| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229925 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 8 Pages |
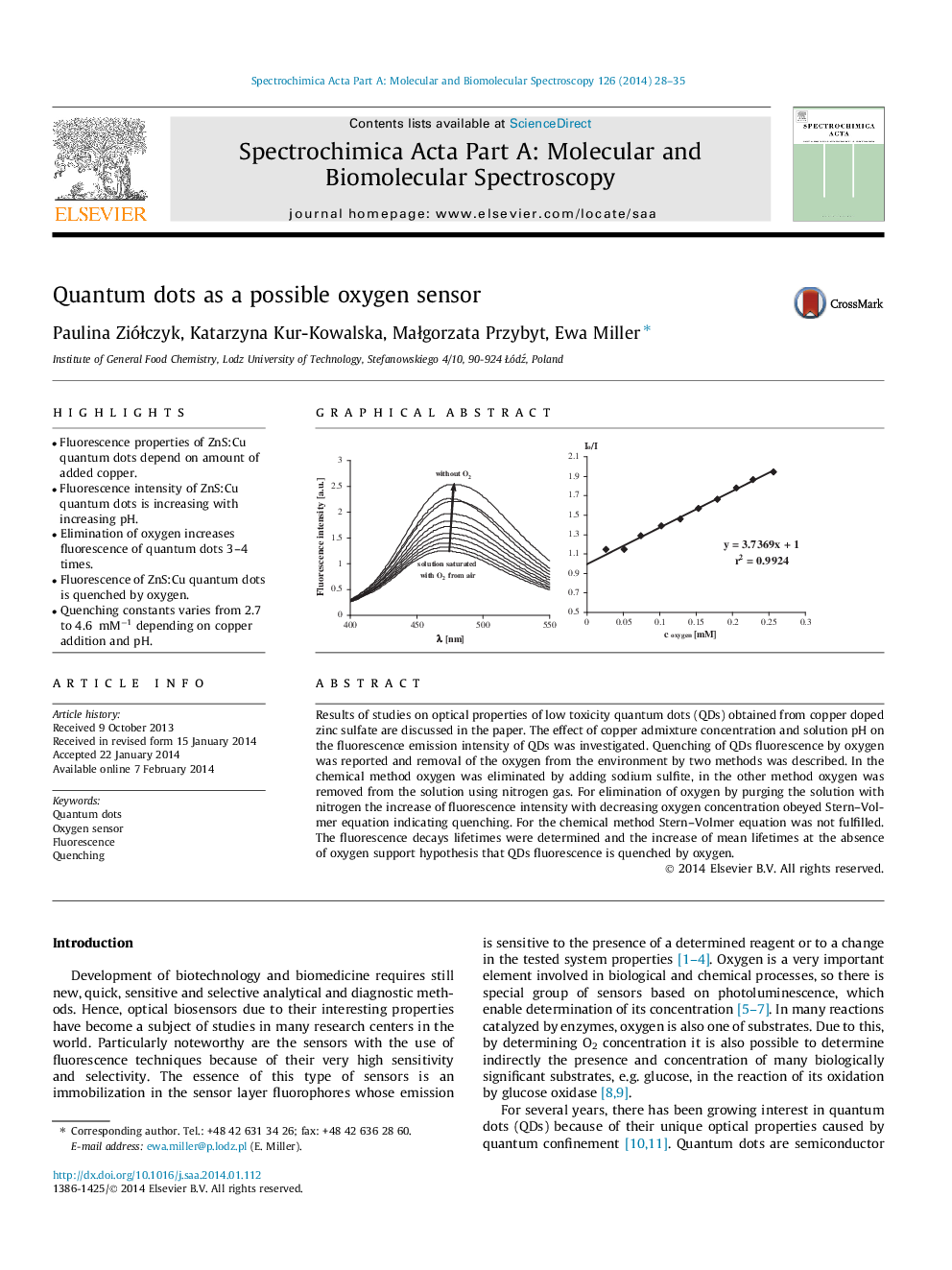
•Fluorescence properties of ZnS:Cu quantum dots depend on amount of added copper.•Fluorescence intensity of ZnS:Cu quantum dots is increasing with increasing pH.•Elimination of oxygen increases fluorescence of quantum dots 3–4 times.•Fluorescence of ZnS:Cu quantum dots is quenched by oxygen.•Quenching constants varies from 2.7 to 4.6 mM−1 depending on copper addition and pH.
Results of studies on optical properties of low toxicity quantum dots (QDs) obtained from copper doped zinc sulfate are discussed in the paper. The effect of copper admixture concentration and solution pH on the fluorescence emission intensity of QDs was investigated. Quenching of QDs fluorescence by oxygen was reported and removal of the oxygen from the environment by two methods was described. In the chemical method oxygen was eliminated by adding sodium sulfite, in the other method oxygen was removed from the solution using nitrogen gas. For elimination of oxygen by purging the solution with nitrogen the increase of fluorescence intensity with decreasing oxygen concentration obeyed Stern–Volmer equation indicating quenching. For the chemical method Stern–Volmer equation was not fulfilled. The fluorescence decays lifetimes were determined and the increase of mean lifetimes at the absence of oxygen support hypothesis that QDs fluorescence is quenched by oxygen.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide