| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230115 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 13 Pages |
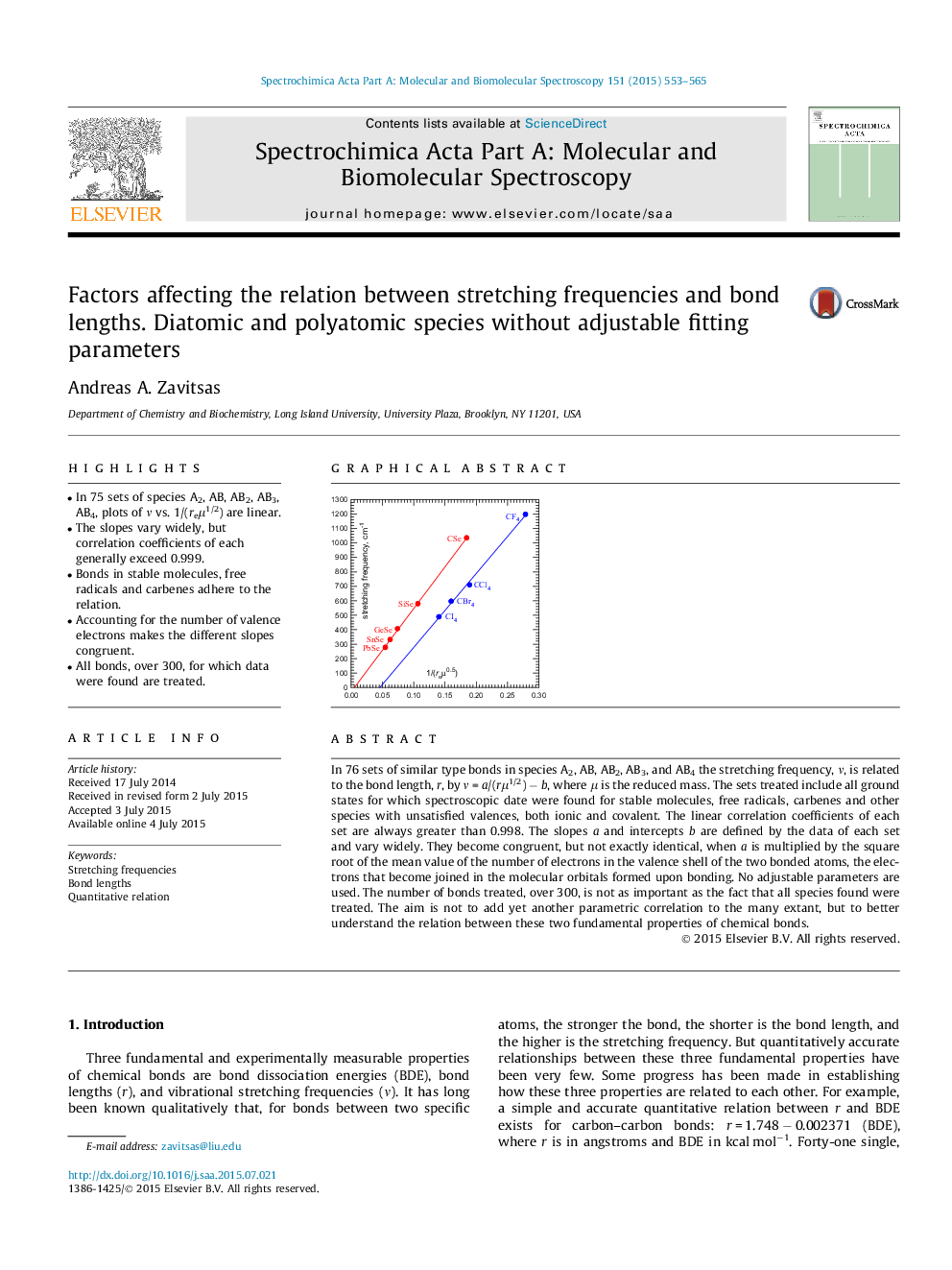
•In 75 sets of species A2, AB, AB2, AB3, AB4, plots of ν vs. 1/(reμ1/2) are linear.•The slopes vary widely, but correlation coefficients of each generally exceed 0.999.•Bonds in stable molecules, free radicals and carbenes adhere to the relation.•Accounting for the number of valence electrons makes the different slopes congruent.•All bonds, over 300, for which data were found are treated.
In 76 sets of similar type bonds in species A2, AB, AB2, AB3, and AB4 the stretching frequency, ν, is related to the bond length, r, by ν = a/(rμ1/2) − b, where μ is the reduced mass. The sets treated include all ground states for which spectroscopic date were found for stable molecules, free radicals, carbenes and other species with unsatisfied valences, both ionic and covalent. The linear correlation coefficients of each set are always greater than 0.998. The slopes a and intercepts b are defined by the data of each set and vary widely. They become congruent, but not exactly identical, when a is multiplied by the square root of the mean value of the number of electrons in the valence shell of the two bonded atoms, the electrons that become joined in the molecular orbitals formed upon bonding. No adjustable parameters are used. The number of bonds treated, over 300, is not as important as the fact that all species found were treated. The aim is not to add yet another parametric correlation to the many extant, but to better understand the relation between these two fundamental properties of chemical bonds.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide