| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230058 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 4 Pages |
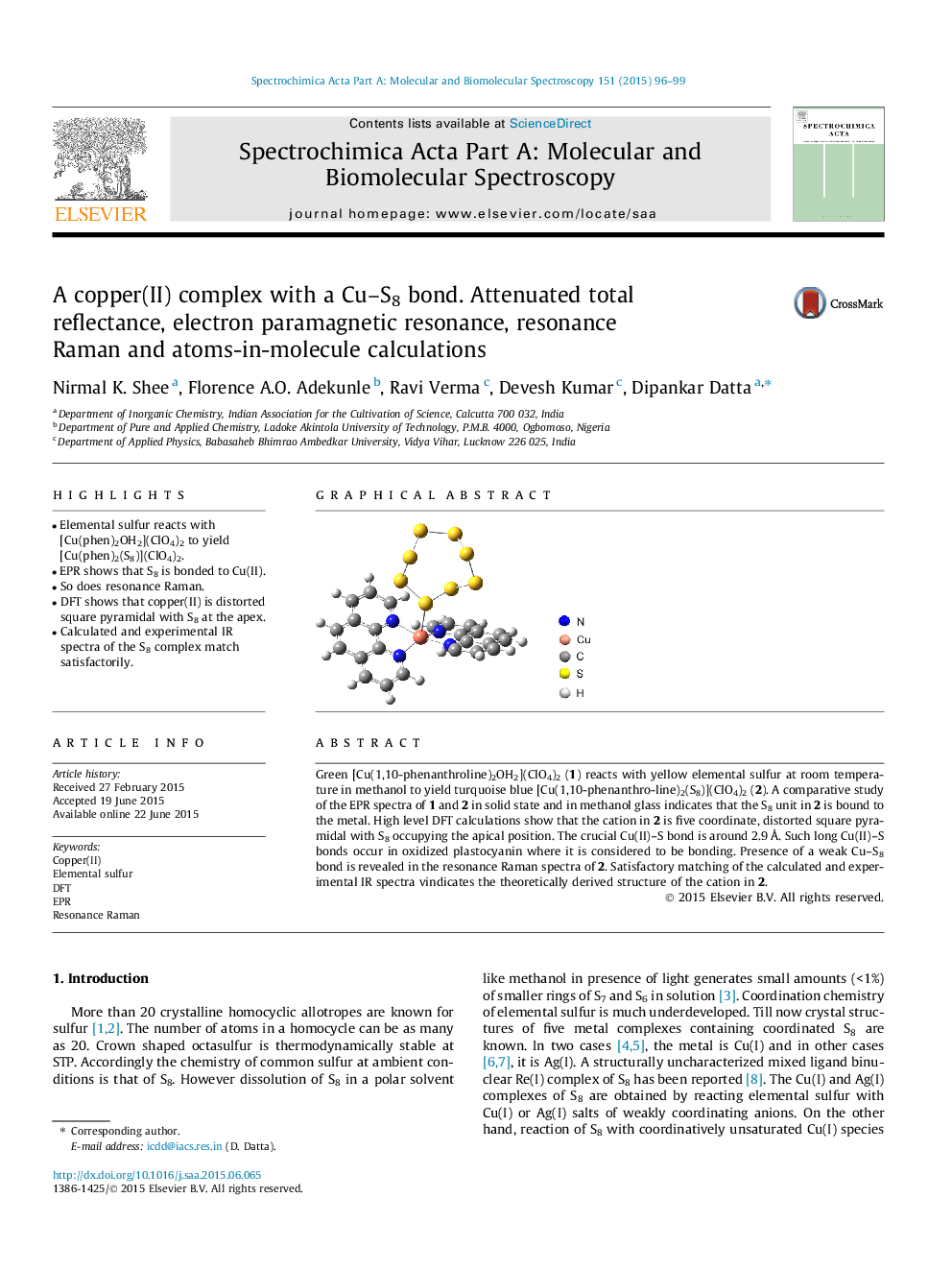
•Elemental sulfur reacts with [Cu(phen)2OH2](ClO4)2 to yield [Cu(phen)2(S8)](ClO4)2.•EPR shows that S8 is bonded to Cu(II).•So does resonance Raman.•DFT shows that copper(II) is distorted square pyramidal with S8 at the apex.•Calculated and experimental IR spectra of the S8 complex match satisfactorily.
Green [Cu(1,10-phenanthroline)2OH2](ClO4)2 (1) reacts with yellow elemental sulfur at room temperature in methanol to yield turquoise blue [Cu(1,10-phenanthro-line)2(S8)](ClO4)2 (2). A comparative study of the EPR spectra of 1 and 2 in solid state and in methanol glass indicates that the S8 unit in 2 is bound to the metal. High level DFT calculations show that the cation in 2 is five coordinate, distorted square pyramidal with S8 occupying the apical position. The crucial Cu(II)–S bond is around 2.9 Å. Such long Cu(II)–S bonds occur in oxidized plastocyanin where it is considered to be bonding. Presence of a weak Cu–S8 bond is revealed in the resonance Raman spectra of 2. Satisfactory matching of the calculated and experimental IR spectra vindicates the theoretically derived structure of the cation in 2.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide