| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230374 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•The fluorescence of native and denatured Lys was quenched by sinomenine at pH 7.4.•The effect of metal ions on the binding constant of sinomenine with Lys was studied.•The pH 7.4 is the optimal acidity in the binding reaction.•Sinomenine was harder to bind to the denatured Lys.
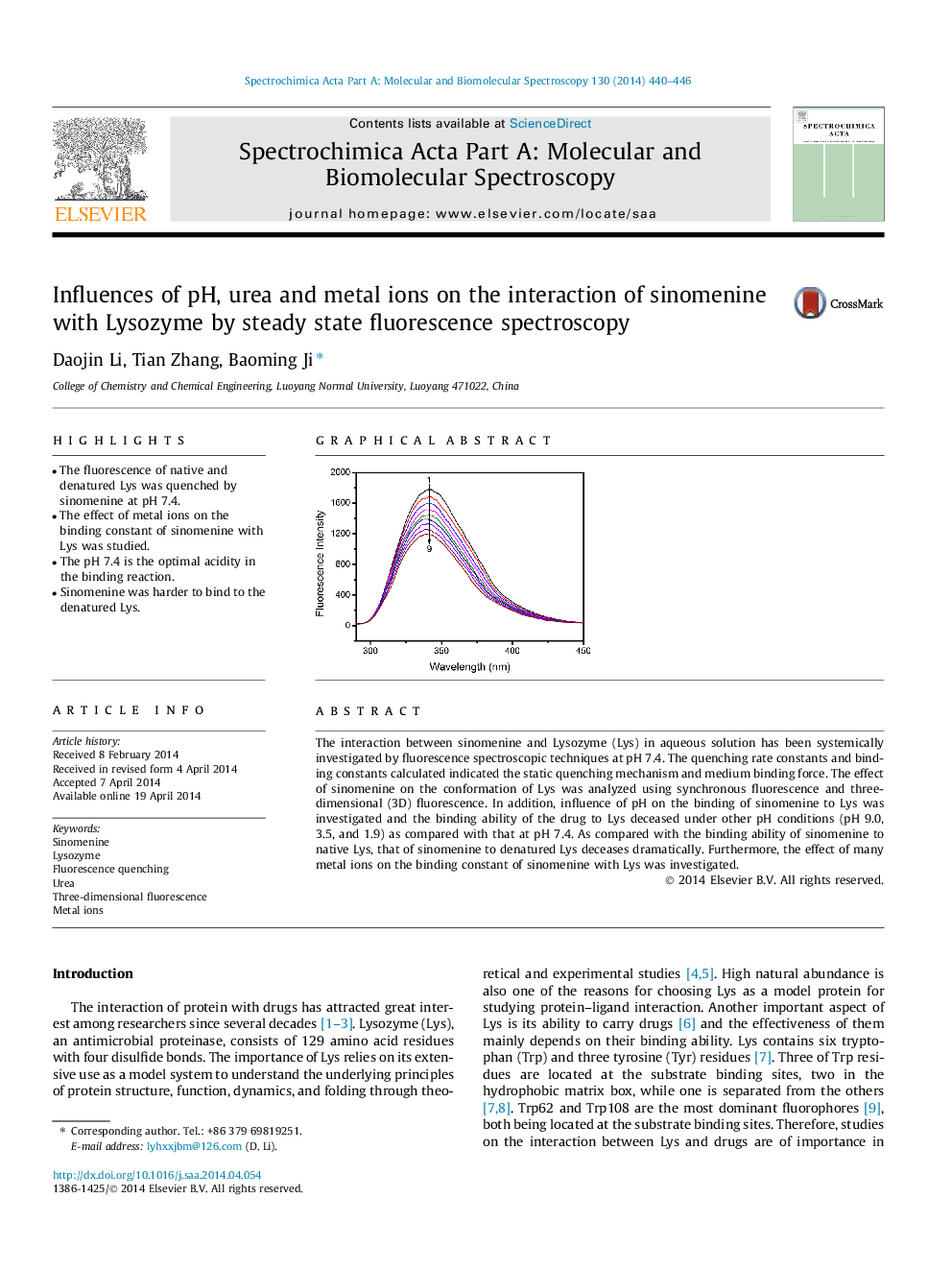
The interaction between sinomenine and Lysozyme (Lys) in aqueous solution has been systemically investigated by fluorescence spectroscopic techniques at pH 7.4. The quenching rate constants and binding constants calculated indicated the static quenching mechanism and medium binding force. The effect of sinomenine on the conformation of Lys was analyzed using synchronous fluorescence and three-dimensional (3D) fluorescence. In addition, influence of pH on the binding of sinomenine to Lys was investigated and the binding ability of the drug to Lys deceased under other pH conditions (pH 9.0, 3.5, and 1.9) as compared with that at pH 7.4. As compared with the binding ability of sinomenine to native Lys, that of sinomenine to denatured Lys deceases dramatically. Furthermore, the effect of many metal ions on the binding constant of sinomenine with Lys was investigated.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide