| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230166 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
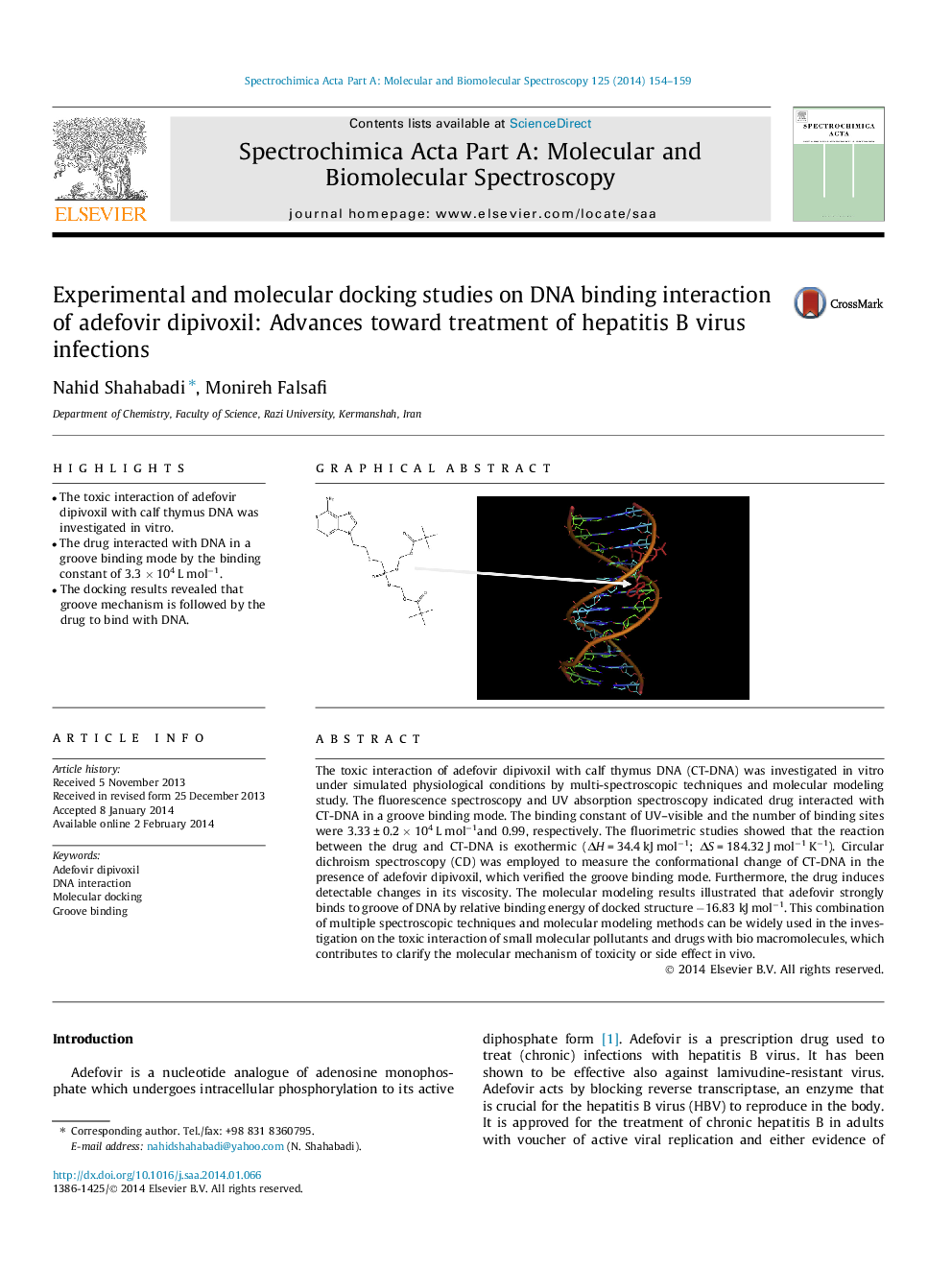
•The toxic interaction of adefovir dipivoxil with calf thymus DNA was investigated in vitro.•The drug interacted with DNA in a groove binding mode by the binding constant of 3.3 × 104 L mol−1.•The docking results revealed that groove mechanism is followed by the drug to bind with DNA.
The toxic interaction of adefovir dipivoxil with calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) was investigated in vitro under simulated physiological conditions by multi-spectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling study. The fluorescence spectroscopy and UV absorption spectroscopy indicated drug interacted with CT-DNA in a groove binding mode. The binding constant of UV–visible and the number of binding sites were 3.33 ± 0.2 × 104 L mol−1and 0.99, respectively. The fluorimetric studies showed that the reaction between the drug and CT-DNA is exothermic (ΔH = 34.4 kJ mol−1; ΔS = 184.32 J mol−1 K−1). Circular dichroism spectroscopy (CD) was employed to measure the conformational change of CT-DNA in the presence of adefovir dipivoxil, which verified the groove binding mode. Furthermore, the drug induces detectable changes in its viscosity. The molecular modeling results illustrated that adefovir strongly binds to groove of DNA by relative binding energy of docked structure −16.83 kJ mol−1. This combination of multiple spectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling methods can be widely used in the investigation on the toxic interaction of small molecular pollutants and drugs with bio macromolecules, which contributes to clarify the molecular mechanism of toxicity or side effect in vivo.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide