| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230174 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
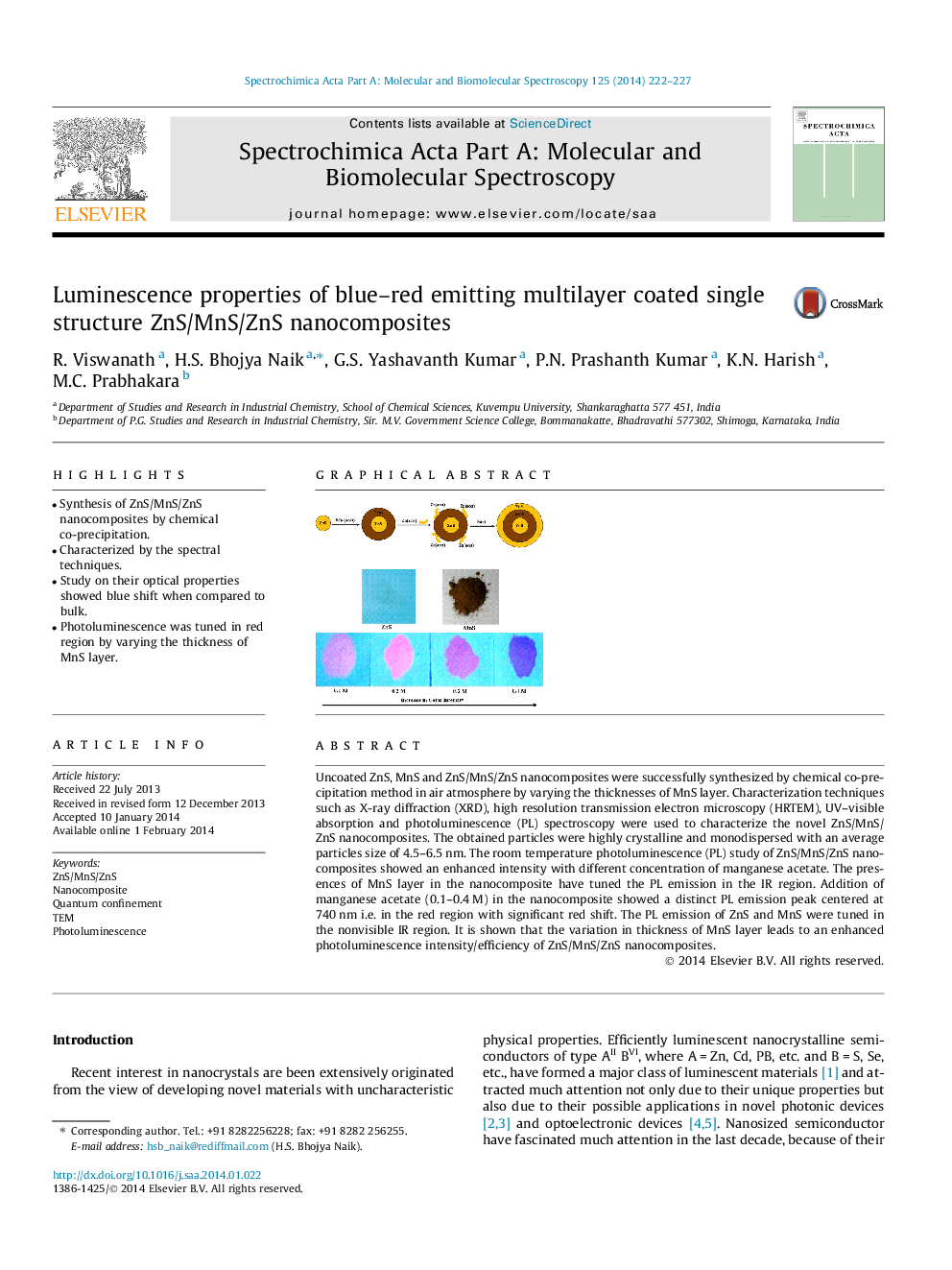
•Synthesis of ZnS/MnS/ZnS nanocomposites by chemical co-precipitation.•Characterized by the spectral techniques.•Study on their optical properties showed blue shift when compared to bulk.•Photoluminescence was tuned in red region by varying the thickness of MnS layer.
Uncoated ZnS, MnS and ZnS/MnS/ZnS nanocomposites were successfully synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method in air atmosphere by varying the thicknesses of MnS layer. Characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), UV–visible absorption and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy were used to characterize the novel ZnS/MnS/ZnS nanocomposites. The obtained particles were highly crystalline and monodispersed with an average particles size of 4.5–6.5 nm. The room temperature photoluminescence (PL) study of ZnS/MnS/ZnS nanocomposites showed an enhanced intensity with different concentration of manganese acetate. The presences of MnS layer in the nanocomposite have tuned the PL emission in the IR region. Addition of manganese acetate (0.1–0.4 M) in the nanocomposite showed a distinct PL emission peak centered at 740 nm i.e. in the red region with significant red shift. The PL emission of ZnS and MnS were tuned in the nonvisible IR region. It is shown that the variation in thickness of MnS layer leads to an enhanced photoluminescence intensity/efficiency of ZnS/MnS/ZnS nanocomposites.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide