| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230128 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•Sodium hexadecyl sulfate (SHS) was successed to be intercalated into the hydrocalumites, which was investigated by XRD, SEM combining with MIR and NIR spectroscopic methods.•SHS could modify hydrocalumites to form organo-LDH.
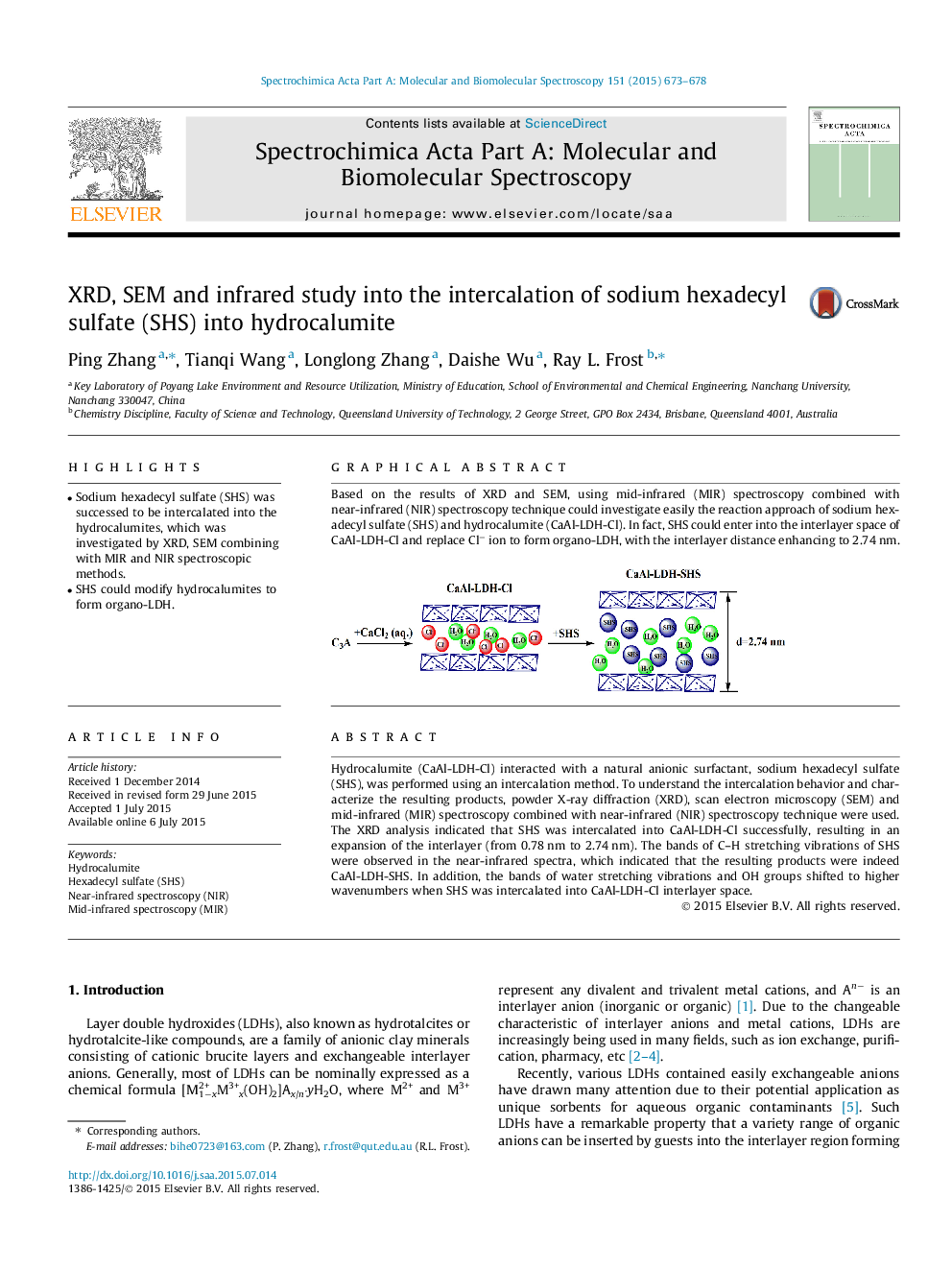
Hydrocalumite (CaAl-LDH-Cl) interacted with a natural anionic surfactant, sodium hexadecyl sulfate (SHS), was performed using an intercalation method. To understand the intercalation behavior and characterize the resulting products, powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scan electron microscopy (SEM) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy combined with near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy technique were used. The XRD analysis indicated that SHS was intercalated into CaAl-LDH-Cl successfully, resulting in an expansion of the interlayer (from 0.78 nm to 2.74 nm). The bands of C–H stretching vibrations of SHS were observed in the near-infrared spectra, which indicated that the resulting products were indeed CaAl-LDH-SHS. In addition, the bands of water stretching vibrations and OH groups shifted to higher wavenumbers when SHS was intercalated into CaAl-LDH-Cl interlayer space.
Graphical abstractBased on the results of XRD and SEM, using mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy combined with near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy technique could investigate easily the reaction approach of sodium hexadecyl sulfate (SHS) and hydrocalumite (CaAl-LDH-Cl). In fact, SHS could enter into the interlayer space of CaAl-LDH-Cl and replace Cl− ion to form organo-LDH, with the interlayer distance enhancing to 2.74 nm.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide