) basis set. All observed vibrational bands have been discussed and assigned to normal mode or to combinations on the basis of our DFT calculations as a primary source of attribution and also by comparison with the previous results for similar compounds. Good consistency is found between the calculated results and the experimental structure, IR, and Raman spectra.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide