| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230441 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 12 Pages |
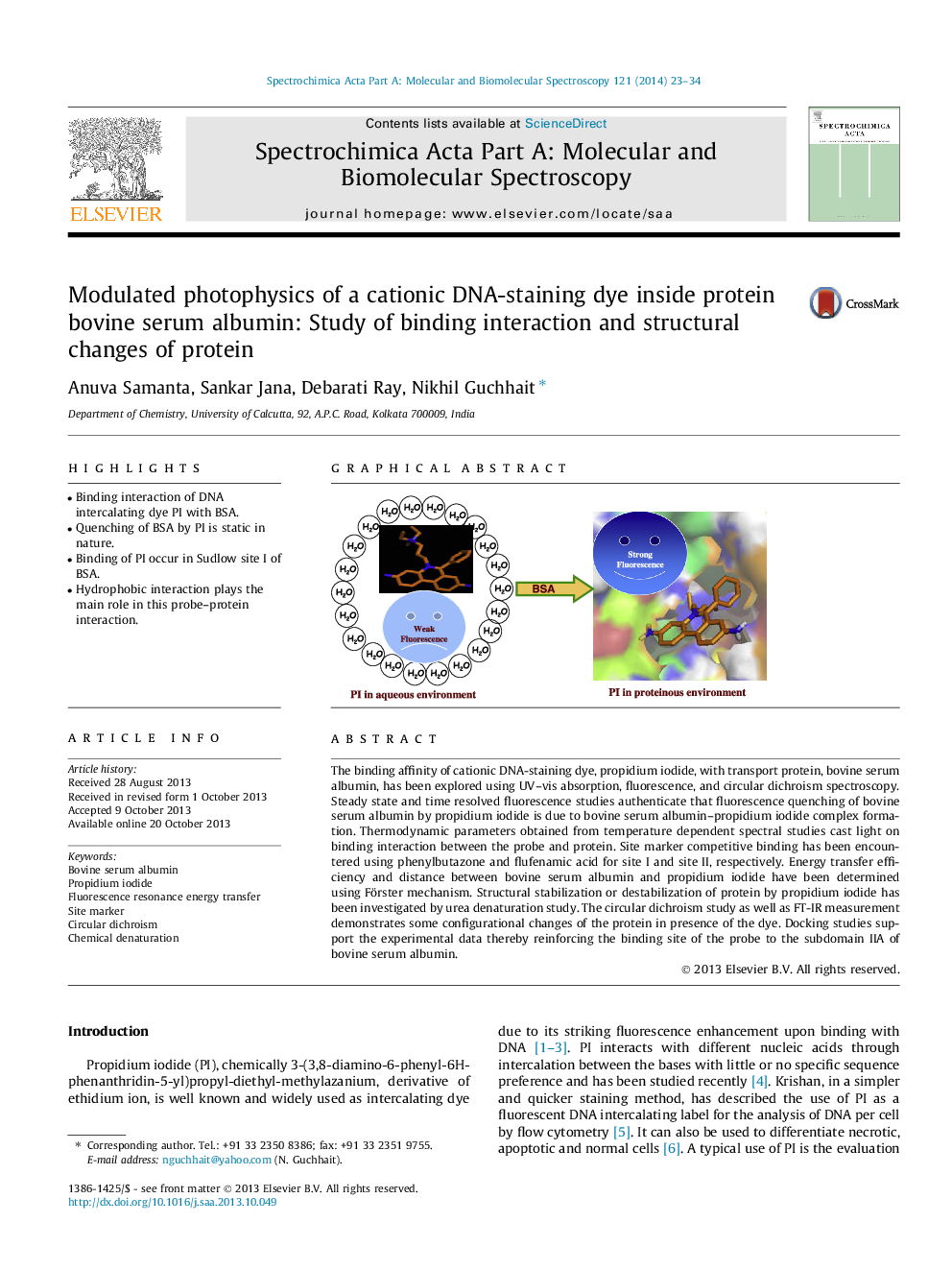
•Binding interaction of DNA intercalating dye PI with BSA.•Quenching of BSA by PI is static in nature.•Binding of PI occur in Sudlow site I of BSA.•Hydrophobic interaction plays the main role in this probe–protein interaction.
The binding affinity of cationic DNA-staining dye, propidium iodide, with transport protein, bovine serum albumin, has been explored using UV–vis absorption, fluorescence, and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Steady state and time resolved fluorescence studies authenticate that fluorescence quenching of bovine serum albumin by propidium iodide is due to bovine serum albumin–propidium iodide complex formation. Thermodynamic parameters obtained from temperature dependent spectral studies cast light on binding interaction between the probe and protein. Site marker competitive binding has been encountered using phenylbutazone and flufenamic acid for site I and site II, respectively. Energy transfer efficiency and distance between bovine serum albumin and propidium iodide have been determined using Förster mechanism. Structural stabilization or destabilization of protein by propidium iodide has been investigated by urea denaturation study. The circular dichroism study as well as FT-IR measurement demonstrates some configurational changes of the protein in presence of the dye. Docking studies support the experimental data thereby reinforcing the binding site of the probe to the subdomain IIA of bovine serum albumin.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide