| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230478 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
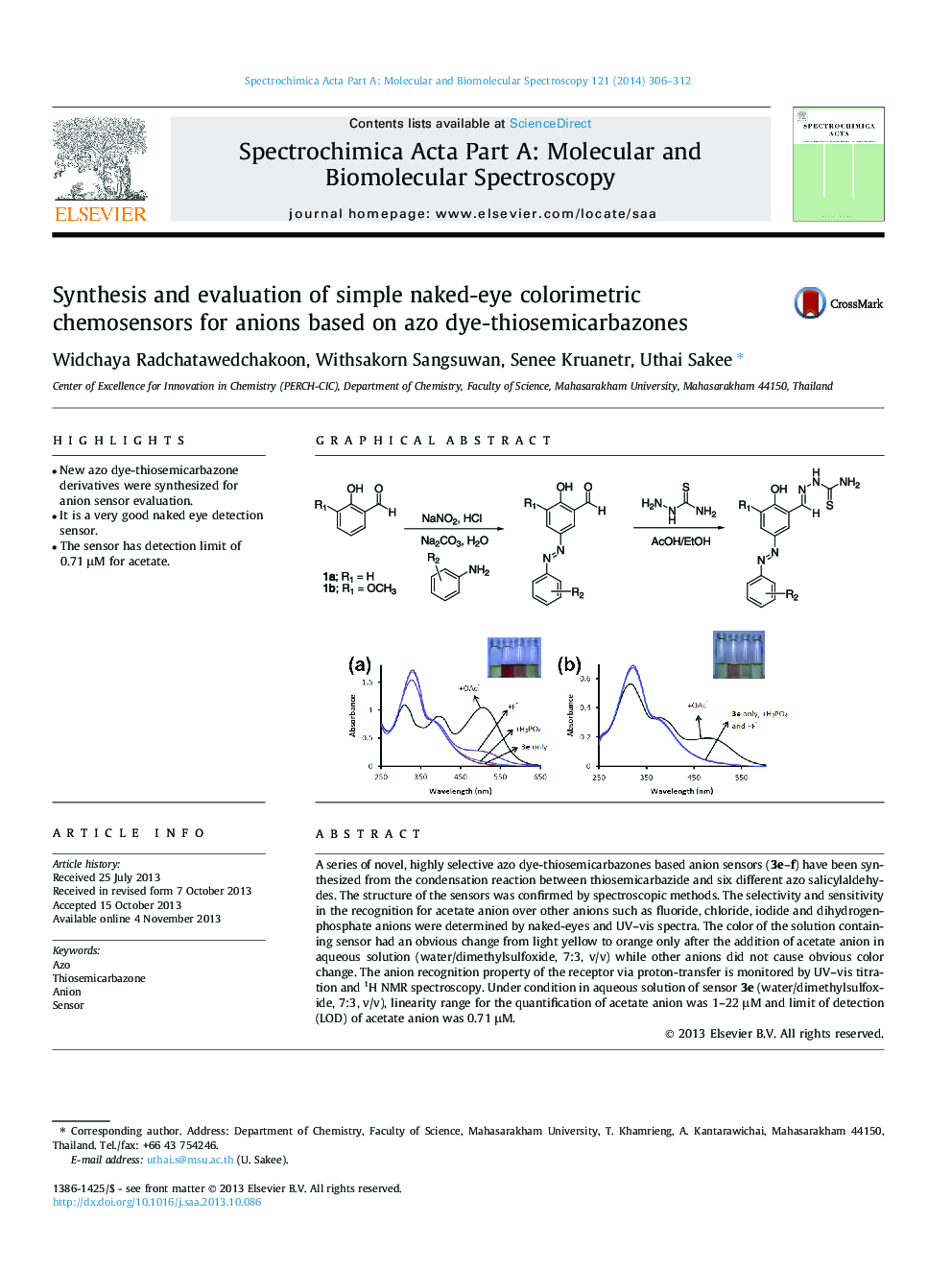
•New azo dye-thiosemicarbazone derivatives were synthesized for anion sensor evaluation.•It is a very good naked eye detection sensor.•The sensor has detection limit of 0.71 μM for acetate.
A series of novel, highly selective azo dye-thiosemicarbazones based anion sensors (3e–f) have been synthesized from the condensation reaction between thiosemicarbazide and six different azo salicylaldehydes. The structure of the sensors was confirmed by spectroscopic methods. The selectivity and sensitivity in the recognition for acetate anion over other anions such as fluoride, chloride, iodide and dihydrogenphosphate anions were determined by naked-eyes and UV–vis spectra. The color of the solution containing sensor had an obvious change from light yellow to orange only after the addition of acetate anion in aqueous solution (water/dimethylsulfoxide, 7:3, v/v) while other anions did not cause obvious color change. The anion recognition property of the receptor via proton-transfer is monitored by UV–vis titration and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Under condition in aqueous solution of sensor 3e (water/dimethylsulfoxide, 7:3, v/v), linearity range for the quantification of acetate anion was 1–22 μM and limit of detection (LOD) of acetate anion was 0.71 μM.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide