| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229900 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 10 Pages |
•Structurally simple Schiff bases or reduced Schiff bases beneficial for selective anion recognition.•Receptor and anions weak interaction studied by simple colorimetry and spectroscopy.•Cheaper and user handling anion sensing test kits for useful practical applications.
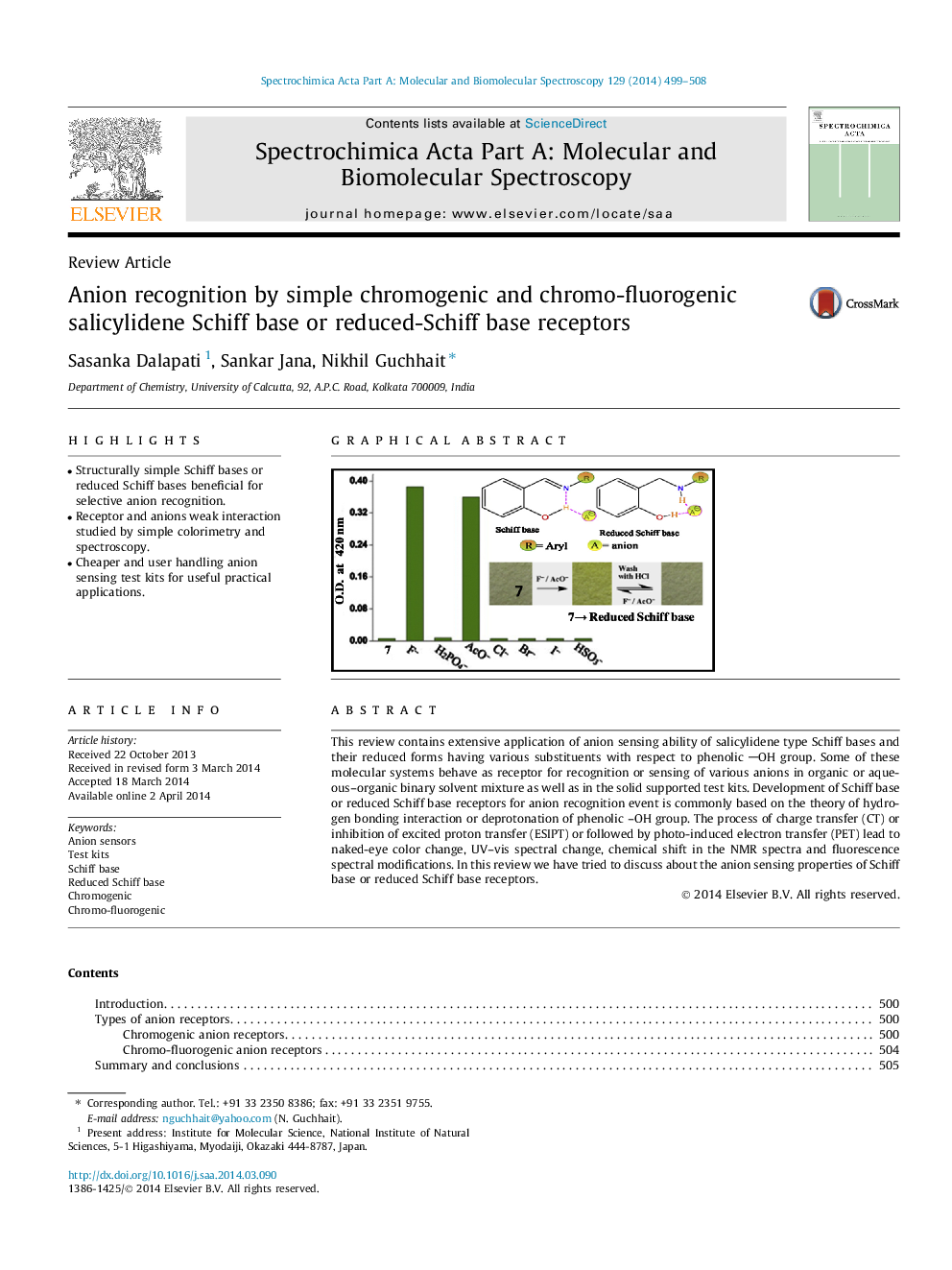
This review contains extensive application of anion sensing ability of salicylidene type Schiff bases and their reduced forms having various substituents with respect to phenolic OH group. Some of these molecular systems behave as receptor for recognition or sensing of various anions in organic or aqueous–organic binary solvent mixture as well as in the solid supported test kits. Development of Schiff base or reduced Schiff base receptors for anion recognition event is commonly based on the theory of hydrogen bonding interaction or deprotonation of phenolic –OH group. The process of charge transfer (CT) or inhibition of excited proton transfer (ESIPT) or followed by photo-induced electron transfer (PET) lead to naked-eye color change, UV–vis spectral change, chemical shift in the NMR spectra and fluorescence spectral modifications. In this review we have tried to discuss about the anion sensing properties of Schiff base or reduced Schiff base receptors.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide