| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230165 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
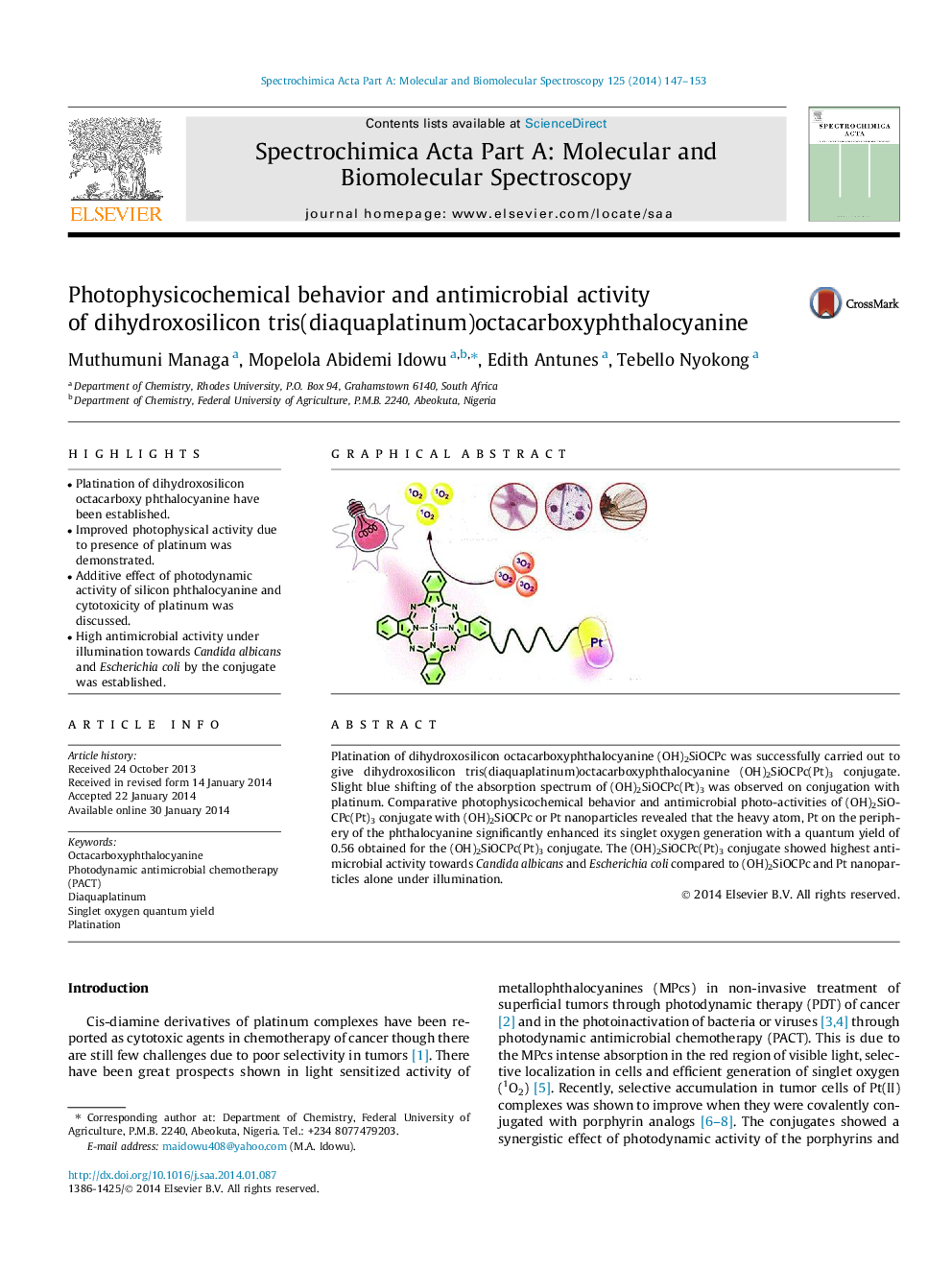
•Platination of dihydroxosilicon octacarboxy phthalocyanine have been established.•Improved photophysical activity due to presence of platinum was demonstrated.•Additive effect of photodynamic activity of silicon phthalocyanine and cytotoxicity of platinum was discussed.•High antimicrobial activity under illumination towards Candida albicans and Escherichia coli by the conjugate was established.
Platination of dihydroxosilicon octacarboxyphthalocyanine (OH)2SiOCPc was successfully carried out to give dihydroxosilicon tris(diaquaplatinum)octacarboxyphthalocyanine (OH)2SiOCPc(Pt)3 conjugate. Slight blue shifting of the absorption spectrum of (OH)2SiOCPc(Pt)3 was observed on conjugation with platinum. Comparative photophysicochemical behavior and antimicrobial photo-activities of (OH)2SiOCPc(Pt)3 conjugate with (OH)2SiOCPc or Pt nanoparticles revealed that the heavy atom, Pt on the periphery of the phthalocyanine significantly enhanced its singlet oxygen generation with a quantum yield of 0.56 obtained for the (OH)2SiOCPc(Pt)3 conjugate. The (OH)2SiOCPc(Pt)3 conjugate showed highest antimicrobial activity towards Candida albicans and Escherichia coli compared to (OH)2SiOCPc and Pt nanoparticles alone under illumination.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide