| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230318 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
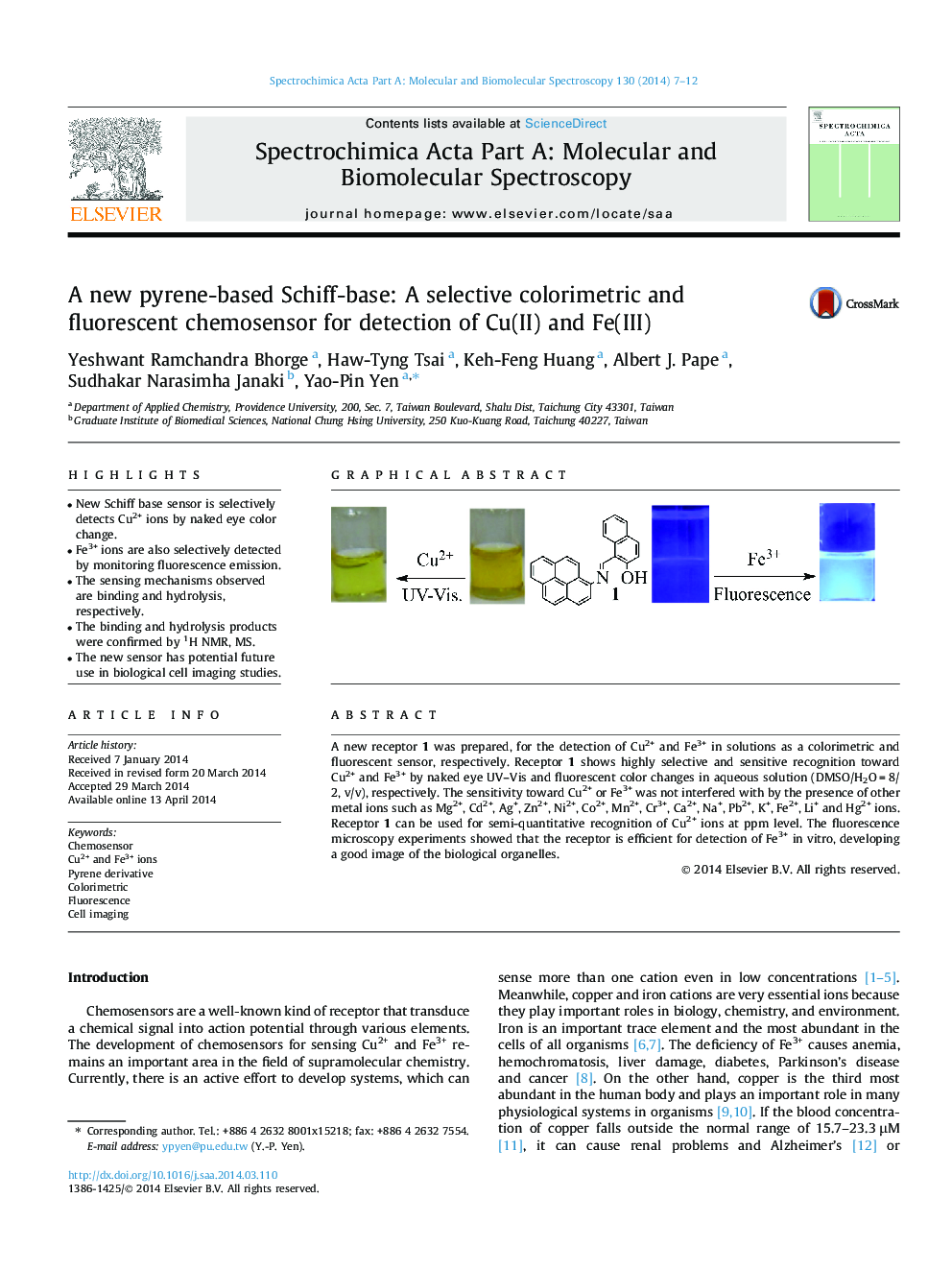
•New Schiff base sensor is selectively detects Cu2+ ions by naked eye color change.•Fe3+ ions are also selectively detected by monitoring fluorescence emission.•The sensing mechanisms observed are binding and hydrolysis, respectively.•The binding and hydrolysis products were confirmed by 1H NMR, MS.•The new sensor has potential future use in biological cell imaging studies.
A new receptor 1 was prepared, for the detection of Cu2+ and Fe3+ in solutions as a colorimetric and fluorescent sensor, respectively. Receptor 1 shows highly selective and sensitive recognition toward Cu2+ and Fe3+ by naked eye UV–Vis and fluorescent color changes in aqueous solution (DMSO/H2O = 8/2, v/v), respectively. The sensitivity toward Cu2+ or Fe3+ was not interfered with by the presence of other metal ions such as Mg2+, Cd2+, Ag+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Mn2+, Cr3+, Ca2+, Na+, Pb2+, K+, Fe2+, Li+ and Hg2+ ions. Receptor 1 can be used for semi-quantitative recognition of Cu2+ ions at ppm level. The fluorescence microscopy experiments showed that the receptor is efficient for detection of Fe3+ in vitro, developing a good image of the biological organelles.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide