| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229911 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Glasses from the SiO2P2O5K2OCaOMgOMnO2 system were prepared and analyzed.•Glasses were characterized by spectroscopic methods.•The relation between the structure and chemical activity of glasses was found.
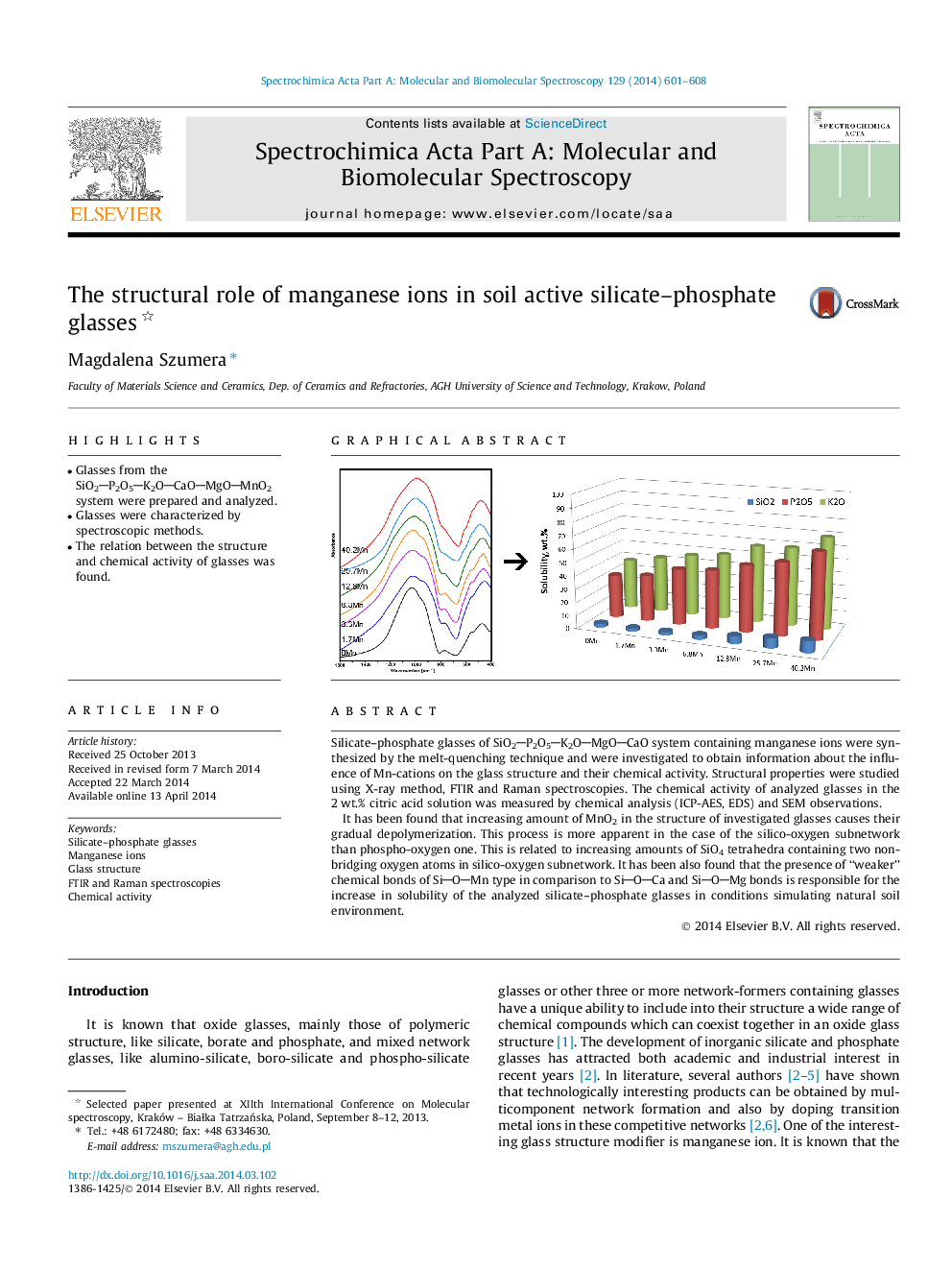
Silicate–phosphate glasses of SiO2P2O5K2OMgOCaO system containing manganese ions were synthesized by the melt-quenching technique and were investigated to obtain information about the influence of Mn-cations on the glass structure and their chemical activity. Structural properties were studied using X-ray method, FTIR and Raman spectroscopies. The chemical activity of analyzed glasses in the 2 wt.% citric acid solution was measured by chemical analysis (ICP-AES, EDS) and SEM observations.It has been found that increasing amount of MnO2 in the structure of investigated glasses causes their gradual depolymerization. This process is more apparent in the case of the silico-oxygen subnetwork than phospho-oxygen one. This is related to increasing amounts of SiO4 tetrahedra containing two nonbridging oxygen atoms in silico-oxygen subnetwork. It has been also found that the presence of “weaker” chemical bonds of SiOMn type in comparison to SiOCa and SiOMg bonds is responsible for the increase in solubility of the analyzed silicate–phosphate glasses in conditions simulating natural soil environment.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide